Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Perioperative Antibiotics For Surgical Prophylaxis
Uploaded by
damondouglasOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Perioperative Antibiotics For Surgical Prophylaxis
Uploaded by
damondouglasCopyright:
Available Formats
University of Maryland Medical Center
Perioperative Antibiotics for Surgical Prophylaxis
Guidelines for Use
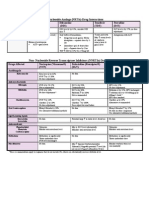
1. The first dose of any antibiotic should be given within 2 hours of incision, preferably
30 minutes prior to incision [1].
2. There is no evidence that continuing prophylactic antibiotics post-operatively further
reduces the risk of infection.
The following practices are also recommended by the CDC [2] and the Surgical
Infection Society [3] to reduce the risk of surgical site infection (SSI). The evidence that
these measures reduce SSI’s is not as strong as the evidence for the guidelines above.
3. The therapeutic concentration of any antibiotic in the tissue needs to be maintained
intra-operatively. Hence perioperative antibiotics should be re-dosed every two to
three hours during the operative procedure (see table below).
4. In patients with obesity (women >80 kg; men > 100 kg), the dose of the antibiotics
should be increased.
5. If blood loss of >1500 cc occurs, the antibiotic should be redosed regardless of when
the last dose was previously given.
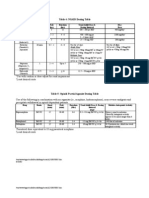
Intra-operative Dosing Guidelines
Antibiotic Dose Half-life Dosing Interval
Cefazolin 1 gm 90-150 min Every 2-3 hours
Ciprofloxacin 400 mg 4 hours Every 8 hours
Clindamycin 600 mg 3 hours Every 6 hours
References
1. Classen DC, Evans RS, Pestotnik SL, Horn SD, Menlove RL, Burke JP. The timing
of prophylactic administration of antibiotics and the risk of surgical-wound infection
[see comments]. N Engl J Med 1992;326:281-6
2. CDC Draft Guideline for the Prevention of Surgical Site Infection. Federal Register
1998;63:33167-33192
3. Page CP, Bohnen JM, Fletcher JR, McManus AT, Solomkin JS, Wittmann DH.
Antimicrobial prophylaxis for surgical wounds. Guidelines for clinical care. Arch Surg
1993;128:79-88
4. Forse RA, Karam B, MacLean LD, Christou NV. Antibiotic prophylaxis for surgery in
morbidly obese patients. Surgery 1989;106:750-6; discussion 756-7
Updated 3/99
You might also like
- Primary Management of PolytraumaFrom EverandPrimary Management of PolytraumaSuk-Kyung HongNo ratings yet
- Antibiotic Prophylaxis in SurgeryDocument23 pagesAntibiotic Prophylaxis in SurgeryRakhmad AdityaNo ratings yet
- Chronic Postsurgical PainDocument19 pagesChronic Postsurgical Painronald97hgNo ratings yet
- Isid Guide Preparing The Patient For Surgery-1Document16 pagesIsid Guide Preparing The Patient For Surgery-1Prunaru BogdanNo ratings yet
- Surgical Care Improvement Project JCIDocument50 pagesSurgical Care Improvement Project JCIKania FitrianiNo ratings yet
- Surgical InfectionDocument108 pagesSurgical InfectionAmrit Preet KaurNo ratings yet
- Prevention of Surgical Site Infections: Surgical Patient Care SeriesDocument11 pagesPrevention of Surgical Site Infections: Surgical Patient Care Seriestien duongNo ratings yet
- Antibiotika Profilaksis Pada Operasi Orthopaedi RevisiDocument30 pagesAntibiotika Profilaksis Pada Operasi Orthopaedi RevisiAnis ChaNo ratings yet
- Preoperative Antibiotic Prophylaxis - StatPearls - NCBI BookshelfDocument7 pagesPreoperative Antibiotic Prophylaxis - StatPearls - NCBI BookshelfMikaela l100% (1)
- Terapi Antibiotik Empirik Pada Sakit Kritis: Rekomendasi Panduan Internasional SepsisDocument64 pagesTerapi Antibiotik Empirik Pada Sakit Kritis: Rekomendasi Panduan Internasional SepsisReendy AfrikoNo ratings yet
- Antibiotics-Generation OperationDocument5 pagesAntibiotics-Generation OperationZamzami Ahmad FahmiNo ratings yet
- Steroid IndicationDocument5 pagesSteroid IndicationAmirah DahalanNo ratings yet
- Steinberg 2009Document7 pagesSteinberg 2009majedNo ratings yet
- MANAJEMEN HAIsDocument43 pagesMANAJEMEN HAIssheeno2607No ratings yet
- Preoperative Antibiotic Prophylaxis StatPearls NCBI BookshelfDocument1 pagePreoperative Antibiotic Prophylaxis StatPearls NCBI BookshelfJEAN BAILEY RAMOS ROXASNo ratings yet
- Profilaxis Antibiótico en TraumaDocument9 pagesProfilaxis Antibiótico en TraumaGlessin MurilloNo ratings yet
- Antibiotics - Chua EDocument29 pagesAntibiotics - Chua EerikaNo ratings yet
- Accepted Manuscript: 10.1016/j.arth.2016.12.027Document21 pagesAccepted Manuscript: 10.1016/j.arth.2016.12.027Han's OfficialNo ratings yet
- Preoperative Antibiotic Prophylaxis - StatPearls - NCBI BookshelfDocument6 pagesPreoperative Antibiotic Prophylaxis - StatPearls - NCBI BookshelfAshen DissanayakaNo ratings yet
- Antibiotic Prophylaxis PDFDocument3 pagesAntibiotic Prophylaxis PDFPadmanabha GowdaNo ratings yet
- RatriDocument3 pagesRatrinanikNo ratings yet
- Surgicalsite InfectionDocument27 pagesSurgicalsite Infectionmsat72No ratings yet
- UntitledDocument9 pagesUntitledherdian ariebowoNo ratings yet
- Clinical Study: Preoperative High-Dose Steroid Has Long-Term Beneficial Effects For Myasthenia GravisDocument7 pagesClinical Study: Preoperative High-Dose Steroid Has Long-Term Beneficial Effects For Myasthenia GravisM Lutfi FananiNo ratings yet
- Stress Ulcer ProphylaxisDocument24 pagesStress Ulcer ProphylaxisredyhataNo ratings yet
- The SURgical PAtient Safety System (SURPASS) Checklist Optimizes Timing of Antibiotic Prophylaxis.Document6 pagesThe SURgical PAtient Safety System (SURPASS) Checklist Optimizes Timing of Antibiotic Prophylaxis.Lucas TobingNo ratings yet
- Surgical Site InfectionsDocument52 pagesSurgical Site Infectionssahabatsalam07100% (5)
- Antibiotics in NeurosurgeryDocument12 pagesAntibiotics in Neurosurgerylouglee9174100% (1)
- CrosstownGeneralSurgeryGuidelineFinal Nov 2007Document8 pagesCrosstownGeneralSurgeryGuidelineFinal Nov 2007Sri Nurliana BasryNo ratings yet
- Paper 26Document4 pagesPaper 26fundj22No ratings yet
- Antibiotic Prophylaxis - Is It Necessary in Clean General Surgery?Document3 pagesAntibiotic Prophylaxis - Is It Necessary in Clean General Surgery?Jade Phoebe AjeroNo ratings yet
- Ischemic Therapy in Musculoskeletal Medicine (4939)Document9 pagesIschemic Therapy in Musculoskeletal Medicine (4939)RexDavidGidoNo ratings yet
- Surgical Antibiotic Prophylaxis Neurosurgery Adult and Paediatric PatientsDocument6 pagesSurgical Antibiotic Prophylaxis Neurosurgery Adult and Paediatric PatientsPraveen PadalaNo ratings yet
- Laskin The Use of Prophylactic AntibioticsDocument6 pagesLaskin The Use of Prophylactic Antibioticsapi-265532519No ratings yet
- PKPD For BeginnersDocument31 pagesPKPD For Beginnerstanty_ukNo ratings yet
- Efficacy of Postoperative Analgesia of Local Ketamine Wound Instillation Following Total ThyroidectomyDocument20 pagesEfficacy of Postoperative Analgesia of Local Ketamine Wound Instillation Following Total ThyroidectomyCristina RamirezNo ratings yet
- Udy 2010Document3 pagesUdy 2010aNo ratings yet
- Cefazolin (Ancef ®) : D5W, NsDocument9 pagesCefazolin (Ancef ®) : D5W, Nsbabe5606No ratings yet
- Antibiotic Prophylaxis-An EssayDocument12 pagesAntibiotic Prophylaxis-An EssayGokul RamakrishnanNo ratings yet
- Intramuscular Injection TechniquesDocument6 pagesIntramuscular Injection TechniquesreinNo ratings yet
- Iraqi Ministry of Health Medical City Baghdad Teaching Hospital Training Center of Clinical PharmacyDocument40 pagesIraqi Ministry of Health Medical City Baghdad Teaching Hospital Training Center of Clinical PharmacyLolo GhostNo ratings yet
- First Page PDFDocument1 pageFirst Page PDFmpaivaecostaNo ratings yet
- Dolor PostoperatorioDocument44 pagesDolor PostoperatorioChurrunchaNo ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument6 pagesCase Studytaiwo.idNo ratings yet
- Surgical Site Infection (SSI) Toolkit: Activity C: ELC Prevention CollaborativesDocument33 pagesSurgical Site Infection (SSI) Toolkit: Activity C: ELC Prevention CollaborativesCarissa SulaimanNo ratings yet
- Wound Infection: Dr. Nisreen Anfanan DR .T.ZamzamiDocument24 pagesWound Infection: Dr. Nisreen Anfanan DR .T.ZamzamimustaafNo ratings yet
- Antimicrobial StewardshipDocument7 pagesAntimicrobial StewardshipJohn TusselNo ratings yet
- Remit1524932006922 1554076912502 PDFDocument21 pagesRemit1524932006922 1554076912502 PDFArthur OliveiraNo ratings yet
- Article-Chronic Pain After Surgery-ReubenDocument9 pagesArticle-Chronic Pain After Surgery-Reubenarifjo7999No ratings yet
- Table 1 Criteria For Antibiotic ProphylaxisDocument11 pagesTable 1 Criteria For Antibiotic ProphylaxisMaria Fernanda Xiqui NavaNo ratings yet
- Antimicrobial Prophylaxis - Takehiro Wakasugi, M.D., PH.DDocument14 pagesAntimicrobial Prophylaxis - Takehiro Wakasugi, M.D., PH.DBhings GaleriesNo ratings yet
- 10 SSI Bundle 'Use CATS To Prevent SSI'Document53 pages10 SSI Bundle 'Use CATS To Prevent SSI'KPJConference100% (2)
- Presentation 1Document24 pagesPresentation 1Nancy JeanetteNo ratings yet
- Safety and Efficacy of CorticosteroidsDocument9 pagesSafety and Efficacy of CorticosteroidsMatt CoghlanNo ratings yet
- Antibiotic 4 SurgicalDocument3 pagesAntibiotic 4 SurgicalNanaDinaWahyuniNo ratings yet
- Bahan ReferatDocument17 pagesBahan ReferatGisma CNo ratings yet
- Antibiotic Selection and Resistance: A Pharmacist'S PerspectiveDocument22 pagesAntibiotic Selection and Resistance: A Pharmacist'S PerspectiveAliyah Tofani PawelloiNo ratings yet
- Journal Surg Ward BorjaDocument4 pagesJournal Surg Ward BorjaYana PotNo ratings yet
- Bladder CancerFrom EverandBladder CancerJa Hyeon KuNo ratings yet
- IV PO Conversion CAPDocument3 pagesIV PO Conversion CAPdamondouglasNo ratings yet
- CAP AlgorithmDocument1 pageCAP AlgorithmdamondouglasNo ratings yet
- NRTI NNRTI Drug Interact TBLDocument1 pageNRTI NNRTI Drug Interact TBLdamondouglasNo ratings yet
- PIs Drug InteractionDocument1 pagePIs Drug InteractiondamondouglasNo ratings yet
- University of Maryland Medical Center Fluconazole (Diflucan®)Document6 pagesUniversity of Maryland Medical Center Fluconazole (Diflucan®)damondouglasNo ratings yet
- IV PO Conversion P&P.V2Document3 pagesIV PO Conversion P&P.V2damondouglasNo ratings yet
- Antimicrobial Renal DosingDocument5 pagesAntimicrobial Renal DosingdamondouglasNo ratings yet
- CAP Guidelines For UseDocument11 pagesCAP Guidelines For Usedamondouglas100% (1)
- CAP Order Form Admission Final VerDocument1 pageCAP Order Form Admission Final VerdamondouglasNo ratings yet
- 3.E.2-Caspofungin Guideline 2003Document3 pages3.E.2-Caspofungin Guideline 2003damondouglasNo ratings yet
- Antibiogram 07Document1 pageAntibiogram 07damondouglas100% (1)
- Pain Guidelines & Range DosingDocument3 pagesPain Guidelines & Range Dosingdamondouglas100% (1)
- In B Deoxycholate Shortage Alternative TherapiesDocument2 pagesIn B Deoxycholate Shortage Alternative TherapiesdamondouglasNo ratings yet
- Sodium Content of Inject Able AntibioticsDocument1 pageSodium Content of Inject Able AntibioticsdamondouglasNo ratings yet
- Sedation Pain AlgorithmDocument1 pageSedation Pain Algorithmdamondouglas100% (2)
- Restricted AntimicrobialsDocument1 pageRestricted AntimicrobialsdamondouglasNo ratings yet
- UMMC Argatroban Protocol Revised 4-2008Document2 pagesUMMC Argatroban Protocol Revised 4-2008damondouglas100% (1)
- Pediatric Antimicrobial DosingDocument3 pagesPediatric Antimicrobial Dosingdamondouglas100% (2)
- PONV GuidelinesDocument3 pagesPONV GuidelinesdamondouglasNo ratings yet
- ICU Neuromuscular BlockadeDocument7 pagesICU Neuromuscular BlockadedamondouglasNo ratings yet
- Opioid Equianalgesic ChartDocument1 pageOpioid Equianalgesic Chartdamondouglas100% (7)
- NSAID Agonist Antagonist TableDocument1 pageNSAID Agonist Antagonist TabledamondouglasNo ratings yet
- IV PO ConversionsDocument1 pageIV PO Conversionsdamondouglas100% (1)
- IV Insulin - FinalDocument18 pagesIV Insulin - Finaldamondouglas100% (2)
- Hyperglycemia Algorithm 2Document1 pageHyperglycemia Algorithm 2damondouglasNo ratings yet
- IV PO Conversion CAPDocument3 pagesIV PO Conversion CAPdamondouglasNo ratings yet
- HIT ProtocolDocument1 pageHIT ProtocoldamondouglasNo ratings yet
- Hypertensive Urgency EmergencyDocument5 pagesHypertensive Urgency Emergencydamondouglas100% (3)
- Guideline For The Prevention of CINDocument2 pagesGuideline For The Prevention of CINdamondouglasNo ratings yet