Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CH07 CHOutline
Uploaded by
Afif NaufalOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
CH07 CHOutline
Uploaded by
Afif NaufalCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 7 Animal Parasites Animal Parasites CLASSIFICATION Protozoa: simple one-celled organisms. Metazoa: complex, multicelled.
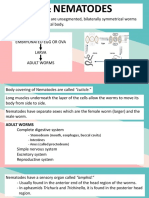
Arthropods: small insects that infest skin. Protozoal Infections MALARIA Transmission by mosquito, occasionally by blood transfusion or hypodermic syringes of illicit drug users. Parasites invade red blood cells and cause febrile illness with red-cell destruction. BABESIOSIS Tick-borne protozoal parasite. Causes malaria-like symptoms. Persons without spleen have severe infection. AMEBIASIS Transmission by contaminated food or water. Invades colon with mucosal ulcers. Occasionally causes liver abscesses. TRICHOMONAD INFECTIONS Cause vaginal infection. Transmission by sexual intercourse. GIARDIASIS Transmission by contaminated food and water. Causes inflammation of small intestine with crampy pain and diarrhea. TOXOPLASMOSIS Parasite in flesh of animals. Infection acquired by eating incompletely cooked meat or from contact with cats who excrete infectious form of parasite. Toxoplasma infection of pregnant women may be transmitted to fetus and cause intrauterine injury. CRYPTOSPORIDIOSIS Animal parasite excreted in stool and contaminates surface water. Infectious oocysts resistant to chlorination. Can be eliminated only by water filtration. People infected from ingestion of unfiltered water from municipal water supplies, swimming pool water, or direct person-to-person spread. Organisms infect small intestine and cause diarrhea, which can be chronic and severe in AIDS patients. No specific treatment available. Metazoal Infections ROUNDWORMS Ascaris Not transmitted person-to-person.
Ingested eggs hatch in intestine. Larvae migrate into circulation and migrate through tissues. Worms lodging in lung are coughed up, swallowed, and mature in intestine. Pinworms Worms live in colon. Migrate out of anus and lay eggs. Cause itching as a result of worm migration. Transmitted by ingestion of eggs on hands and in bedclothes. Trichinella Parasite in flesh of pigs and other animals. Human beings usually infected by eating improperly cooked pork. Worms hatch in intestine; larvae enter circulation and are filtered out in tissues. Worm migration causes systemic symptoms, eosinophilia, and evidence of disturbed organ function. TAPEWORMS Live in intestinal tract and consume nutrients ingested by host. FLUKES Short, fleshy worms that live in liver, intestine, or lung. Human fluke infections not seen in the United States and Canada. Bird or animal flukes (schistosomes) may cause skin inflammation (dermatitis) in people who swim in schistosomeinfested water. Arthropods SCABIES Small parasite burrows in skin, lays eggs, and causes severe itching. Spread by close physical or sexual contact. Responds to antiparasitic medications. CRAB LOUSE Lives in pubic hair and lays eggs that are attached to hair shafts. Causes intense itching. Spread by close physical and sexual contact. Responds to antiparasitic medications.
You might also like
- 911 Pigeon Disease & Treatment Protocols!From Everand911 Pigeon Disease & Treatment Protocols!Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Luminal Protozoan Infections of the Gastrointestinal TractDocument68 pagesLuminal Protozoan Infections of the Gastrointestinal TractHeni Tri RahmawatiNo ratings yet
- ROLL NO 30 (Assignment On Zoonotic Importance of Nematodes)Document3 pagesROLL NO 30 (Assignment On Zoonotic Importance of Nematodes)barsha subediNo ratings yet
- Protozoan and Helminths Disease of ManDocument18 pagesProtozoan and Helminths Disease of ManZairene Jane del RosarioNo ratings yet
- Typesofpathogen 210310051652Document24 pagesTypesofpathogen 210310051652Shana Mae L. BalahayNo ratings yet
- Cleanup Run Me FirstDocument12 pagesCleanup Run Me FirstJesus BerriosNo ratings yet
- AkamwonaDocument1 pageAkamwonaJose WriterNo ratings yet
- Project IN Parasitology: Submitted To: Dr. Ed de Vera Submitted By: Francesca Angela Nervar BSN - 2Document36 pagesProject IN Parasitology: Submitted To: Dr. Ed de Vera Submitted By: Francesca Angela Nervar BSN - 2Catherine MetraNo ratings yet
- Project IN Parasitology: Submitted To: Dr. Ed de Vera Submitted By: Francesca Angela Nervar BSN - 2Document38 pagesProject IN Parasitology: Submitted To: Dr. Ed de Vera Submitted By: Francesca Angela Nervar BSN - 2Catherine MetraNo ratings yet
- Helminthic Medical ImportanceDocument11 pagesHelminthic Medical ImportanceRizalyn Padua ReyNo ratings yet
- General Parasitology L2Document27 pagesGeneral Parasitology L2kayse abtidoonNo ratings yet
- COMMON WORM INFESTATION DrASBDocument54 pagesCOMMON WORM INFESTATION DrASBDr AMAL S BABUNo ratings yet
- Worm ParasitesDocument3 pagesWorm Parasitespaolospadera72No ratings yet
- Parasitology Lab Activity Protozoans & NematodesDocument16 pagesParasitology Lab Activity Protozoans & NematodesJollan Marie BuenvenidaNo ratings yet
- T Spiralis and FriendsDocument4 pagesT Spiralis and Friendssmcm11No ratings yet
- Ascari As IsDocument16 pagesAscari As IsCici Novelia ManurungNo ratings yet
- Bacterial PathogenesisDocument53 pagesBacterial PathogenesisbruhwahatNo ratings yet
- Week 8 Protozoology and ParasitologyDocument48 pagesWeek 8 Protozoology and ParasitologySAMSON, MAXZENE ANICKANo ratings yet
- Kinds 2 RoundwormsDocument10 pagesKinds 2 RoundwormsMelanie perez cortezNo ratings yet
- Infectious DiseasesDocument65 pagesInfectious DiseasesFathimah UswahNo ratings yet
- Parasite Packet 1Document12 pagesParasite Packet 1api-595420397No ratings yet
- L:6 Parasitology: Prof. Dr. Nada KhazalDocument18 pagesL:6 Parasitology: Prof. Dr. Nada KhazalMasar ElfNo ratings yet
- Microbiology and Parasitology #2Document12 pagesMicrobiology and Parasitology #2Nurse TinNo ratings yet
- Defecating in The Morning, Because The Gravid Female Worms Usually Migrate at Night To The Perianal Region To Deposit EggsDocument4 pagesDefecating in The Morning, Because The Gravid Female Worms Usually Migrate at Night To The Perianal Region To Deposit EggsDaniella TupasNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument91 pagesIntroductionJayson BasiagNo ratings yet
- Hookworm Diseases: (Ancylostomiasis /Miner'S Disease/Egyptian Chlorisis)Document21 pagesHookworm Diseases: (Ancylostomiasis /Miner'S Disease/Egyptian Chlorisis)Mel Izhra N. Margate100% (1)
- Bahsakam KotaeyDocument19 pagesBahsakam Kotaeysoran najebNo ratings yet
- Ministry of Higher Education and Science Research Sulaimani Polytechnic University Kalar Technical Institute ..Department SubjectDocument20 pagesMinistry of Higher Education and Science Research Sulaimani Polytechnic University Kalar Technical Institute ..Department Subjectsoran najebNo ratings yet
- Lecture Parasites in Immunocompromised PatientDocument50 pagesLecture Parasites in Immunocompromised PatientalgutNo ratings yet
- INTESTINAL NEMATODES Hand Out 10 - 11Document6 pagesINTESTINAL NEMATODES Hand Out 10 - 11microperadeniyaNo ratings yet
- Exotic Animal ParasitesDocument37 pagesExotic Animal ParasitesSUTHANNo ratings yet
- Study of These Parasitic Worms and Their Medical ConsequenceDocument33 pagesStudy of These Parasitic Worms and Their Medical Consequenceabel semuNo ratings yet
- Soil-Transmitted Helminth InfectionsDocument7 pagesSoil-Transmitted Helminth InfectionsDiane GaliNo ratings yet
- CRYPTOSPORIDIUMDocument65 pagesCRYPTOSPORIDIUMRajkishor YadavNo ratings yet
- ParasitesDocument12 pagesParasitesfumi100% (8)
- 10 ParasitesDocument10 pages10 ParasitesErin Trisha Kristel GaspanNo ratings yet
- AscariasisDocument6 pagesAscariasisbhelle11No ratings yet
- Introduction To Parasitology & Lab Diagnosis of ParasiticDocument33 pagesIntroduction To Parasitology & Lab Diagnosis of ParasiticMaharRkpNo ratings yet
- Parasites 101Document12 pagesParasites 101johnnemanic100% (5)
- General Parasitology L4Document12 pagesGeneral Parasitology L4kayse abtidoonNo ratings yet
- Hookworm Infection: Causes, Symptoms, TreatmentDocument6 pagesHookworm Infection: Causes, Symptoms, Treatmentcooky maknaeNo ratings yet
- 8.health Communicable DiseasesDocument50 pages8.health Communicable DiseasesCatherine Joy De ChavezNo ratings yet
- HelminthDocument2 pagesHelminthMaya MiaNo ratings yet
- Avian-Parasites UpdateDocument5 pagesAvian-Parasites UpdateCody CodyNo ratings yet
- Types of Roundworms That Can Infect HumansDocument30 pagesTypes of Roundworms That Can Infect HumansMelanie perez cortezNo ratings yet
- Post Lab MidtermsDocument18 pagesPost Lab MidtermsRaven TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Parasitiology Semi ExamDocument26 pagesParasitiology Semi ExamHILVANO, HEIDEE B.No ratings yet
- Food Poisoning & Worm InfestationDocument13 pagesFood Poisoning & Worm InfestationPujani SenevirathnaNo ratings yet
- Ascaris Lumbricoides: I. MorphologyDocument6 pagesAscaris Lumbricoides: I. MorphologyJoseline SorianoNo ratings yet
- Fasciola HepaticaDocument19 pagesFasciola HepaticaNaila NawazNo ratings yet
- Zoonoses: Prof - DR.DR - Efrida Warganegara, M.Kes.,Sp - MKDocument64 pagesZoonoses: Prof - DR.DR - Efrida Warganegara, M.Kes.,Sp - MKakun internetNo ratings yet
- Ascaris LumbricoidesDocument15 pagesAscaris LumbricoidesJyoti DasNo ratings yet
- AscariasisDocument7 pagesAscariasisMia Angela Del MundoNo ratings yet
- Infeksi parasit di saluran cerna: Diagnosis dan pengobatan protozoa dan helminta penyebab diareDocument69 pagesInfeksi parasit di saluran cerna: Diagnosis dan pengobatan protozoa dan helminta penyebab diareRangga DarmawanNo ratings yet
- Medical HelminthologyDocument85 pagesMedical HelminthologyMegbaruNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15 NematodesDocument73 pagesChapter 15 NematodesNicole NipasNo ratings yet
- Rodent Borne DiseaseDocument6 pagesRodent Borne DiseasecallmejusNo ratings yet
- Helminths - Parasitic Worms and Their Life CyclesDocument2 pagesHelminths - Parasitic Worms and Their Life CyclesLightless AyuNo ratings yet
- Literacy Initial Assessment Marking Scheme and GuideDocument30 pagesLiteracy Initial Assessment Marking Scheme and GuidestanleyNo ratings yet
- Malaria Updates in Indonesia - KemenkesDocument17 pagesMalaria Updates in Indonesia - KemenkesAmirullah ArsyadNo ratings yet
- Teoh Cher ShongDocument3 pagesTeoh Cher ShongAaron Cheah OJNo ratings yet
- Intellectual DiabilityDocument10 pagesIntellectual DiabilityAngelo PapimNo ratings yet
- Achilles Tendon Injury Rehab Exercises GuideDocument6 pagesAchilles Tendon Injury Rehab Exercises GuideKEVIN NGUYENNo ratings yet
- De Torres Labor Law I ReportDocument11 pagesDe Torres Labor Law I ReportErole John AtienzaNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Reading: Sit Dolor AmetDocument20 pagesJurnal Reading: Sit Dolor AmetLiri AndiyaniNo ratings yet
- CH 12Document36 pagesCH 12api-25474891367% (3)
- Rights of The Child SummarizeDocument29 pagesRights of The Child SummarizeGretel R. MadanguitNo ratings yet
- Sychology of Disability Sport - Participation and PerformanceDocument14 pagesSychology of Disability Sport - Participation and PerformanceCatarina GrandeNo ratings yet
- Missed MiscarriageDocument2 pagesMissed MiscarriageELyssa Anne Maristelle DizonNo ratings yet
- Nursing Diagnosis Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesNursing Diagnosis Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationDanica Fave AndiamNo ratings yet
- Australian Immunisation Register Immunisation History Form: When To Use This FormDocument3 pagesAustralian Immunisation Register Immunisation History Form: When To Use This FormVaccine ScamNo ratings yet
- Arihant DRX Ascend Case Study PDFDocument2 pagesArihant DRX Ascend Case Study PDFsaurav.martNo ratings yet
- Multiple SclerosisDocument3 pagesMultiple SclerosisCarmella CollantesNo ratings yet
- Matalam 18jan2023 FinalDocument3 pagesMatalam 18jan2023 FinalPhilippe Ceasar C. BascoNo ratings yet
- The 5 Fundamental of Fat LossDocument16 pagesThe 5 Fundamental of Fat LossAndrés Jimenez100% (2)
- Job Safety Analysis and Risk AssessmentDocument12 pagesJob Safety Analysis and Risk AssessmentRejib Kibar0% (1)
- EmpyemaDocument9 pagesEmpyemaJoePutraNo ratings yet
- Aripiprazol in TAB 2Document61 pagesAripiprazol in TAB 2Robert MovileanuNo ratings yet
- The Radiation Boom - Case Studies - When Medical Radiation Goes Awry - NYTimesDocument4 pagesThe Radiation Boom - Case Studies - When Medical Radiation Goes Awry - NYTimesMuh Taufik Dwi PutraNo ratings yet
- Positron Emission TomographyDocument2 pagesPositron Emission TomographyRadlinkSingaporeNo ratings yet
- ICD-10 Neoplasm Coding GuidelinesDocument59 pagesICD-10 Neoplasm Coding GuidelinesMuhammad Syamsul ArifinNo ratings yet
- NUHS Alumnus Vol. 50, Issue No. 2Document4 pagesNUHS Alumnus Vol. 50, Issue No. 2National University of Health SciencesNo ratings yet
- NUR 200 Week 8 Pre-Class Assignments - Caitlyn CornettDocument6 pagesNUR 200 Week 8 Pre-Class Assignments - Caitlyn CornettCaitlyn CornettNo ratings yet
- Asbestos Awareness PresentationDocument87 pagesAsbestos Awareness PresentationMmamoraka Christopher MakhafolaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To The Principles of Food Hygiene and SafetyDocument15 pagesIntroduction To The Principles of Food Hygiene and SafetyYasiqyhaidarNo ratings yet
- Abnormal Psychology Final CoachingDocument638 pagesAbnormal Psychology Final Coachingmonne100% (1)
- Case-Based Discussion (CBD) Assessment FormDocument4 pagesCase-Based Discussion (CBD) Assessment Formibbs91No ratings yet
- Interpretation MRCPCH 2009 Site: For Part 2 Exam For Part 2 ExamDocument35 pagesInterpretation MRCPCH 2009 Site: For Part 2 Exam For Part 2 Examyassine100% (1)
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityFrom EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (18)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityFrom EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Summary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedFrom EverandSummary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (78)
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossFrom EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)
- By the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsFrom EverandBy the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsNo ratings yet
- LIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionFrom EverandLIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (403)
- Summary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (42)
- 12 Rules for Life by Jordan B. Peterson - Book Summary: An Antidote to ChaosFrom Everand12 Rules for Life by Jordan B. Peterson - Book Summary: An Antidote to ChaosRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (207)
- Raising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsFrom EverandRaising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeFrom EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeNo ratings yet
- The Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsFrom EverandThe Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Raising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsFrom EverandRaising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (169)
- The Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaFrom EverandThe Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Cult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryFrom EverandCult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (44)
- Mindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessFrom EverandMindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (328)
- Dark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.From EverandDark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (110)
- The Happiness Trap: How to Stop Struggling and Start LivingFrom EverandThe Happiness Trap: How to Stop Struggling and Start LivingRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Algorithms to Live By: The Computer Science of Human DecisionsFrom EverandAlgorithms to Live By: The Computer Science of Human DecisionsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (722)
- Summary: How to Be an Adult in Relationships: The Five Keys to Mindful Loving by David Richo: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedFrom EverandSummary: How to Be an Adult in Relationships: The Five Keys to Mindful Loving by David Richo: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (11)
- Gut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerFrom EverandGut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (392)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Secure Love: Create a Relationship That Lasts a LifetimeFrom EverandSecure Love: Create a Relationship That Lasts a LifetimeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (18)
- Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandOutlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)