Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Urinary Tract Infection pATho SHEENA
Uploaded by
Sheena Arnoco ToraynoOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Urinary Tract Infection pATho SHEENA
Uploaded by
Sheena Arnoco ToraynoCopyright:
Available Formats
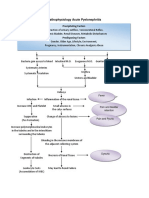
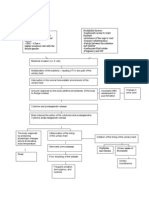
Urinary Tract Infection (UTI)
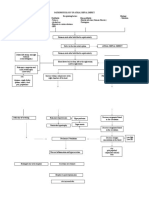
Pathophysiology (book based) Non-modifiable factors: AGE UTI is a prevalent disease among children and elderly SEX it has a higher incidence rate with the female gender Modifiable factors: Inadequate access to toilet facilities Avoidance of the urge to void Urinary catheterization Fistula between the intestine and bladder Inadequate fluid intake Pregnancy, and DM
Bacterial invasion (i.e. E.coli) Multiplication of the bacteria causing UTI in any part of the urinary tract Interruption in the normal homeostatic environment of the urinary tract Immune response by the body (defense mechanism of the body to foreign bodies) Cytokine and prostaglandin release Body induces the action of the cytokines and prostaglandins Change in urine color
Increased WBC subsequent to pus formation
The body responds by producing physiologic changes aimed at elevating
Inflammation of the lining of the urinary tract. Narrowed urine passage
Irritation of the lining of the urinary tract
Fever Poor emptying of the bladder
Urethrits and dysuria
Spasm of the bladder
Frequent urination and urgency, and nocturia
Urinary incontinen -ce
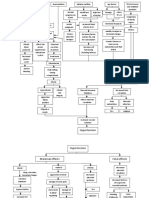
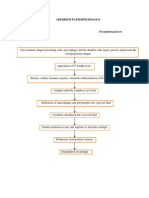
Pathophysiology (Client Centered)
Non-modifiable factor: Age Among elderly UTI frequency is roughly equal proportions in women and men.
Modifiable factors: Avoidance of the urge to void Inadequate fluid intake
Bacterial invasion (i.e. E.coli) Multiplication of the bacteria causing UTI in any part of the urinary tract Interruption in the normal homeostatic environment of the urinary tract Immune response by the body (defense mechanism of the body to foreign bodies) Body induces the action of the cytokines and prostaglandins The body responds by producing physiologic changes aimed at elevating body temperature. Cytokine and prostaglandin release Increased WBC subsequent to pus formation
Fever Nov. 13. 2011
Change in urine color
You might also like
- grp52 UTI PathoDocument3 pagesgrp52 UTI Pathokcdgrvn100% (3)
- Pre Eclampsia of Severe FeaturesDocument3 pagesPre Eclampsia of Severe FeaturesPrincess Diane S. VillegasNo ratings yet
- Marjorie A. Carganilla BSN 3-2 Pathophysiology of Urinaryy Tract Infection Precipitating FactorsDocument8 pagesMarjorie A. Carganilla BSN 3-2 Pathophysiology of Urinaryy Tract Infection Precipitating FactorsMarjorie CarganillaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Acute GastroenteritisDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Acute GastroenteritisAlliah Grejie AnneNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Atrial Septal DefectDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of Atrial Septal Defectbobtaguba50% (2)
- Pathophsyiology of AGEDocument1 pagePathophsyiology of AGEmariaNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Hyperemesis Gravidarum DiagramDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Hyperemesis Gravidarum DiagramQuintin MangaoangNo ratings yet
- Etiology: Predisposing Factors: Precipitating FactorsDocument5 pagesEtiology: Predisposing Factors: Precipitating FactorsJanelle NarcisoNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology (Book-Based) : CystitisDocument9 pagesPathophysiology (Book-Based) : CystitisIrish EspinosaNo ratings yet
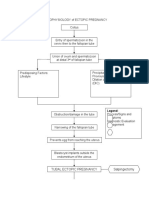
- Pathophysiology of Ectopic PregnancyDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of Ectopic PregnancyJulienne Sanchez-Salazar100% (1)
- Normal Spontaneous Vaginal DeliveryDocument35 pagesNormal Spontaneous Vaginal DeliveryJohn Edward EscoteNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Rheumatic Heart DiseaseDocument6 pagesPathophysiology of Rheumatic Heart DiseaseVince John Sevilla100% (2)
- Pathophy (Age)Document1 pagePathophy (Age)Michelle Ann CasamayorNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Acute GastroenteritisDocument5 pagesPathophysiology of Acute Gastroenteritisheron_bayanin_15No ratings yet
- Abruptio Placenta PathophysiologyDocument4 pagesAbruptio Placenta Pathophysiologyjamie carpioNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Colon Cancer Predisposing Factors: Etiology: Precipitating Factors: Precipitating FactorsDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Colon Cancer Predisposing Factors: Etiology: Precipitating Factors: Precipitating FactorstatiNo ratings yet
- MYOMA PathoDocument1 pageMYOMA Pathobsn2011100% (1)
- Case Study of Cesarean SectionDocument9 pagesCase Study of Cesarean SectionErika Joy Imperio0% (1)
- Ectopic Pregnancy PathophysiologyDocument5 pagesEctopic Pregnancy Pathophysiologyjoyrena ochondraNo ratings yet
- NCP Abruptio PlacentaDocument2 pagesNCP Abruptio PlacentaCarson Birth100% (1)
- Acute Glomrulonephritis PathophysiologyDocument2 pagesAcute Glomrulonephritis PathophysiologyJai - HoNo ratings yet
- Myoma PathoniixDocument1 pageMyoma PathoniixRendel FernandezNo ratings yet
- PATHOPHYSIOLOGY of ECTOPIC PREGNANCYDocument2 pagesPATHOPHYSIOLOGY of ECTOPIC PREGNANCYrye100% (2)
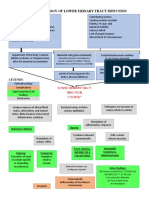
- Pathophysiology of Lower Urinary Tract InfectionDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Lower Urinary Tract InfectionSTORAGE FILENo ratings yet
- Patho MyomaDocument1 pagePatho MyomaJurilyne Rose TundagNo ratings yet
- Case Presentation (Age) NG Grp. A2 FinalDocument43 pagesCase Presentation (Age) NG Grp. A2 Finaljean therese83% (6)
- NCP Hyperbilirubinemia Staff NursingDocument3 pagesNCP Hyperbilirubinemia Staff NursingVerajoy DaanNo ratings yet
- D and CDocument37 pagesD and CMary Grace MasNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology Dengue Hemorrhagic FeverDocument1 pagePathophysiology Dengue Hemorrhagic FeverShiella Heart Malana100% (1)
- Amoebiasis PathophysiologyDocument3 pagesAmoebiasis PathophysiologyApril CornejoNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology AGEDocument2 pagesPathophysiology AGEMareeze Hatta100% (1)
- Acute PyelonephritisDocument53 pagesAcute Pyelonephritiseeymee100% (1)
- Patho Pott's DseDocument2 pagesPatho Pott's Dsexai_teovisioNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology Acute Pyelonephritis: Precipitating FactorsDocument2 pagesPathophysiology Acute Pyelonephritis: Precipitating Factorsgodwinkent888No ratings yet
- Pregnancy Induced Hypertension PathophysiologyDocument2 pagesPregnancy Induced Hypertension PathophysiologyCamille Grace100% (1)
- Case Study AppendicitisDocument6 pagesCase Study AppendicitisPrincess Camille ArceoNo ratings yet
- LFD CHNDocument4 pagesLFD CHNKaren Joyce Costales MagtanongNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The GallbladderDocument1 pageAnatomy and Physiology of The GallbladderRojanisa Baculi RomathoNo ratings yet
- Urinary Tract Infectio Case StudyDocument17 pagesUrinary Tract Infectio Case Studyjunex123No ratings yet
- PATHOPHYSIOLOGY of PreeclampsiaDocument1 pagePATHOPHYSIOLOGY of PreeclampsiaPearl IbisateNo ratings yet
- Acute PyelonephritisDocument59 pagesAcute PyelonephritisKylie Golindang100% (1)
- Pathophysiology-Ng Hirschsprung DiseaseDocument3 pagesPathophysiology-Ng Hirschsprung DiseaseJan Rae Barnatia AtienzaNo ratings yet
- Pcap Pathophysiology PDFDocument3 pagesPcap Pathophysiology PDFMikaela RamosNo ratings yet
- Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Pathophysiology: Predisposing Factors: Etiology: Precipitating FactorsDocument3 pagesAcute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Pathophysiology: Predisposing Factors: Etiology: Precipitating FactorsKyla ValenciaNo ratings yet
- Ovarian New GrowthDocument1 pageOvarian New GrowthZhy CaluzaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Urinary Tract Infection UTIDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Urinary Tract Infection UTITrida Hermano CabansagNo ratings yet
- Family Nursing Care Plan: Partially AchievedDocument3 pagesFamily Nursing Care Plan: Partially AchievedENKELI VALDECANTOSNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Cervical Cancer: High Risk HPV (16, 18, 31)Document2 pagesPathophysiology of Cervical Cancer: High Risk HPV (16, 18, 31)Moses Gabriel ValledorNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of UTIDocument1 pagePathophysiology of UTIKeannepotz80% (5)
- PathophyDocument1 pagePathophyMaria MargarethNo ratings yet
- - case History E. Coli - نسخةDocument6 pages- case History E. Coli - نسخةSamarNo ratings yet
- Urogenital InfectionsDocument24 pagesUrogenital InfectionsGaurav100% (1)
- Symptoms: For Bladder InfectionsDocument5 pagesSymptoms: For Bladder InfectionsGene Ryuzaki SeseNo ratings yet
- Arthritis and Uti Patho-PhysioDocument2 pagesArthritis and Uti Patho-PhysioIrene NecesitoNo ratings yet
- Urinary Tract InfectionsDocument71 pagesUrinary Tract Infectionsdayibon499No ratings yet
- Urinary Tract InfectionDocument24 pagesUrinary Tract InfectionraddagNo ratings yet
- CASE STUDY #3 Urinary System (Urninary Tract Infection or UTI)Document5 pagesCASE STUDY #3 Urinary System (Urninary Tract Infection or UTI)Lerma PagcaliwanganNo ratings yet
- Uti ReadingsDocument6 pagesUti ReadingskarenbelnasNo ratings yet
- 8.urinary Tract Infections-1Document82 pages8.urinary Tract Infections-1fikirjohn8No ratings yet
- Infectious Diseases - 04Document21 pagesInfectious Diseases - 04Arthur YanezNo ratings yet
- Lyre 2Document30 pagesLyre 2Sheena Arnoco Torayno100% (3)
- Typhus Paratyphoid Fever Elektra Typhoid (Elektra)Document11 pagesTyphus Paratyphoid Fever Elektra Typhoid (Elektra)Sheena Arnoco ToraynoNo ratings yet
- Urinary Tract Infection pATho SHEENADocument2 pagesUrinary Tract Infection pATho SHEENASheena Arnoco ToraynoNo ratings yet
- Pedia Ward Drug Study...Document12 pagesPedia Ward Drug Study...Sheena Arnoco ToraynoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan CoughDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Coughderic90% (89)
- Asthma: For Other Uses, SeeDocument37 pagesAsthma: For Other Uses, SeeSheena Arnoco ToraynoNo ratings yet
- Hematology Studies: Test: Total Hemoglobin (HGB or HB) CDocument13 pagesHematology Studies: Test: Total Hemoglobin (HGB or HB) CSheena Arnoco ToraynoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!Document11 pagesDrug Study!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!Bern Jujoy BetayoNo ratings yet
- English Book ReportDocument1 pageEnglish Book ReportSheena Arnoco ToraynoNo ratings yet
- Name Action Indication Contraindica Tion Adverse Effect Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument4 pagesName Action Indication Contraindica Tion Adverse Effect Nursing ResponsibilitiesSheena Arnoco ToraynoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology: The Urinary SystemDocument5 pagesAnatomy & Physiology: The Urinary SystemSheena Arnoco ToraynoNo ratings yet