Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pe Lab Manual E&c Dept Dsce
Uploaded by
Jeevan PreethuOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Pe Lab Manual E&c Dept Dsce
Uploaded by
Jeevan PreethuCopyright:
Available Formats
Department of Electronics and Communication
DSCE, Bangalore78
POWER ELECTRONICS LAB
Subject Code: 06ECL78 No. of Practical Hrs/Week: 03 Total no. of Practical Hrs: 42
1. Static characteristics of DIAC 2. Static characteristics of SCR 3. Static characteristics of MOSFET 4. Static characteristics of IGBT 5. Controlled HWR and FWR using RC triggering circuit 6. SCR turn off using LC circuit 7. SCR turn off using Auxiliary Commutation 8. UJT firing circuit for HWR and FWR circuits 9. Generation of firing signals for thyristors/ trials using digital circuits/ Microprocessor 10. AC voltage controller using TRIAC DIAC combination 11. Single phase Fully Controlled Bridge Converter with R and RL loads 12. Voltage (Impulse) commutated chopper both constant frequency and Variable frequency operations 13. Speed control of a separately exited DC motor 14. Speed control of universal motor 15. Speed control of stepper motor 16. Parallel / series inverter
IA Marks : 25 Exam Hours : 03 Exam Marks : 50
Power Electronics Laboratory
Page 1
Department of Electronics and Communication
DSCE, Bangalore78
Set of Experiment I Cycle
1. Static characteristics of DIAC 2. Static characteristics of SCR 3. Static characteristics of IGBT 4. Controlled HWR and FWR using RC triggering circuit 5. Speed control of a separately exited DC motor 6. Single phase Fully Controlled Bridge Converter with R and RL loads 7. Generation of firing signals for Thyristors/ trials using digital circuits/ Microprocessor 8. SCR turn off using LC circuit
IICycle
1. Static characteristics of MOSFET 2. UJT firing circuit for HWR and FWR circuits 3. Voltage (Impulse) commutated chopper constant frequency and variable frequency Operations 4. Parallel / series inverter 5. Speed control of stepper motor 6. SCR turn off using Auxiliary Commutation 7. AC voltage controller using TRIAC DIAC combination 8. Speed control of universal motor
Power Electronics Laboratory
Page 2
Department of Electronics and Communication
DSCE, Bangalore78
Experiment No.1
Static characteristics of DIAC
Aim : To determine the forward and reverse characteristic of DIAC Apparatus Required: Resistor 1k1No, Voltmeter (060v)1 No, DIAC1No, Ammeter (0250mA)1No, Connecting Wires, Connecting Board1No.
Circuit Diagram:
Procedure:
(1). Rig up the circuit as shown in the circuit diagram (2). Switch on the Regulated power supply by keeping the voltage course fine in minimum position (3). Increase the voltage in steps and note down the corresponding voltage and Current in the tabular column (4). Reduce the voltage to the minimum position and switch off the power supply (5). To determine the reverse characteristics interchange the DIAC terminals and repeat the above steps (6). Plot the graph of Voltage versus Current
Applications:
Power Electronics Laboratory
Page 3
Department of Electronics and Communication
DSCE, Bangalore78
Tabular Column: Forward V ( volts) I (ma) Reverse V ( volts) I (ma)
Graph:
Result:
Power Electronics Laboratory
Page 4
Department of Electronics and Communication
DSCE, Bangalore78
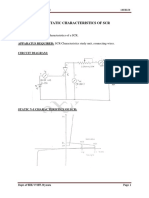
Experiment No.2 Static characteristics of SCR Aim: To determine the VI characteristics of the given SCR Apparatus Required: Resistor 1k, 470E/5w 1No, SCR TYN604/4101No, Voltmeter
(060v)1 No, Ammeter (0100mA)2No, connecting Board1No, Connecting Wires.
SYMBOL:
Circuit Diagram:
Procedure:
(1). Rig up the circuit as shown in the circuit diagram (2). Set Ig=7ma, Keeping Ig constant, vary the anode voltage VAK and note down the anode current Ia and anode voltage Vak (3). Tabulate the readings and plot the graph of Vak Versus Ia (4). Repeat the above steps for for different gate current (Ig) (5). From the graph determine holding current (IH), Latching current (IL) and Forward Break over voltage (VBO)
Power Electronics Laboratory Page 5
Department of Electronics and Communication
DSCE, Bangalore78
Applications: Graph:
Tabular Column: I g =_____________ma V ak (volts) I a (mA) IL = ____________ma IH =____________ma
Result:
Power Electronics Laboratory
Page 6
Department of Electronics and Communication
DSCE, Bangalore78
Experiment No.3 Static characteristics of MOSFET Aim: To obtain the drain and transfer characteristics of MOSFET Apparatus Required: Resistor 10k, 50E/5w 1No, MOSFET (IRF 450)1No,
Voltmeter (060v)1 No, Ammeter (0100mA)2No, Connecting Board1No, Connecting Wires.
SYMBOL:
Circuit Diagram:
Procedure:
(1).Rig up the circuit as shown in the circuit diagram (2).Switch on the power supply and keep Vgs to a constant value (1, 2,3V etc) (3).By varying the voltage across drain and source and note down the corresponding voltage Vds and current Id (4).Tabulate the readings plot the graph of V ds v/s Id for different Vgs determine Rd
Power Electronics Laboratory Page 7
Department of Electronics and Communication
DSCE, Bangalore78
(5).To determine the transfer characteristics set Vds to a specified value and vary Vgs (6).For each variations of Vgs note down the drain current Id, tabulate the readings and plot the graph of Vgs v/s Id for constant Vds (7). Determine the Tran conductance Gm and Amplification factor () Rd = V ds / Id Gm= Id / Vgs = Gm* Rd
Applications: Graph: Output Characteristics:
Transfer Characteristics
Tabular Column: Vgs1= V ds (volts) I d (mA)
Output Characteristics Vgs2= V ds (volts) I d (mA)
Transfer Characteristics Vds= V gs(volts) I d (mA) Result:
Power Electronics Laboratory
Page 8
Department of Electron and Communication D t nics
DSCE, Ba angalore78 8
Ex xperiment No.4 t Static characteristics of IGB BT Aim: To plot the VI and Transfer characteristics of IGBT A t s Apparatus Required: IGBT, Voltm A meter (060v No, Amm v)1 meter (0100 0mA)1No,
Co onnecting W Wires.
Circuit Diag C gram:
ower Electron Laborato nics ory Po
Page 9
Department of Electronics and Communication
DSCE, Bangalore78
Procedure:
(1). Rig up the circuit as shown in the circuit diagram (2). Switch on the supply by keeping in minimum position of Vge and Vce (3). Set the value for Vge=5.32v (4). Increase Vce in steps and note down the corresponding voltage of Vce and Current Ic (5).Tabulate the readings plot the graph of Ic versus Vce (6).To determine the transfer characteristics set Vce to a specified value (7). By increasing Vge in steps note down the corresponding values of Ic and plot the graph of Vge versus Ic for constant Vce
Applications: Graph: Transfer Characteristics:
Output Characteristics:
Tabular Column:
VI Characteristics
Vge1= V ce (volts) I c(mA)
Transfer Characteristics
Vge2=
Vce1= V ge(volts) I d(mA)
Vce2=
Result:
Power Electronics Laboratory Page 10
Department of Electronics and Communication
DSCE, Bangalore78
Experiment No.5 Controlled HWR and FWR using RC triggering Circuit Aim: To rig up a circuit for controlled HWR and FWR using RC Triggering circuit Apparatus Required: SCR (2P4M)2No, Diode (BY127)2No, Resistor 100E/5W, Pot
1M, Capacitor (0.47F),Transformer (12012) Voltmeter(060v), Connecting Board, Connecting Wires and CRO probe.
Circuit Diagram: HALF WAVE RECTIFIER
v
FULL WAVE RECTIFIER
v
230V 50HZ
Power Electronics Laboratory
Page 11
Department of Electronics and Communication
DSCE, Bangalore78
INPUT AND OUTPUT WAVEFORMS:
Procedure:
(1). Rig up the circuit as shown in the circuit diagram (2). Switch on the Power supply (3). Observe the wave forms across SCR and Load for HWR and FWR (4). By varying the potentiometer (1M) note down the delay angle and output voltage (5).Compare the results with the theoretical value Vdc=Vm [1+cos]/2 for HWR, Vdc=Vm [1+cos]/ for FWR
Tabular Column: Delay Angle() V practical (volts) V theoretical (volts)
Applications:
Result:
Power Electronics Laboratory
Page 12
Department of Electron and Communication D t nics
DSCE, Ba angalore78 8
Ex xperiment No.6 t SCR turnon cir t rcuit using Synchronized UJT re elaxation o oscillator Aim: To stud the turn o of SCR using UJT in Sy A dy on ynchronous mode, for HWR and FW WR
Circuit t
Apparatus Required: SCR (2P4M) A )2No,UJT(2N2646),Diod de(BY127)3No,Resistor1 1k,
100E/5W,Po 1 ot100K,Capacitor(0.47F F),Transform mer(12012), Pulse Transf P former, Voltm meter(060v v),Connectin Board, ng Connecting W C Wires, and C probe. CRO
Circuit Diag C gram:
ower Electron Laborato nics ory Po
Page 13
Department of Electronics and Communication
DSCE, Bangalore78
HALF WAVE CONTROLLER
R5 100E/5W 1k
VS 6V/12V
VA
Vz
1k 1k 100k B2 E 2N2646 B! VB1 0.47MF SCR
230V 50Hz 6V/12V
Z6.5
VC
FULL WAVE CONTROLLER
D VS 6V/12V 230V/50HZ Z 6.5 6V/12V D 0.47MF VC VA R8 1k VZ Vz 1k 1k B2 100k E 2N2646 B1 VB1 SCR2 100E/5W SCR1
Procedure:
(1). Rig up the circuit as shown in the circuit diagram (2). Switch on the A.C supply (3). Observe the wave forms at Vs, Va, Vz, Vc Vb1, VSCR and across the load (4). By varying the potentiometer (100K) note down the delay angle and output voltage
Applications:
Power Electronics Laboratory
Page 14
Department of Electronics and Communication
DSCE, Bangalore78
Result:
Power Electronics Laboratory Page 15
Department of Electronics and Communication
DSCE, Bangalore78
Experiment No.7 SCR turnoff using LC circuit Aim: To study the basic working of LC Commutation Apparatus Required: Multimeter, Patch chords, CRO probes Circuit Diagram:
Procedure:
(1). Rig up the circuit as shown in the circuit diagram (2). Switch on the triggering circuit and observe the triggering pulses with the help of CRO (3). Switch on the chopper switch keeping the potentiometer of the triggering circuit in Minimum position (4). Note down the output Voltage, Duty cycle and Plot the graph
Tabular Column: VL (volts) Ton (ms) Toff (ms) T (ms) Duty Cycle Applications:
Power Electronics Laboratory
Page 16
Department of Electronics and Communication
DSCE, Bangalore78
Graph:
VL
Duty cycle
Result:
Power Electronics Laboratory
Page 17
Department of Electronics and Communication
DSCE, Bangalore78
Experiment No.8 SCR turnoff using Auxilliary Commutation Aim: To study the SCR Turn Off using Auxilliary Commutation Apparatus Required: Multimeter, Patch chords, CRO probes, Lamp load. Circuit Diagram:
Power Electronics Laboratory
Page 18
Department of Electronics and Communication
DSCE, Bangalore78
Procedure:
(1). Rig up the circuit as shown in the circuit diagram (2). Switch on the triggering circuit and observe the triggering pulses with the help of CRO (3). Keep the selector switch of the DC supply in the second position i.e. 30V (4). Switch on the DC supply of the firing circuit keeping the chopper switch in the Off Position (5). Switch on the chopper switch keeping the potentiometer of the triggering circuit in the Minimum position (6). Observe the waveforms across the SCR, capacitor and Load (7). By varying the firing pulses measure Ton, Toff and output voltage across the Load (8). Compare the practical value with the theoretical value Vdc=Ton/Ton+Toff x Vin, Vdc=Ton/T x Vin, Vdc = duty cycle x Vin (9).Plot the graph of Duty cycle v/s output voltage
Tabular Column: VL (volts) Ton (ms) Toff (ms) T (ms) Duty Cycle Applications: Graph:
Result:
Power Electronics Laboratory Page 19
Department of Electronics and Communication
DSCE, Bangalore78
Experiment No.9 Digital Triggering of SCR Aim: To study the triggering of SCR using digital triggering Method Apparatus Required: Multimeter, Transformer (12012), Resistor 100E/5w, Patch
chords, CRO probes.
Circuit Diagram:
To HWR
Power Electronics Laboratory
Page 20
Department of Electronics and Communication
DSCE, Bangalore78
Procedure:
(1). Switch on the Digital Triggering circuit module and check the Triggering pulses of the digital triggering using CRO (2). Note down the wave forms at different terminal points of the module [A,C, Tp, Tn] (3). Rig up the circuit as shown in the circuit diagram (4). Vary the Triggering angle in steps and note down the output voltage [vdc] across the load (5). Bring back the Triggering angle to zero and switch off the module (6). Plot the graph of vdc v/s
Tabular Column: Load Voltage (volts) Delay angle () Applications: Graph:
Result:
Power Electronics Laboratory
Page 21
Department of Electronics and Communication
DSCE, Bangalore78
Experiment No.10 AC voltage controller using TRIACDIAC combination Aim: To study AC voltage controller Apparatus Required: TRIAC module, differential module, Lamp, Multimeter,
BNC to BNC probe.
Circuit Diagram:
Procedure:
(1). Rig up the circuit as shown in the circuit diagram (2). Switch on the power supply to the circuit (3). Vary the potentiometer and note down the load voltage and delay angle (4). Plot the graph of delay angle versus voltage
Tabular Column: Load Voltage (volts) Delay angle () Applications: Graph:
Result:
Power Electronics Laboratory Page 22
Department of Electron and Communication D t nics
DSCE, Ba angalore78 8
Ex xperiment No.11 Single phase fully controlle Bridge Converter with R an RL loads ed r nd s Aim: To stud the conve A dy ersion of AC to DC using single phase fully contro e olled Bridge
Conver with R and RL loads rter
Apparatus Required: Multimeter Patch card Transform [12012 100e/5w, A r, ds, mer 2]
In nductor, CRO Probe, Con O nnecting wir res.
Circuit Diag C gram:
ower Electron Laborato nics ory Po
Page 23
Department of Electronics and Communication
DSCE, Bangalore78
Procedure:
(1). Rig up the circuit as shown in the circuit diagram (2). Switch on the Triggering circuit and check the Triggering pulses with the help of CRO Keeping the potentiometer in minimum position (3). By varying the Triggering pulses note down the corresponding output voltage and Delay angle (4). Plot the graph of delay angle V/s output voltage (5). Decrease the Triggering pulses to the minimum position and switch off the circuit
Tabular Column: Load Voltage (volts) Delay angle () Applications: Graph:
Result:
Power Electronics Laboratory
Page 24
Department of Electronics and Communication
DSCE, Bangalore78
Experiment No.12 Speed control of separately excited DC Motor Aim: To study the speed control of separately excited DC motor using single phase full
Wave half controlled rectifier
Apparatus Required: Isolation transformer, patch cords, Multimeter, and
Tachometer.
Circuit Diagram:
Procedure:
(1). Rig up the circuit as shown in the circuit diagram (2). Switch on the firing circuit and check the firing pulses with the help of CRO (3). Switch on the AC supply of the isolation transformer (4). By varying the firing circuit note down the output voltage and speed
Tabular Column: Load Voltage (volts) Speed (rpm) Applications: Graph:
Result:
Power Electronics Laboratory
Page 25
Department of Electronics and Communication
DSCE, Bangalore78
Experiment No.13 Speed Control of Universal Motor Aim: To study the speed control of Universal Motor Apparatus Required: TRIAC module, differential module, Universal motor,
Multimeter.
Procedure:
(1). Rig up the circuit as shown in the circuit diagram (2). Switch on the power supply to the circuit (3). Vary the potentiometer and note down the load voltage and speed (4). Plot the graph of voltage v/s speed
Tabular Column: Load Voltage (volts) Speed (rpm) Graph:
Result:
Power Electronics Laboratory Page 26
Department of Electronics and Communication
DSCE, Bangalore78
Experiment No.14 Stepper Motor Aim: To study the speed control of stepper motor Apparatus Required: Stepper motor, Stepper motor controller. Circuit Diagram:
LOGIC CONTROLLER FREEWHEELING DIODES
RED WHITE GREEN -ve BLUE BLACK BLACK RS + ve RS
SWITCHING TRANSISTORS
SWITCHING LOGIC SEQUENCE Half Step A1 Red 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 0 A2 B1 B2 Green Blue Black 1 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 1 1 0 1 0 0 A1 Red 0 0 1 1 Q1 Full Step A2 B1 B2 Green Blue Black 1 0 1 1 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 Q2 Q3 Q4
Power Electronics Laboratory
Page 27
Department of Electronics and Communication
DSCE, Bangalore78
Procedure: (1). Connect A1, A2, B1 and B2 leads of stepper motor to the corresponding
Terminals of the Control module (2). Set the appropriate number of steps (3). Set the stepper motor to operate in half step or full step mode (4). Observe the rotation of the motor for different type of settings
Motor Ratings:
Permanent magnet, bifilar wound two phase Steps per revaluation : 200 No. of Leads : 06 Step angle : 1.80 + 02 0.10 non cumulative. 3 kg.cm = 0.1 N.m = 13.0 OZ in
Applications: Graph: Result:
Power Electronics Laboratory
Page 28
Department of Electronics and Communication
DSCE, Bangalore78
Experiment No.15 Series Inverter Aim: To study the basic working of series Inverter Apparatus Required: Inverter module, Patch chord, Multimeter, CRO probes,
Resistor 50 /5w, DC Power supply.
Circuit Diagram:
T1 Firing Circuit T2
G K G K
Procedure:
(1). Switch on the module to check the triggering pulses on the CRO (2). Rig up the circuits as shown in the circuits diagram (3). Switch on the power supply and observe the wave forms across the load (4). Measure the output voltage and output frequency by varying the frequency of the triggering circuits (5). Repeat the above procedure for different values of Inductance and Capacitance (6). Bring back the triggering angle to zero and switch off the module
Tabular Column: Inductance (H) Capacitance(f) Frequency (Hz) VL (volts)
Power Electronics Laboratory
Page 29
Department of Electronics and Communication
DSCE, Bangalore78
Applications:
Graph:
Resonance Frequency [Fr] = Result:
Power Electronics Laboratory
Page 30
Department of Electronics and Communication
DSCE, Bangalore78
Experiment No.16 Parallel Inverter Aim: To study the basic working of parallel Inverter Apparatus Required: Inverter module, Patch chords, Triggering module. Circuit Diagram:
D1
T1 Firing Circuit T2
G
L
SCR1 C
KVL
RL
K G K
Vdc
+
SCR2
D2
Procedure:
(1). Rig up the circuits as shown in the circuits diagram (2).Connect the +15, 15, Gnd and supply to the Triggering circuit. Check the output of the trigger circuit at various points (3).Connect the gate of SCR1 and SCR2 to the triggering circuit and oscilloscope to the load (4).Observe the waveform and measure the frequency across the load
Applications: Graph:
Result:
Power Electronics Laboratory
Page 31
Department of Electronics and Communication
DSCE, Bangalore78
MODEL QUESTION BANK
[1] Obtain the static characteristics of SCR and hence determine the holding current [2] Conduct a suitable experiment to determine VI characteristics of unidirectional four layer switches. Determine breakdown voltage and holding current [3] Obtain a variable DC output voltage using LC communication and plot the graph of Duty cycle v/s output voltage [4] Rig up and test an oscillator chopper circuit to produce variable DC output. Draw the output voltage v/s duty cycle [5] Conduct a suitable experiment to obtain an output voltage of a fully controlled bridge rectifier using resistive load. Plot the output voltage v/s delay angle [6] Conduct a suitable experiment to obtain an output voltage of a fully controlled bridge rectifier for R and RL load with and without free wheeling diode. Plot the output voltage v/s delay angle for R load [7] Conduct a suitable experiment to convert fixed DC voltage to variable DC voltage with the duty cycle of and verify [8] Conduct a suitable experiment to convert fixed DC voltage to variable DC voltage with a fixed frequency [9] Conduct a suitable experiment to control the speed of a given DC motor using single phase half controlled bridge rectifier. Draw the speed v/s output voltage [10]Control the RPM and step size of a stepper motor tabulate the readings for different settings [11]Conduct a suitable experiment to obtain the AC output from a DC input using a basic series inverter [12]Conduct a suitable experiment to verify the operating principle of a single phase series inverter [13]For single phase fully controlled bridge rectifier circuit with R load plot the graph of Alpha v/s output voltage using digital firing circuit [14]By conducting suitable experiment on a given MOSFET obtain the drain and transfer characteristics [15]By conducting suitable experiment on a given MOSFET determine Rd, , gm [16]Conduct a suitable experiment to draw VI characteristics of the given IGBT and comment on its switching characteristics [17]Conduct a suitable experiment to draw transfer and output characteristics of given IGBT [18]Conduct a suitable experiment to control intensity of light using bidirectional switch and plot output voltage v/s delay angle [19]Conduct a suitable experiment to control the speed of a single phase universal motor and plot the graph of output voltage v/s speed [20]Conduct a suitable experiment to trigger SCR using a UJT relaxation oscillator [21]Using RC only rig up a suitable experiment to trigger SCR and hence obtain the output voltages for different angles Power Electronics Laboratory Page 32
Department of Electronics and Communication
DSCE, Bangalore78
[22]Using RC triggering for HWR and FWR obtain firing angle v/s output voltage. Study the relevant waveforms [23]Conduct a suitable experiment to obtain VI characteristics of a given 4layer 2 terminal device. Find the breakdown voltage for both directions
Power Electronics Laboratory
Page 33
Department of Electronics and Communication
DSCE, Bangalore78
Power Electronics Laboratory
Page 34
Department of Electronics and Communication
DSCE, Bangalore78
Power Electronics Laboratory
Page 35
Department of Electronics and Communication
DSCE, Bangalore78
Power Electronics Laboratory
Page 36
Department of Electronics and Communication
`````````````````
DSCE, Bangalore78
Power Electronics Laboratory
Page 37
Department of Electronics and Communication
DSCE, Bangalore78
Power Electronics Laboratory
Page 38
Department of Electronics and Communication
DSCE, Bangalore78
Power Electronics Laboratory
Page 39
Department of Electronics and Communication
DSCE, Bangalore78
Power Electronics Laboratory
Page 40
Department of Electronics and Communication
DSCE, Bangalore78
Power Electronics Laboratory
Page 41
Department of Electronics and Communication
DSCE, Bangalore78
Power Electronics Laboratory
Page 42
Department of Electronics and Communication
DSCE, Bangalore78
Power Electronics Laboratory
Page 43
Department of Electronics and Communication
DSCE, Bangalore78
Power Electronics Laboratory
Page 44
Department of Electronics and Communication
DSCE, Bangalore78
Power Electronics Laboratory
Page 45
You might also like
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- Power Lab Manual 7th Sem 2011 - BGSDocument109 pagesPower Lab Manual 7th Sem 2011 - BGSSumanth Sathyanarayana100% (1)
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Pe Lab Manual 2016Document44 pagesPe Lab Manual 2016MukundKulkarniNo ratings yet
- VSC-FACTS-HVDC: Analysis, Modelling and Simulation in Power GridsFrom EverandVSC-FACTS-HVDC: Analysis, Modelling and Simulation in Power GridsNo ratings yet
- 18EEL58 - Power Electronics Lab NewDocument19 pages18EEL58 - Power Electronics Lab NewSrinivasNo ratings yet
- PE & S Lab Manual (Student Copy)Document67 pagesPE & S Lab Manual (Student Copy)Chunduri Rambabu100% (4)
- Power Electronics Applied to Industrial Systems and Transports, Volume 2: Power Converters and their ControlFrom EverandPower Electronics Applied to Industrial Systems and Transports, Volume 2: Power Converters and their ControlRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Power Electronics Lab ManualDocument28 pagesPower Electronics Lab ManualManjunath KalkutagiNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Electronics 1: Electronic Components and Elementary FunctionsFrom EverandFundamentals of Electronics 1: Electronic Components and Elementary FunctionsNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics ManualDocument61 pagesPower Electronics ManualS Piyush Piyush0% (1)
- Power Electronics Lab ManualDocument49 pagesPower Electronics Lab ManualNeelakanth BenakalNo ratings yet
- Physics and Technology of Crystalline Oxide Semiconductor CAAC-IGZO: Application to LSIFrom EverandPhysics and Technology of Crystalline Oxide Semiconductor CAAC-IGZO: Application to LSINo ratings yet
- Ee2304 Lab ManualDocument49 pagesEe2304 Lab ManualSohail KhanNo ratings yet
- Power Systems-On-Chip: Practical Aspects of DesignFrom EverandPower Systems-On-Chip: Practical Aspects of DesignBruno AllardNo ratings yet
- Python Programming 2nd EditionDocument106 pagesPython Programming 2nd Editionshivanand_shettennav100% (1)
- 7th Sem Power Electronics Lab ManualDocument88 pages7th Sem Power Electronics Lab ManualRavi Hatti100% (1)
- 110 Waveform Generator Projects for the Home ConstructorFrom Everand110 Waveform Generator Projects for the Home ConstructorRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- BTL 4th Sem Power Electronics Lab ManualDocument88 pagesBTL 4th Sem Power Electronics Lab ManualGopinath B L NaiduNo ratings yet
- Power System Transient Analysis: Theory and Practice using Simulation Programs (ATP-EMTP)From EverandPower System Transient Analysis: Theory and Practice using Simulation Programs (ATP-EMTP)No ratings yet
- Power Electronics LabDocument34 pagesPower Electronics LabanaatmandarthiNo ratings yet
- Analog Circuit Design Volume Three: Design Note CollectionFrom EverandAnalog Circuit Design Volume Three: Design Note CollectionRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Power Electronics Lab ManualDocument89 pagesPower Electronics Lab ManualPartha DewriNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics Lab ManualDocument66 pagesPower Electronics Lab Manualm_javaidkhanNo ratings yet
- EE8661-Power Electronics and Drives-Lab ManualDocument117 pagesEE8661-Power Electronics and Drives-Lab ManualSam Jasper80% (5)
- Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book (Linear IC): Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book, Volume 1From EverandNewnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book (Linear IC): Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book, Volume 1Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Power Electronics Lab Manual For ECE (Vtu)Document87 pagesPower Electronics Lab Manual For ECE (Vtu)Sathish KumarNo ratings yet
- Analog Circuit Design: A Tutorial Guide to Applications and SolutionsFrom EverandAnalog Circuit Design: A Tutorial Guide to Applications and SolutionsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (6)
- Power ElectronicsDocument16 pagesPower ElectronicsPerumal NamasivayamNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Design and Test Case AnalysisFrom EverandElectromagnetic Compatibility (EMC) Design and Test Case AnalysisNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics Lab Manual PDFDocument16 pagesPower Electronics Lab Manual PDFBiradar ShivshankerNo ratings yet
- List of ExperimentsDocument78 pagesList of ExperimentsmurthyNo ratings yet
- Lmele308 PDFDocument29 pagesLmele308 PDFAbhinit GauravNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics Lab ManualDocument51 pagesPower Electronics Lab ManualArun DasNo ratings yet
- PE Manual 10ECL78Document62 pagesPE Manual 10ECL78techimranNo ratings yet
- EE6611-Power Electronics and Drives LaboratoryDocument136 pagesEE6611-Power Electronics and Drives Laboratoryswathi100% (1)
- Esd Manual With Viva QuestionDocument100 pagesEsd Manual With Viva QuestionrubiniravichandranNo ratings yet
- Edc Manual RoseDocument48 pagesEdc Manual RoseRagabindu GuruNo ratings yet
- 18EEL58Document39 pages18EEL58Rajendra VirajendraNo ratings yet
- Pelab NewDocument60 pagesPelab NewRaghu PathyNo ratings yet
- CH-5 EdcDocument13 pagesCH-5 EdcOTHEOZ NFTNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics Lab ManualDocument72 pagesPower Electronics Lab Manualrajeshbv056135100% (3)
- Power Manual1Document5 pagesPower Manual1Krunal GandhiNo ratings yet
- EDC Lab ManualDocument48 pagesEDC Lab ManualDishan D Shah100% (1)
- Lab Manual: Electrical Engineering Materials & Semiconductor Devices Lab (EC-317-F)Document41 pagesLab Manual: Electrical Engineering Materials & Semiconductor Devices Lab (EC-317-F)Ilavarasan TamizhNo ratings yet
- Ee-8661 Power Electronics and Drives Lab ManualDocument88 pagesEe-8661 Power Electronics and Drives Lab ManualgangshNo ratings yet
- Exp 1: SCR SwitchDocument4 pagesExp 1: SCR Switchprop_kcpNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual: (2015 - 16) 10 EEL 48 Power Electronics LabDocument76 pagesLab Manual: (2015 - 16) 10 EEL 48 Power Electronics LabSadanandMaskaleSadanandMaskaleNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics Lab Manual of 4th Sem EEEDocument32 pagesPower Electronics Lab Manual of 4th Sem EEETusshar Kamath0% (1)
- Power Electronics Lab Manual PDFDocument72 pagesPower Electronics Lab Manual PDFGopinath B L NaiduNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics Lab Manual With LogoDocument69 pagesPower Electronics Lab Manual With LogoPunith Gowda M BNo ratings yet
- 3-2power Electronics Lab ManualDocument50 pages3-2power Electronics Lab ManualSivareddy MudiyalaNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics ManualDocument57 pagesPower Electronics Manualkarthime27No ratings yet
- III I PE Lab ManualDocument138 pagesIII I PE Lab ManualRakibuzzaman TonmoyNo ratings yet
- Additions, Revisions, or Updates: Subject DateDocument7 pagesAdditions, Revisions, or Updates: Subject DateRuthAnayaNo ratings yet
- MEC20-902 Controlador Gran Plaza PDFDocument101 pagesMEC20-902 Controlador Gran Plaza PDFCesar AmloNo ratings yet
- Chasis TelevisorDocument49 pagesChasis TelevisorReynaldo MarcaNo ratings yet
- Cables Theory DesignDocument25 pagesCables Theory DesignA. HassanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 31Document22 pagesChapter 31OmarWaelNo ratings yet
- Pe Lab ManualDocument41 pagesPe Lab ManualGopalakrishna Murthy C RNo ratings yet
- Solar Pv200 Manual v1.6Document25 pagesSolar Pv200 Manual v1.6maguado1992No ratings yet
- 1420Document14 pages1420ANVNo ratings yet
- 2021 WC Mced Physci GR 12 Sep Exam p1 EngDocument18 pages2021 WC Mced Physci GR 12 Sep Exam p1 Engtshepangbokamoso36No ratings yet
- EA230 Manual PDFDocument4 pagesEA230 Manual PDFJulia ArguetaNo ratings yet
- Home Power Magazine - Issue 003 - Feb 1988 - Renewable Solar Wind Energy PDFDocument48 pagesHome Power Magazine - Issue 003 - Feb 1988 - Renewable Solar Wind Energy PDFCharlieeMIFNo ratings yet
- AEM For Series SE and SEHDocument30 pagesAEM For Series SE and SEHdimNo ratings yet
- Schneider Electric Lexium LMX23A Product ManualDocument466 pagesSchneider Electric Lexium LMX23A Product Manualtranhuutri1987quangngaiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 21: Electric Charge and Electric FieldDocument30 pagesChapter 21: Electric Charge and Electric FieldNguyễn Ngoc AnhNo ratings yet
- Practical ElectricityDocument104 pagesPractical Electricityray davis100% (1)
- Class Xii Sample PapersDocument110 pagesClass Xii Sample PapersSaurav Singh MohantaNo ratings yet
- Maintenance of Electropneumatic Contactor of Electric Locomotive-EngDocument56 pagesMaintenance of Electropneumatic Contactor of Electric Locomotive-EngRodrigo Hernández AbarzúaNo ratings yet
- Saturn Geo: Earth-/ Ground-TesterDocument2 pagesSaturn Geo: Earth-/ Ground-TesterTecno ArteNo ratings yet
- BDI 803 SeriesDocument21 pagesBDI 803 Series최영진No ratings yet
- Festo ElectroPneumatics Basic Level TP201 012002 294Document294 pagesFesto ElectroPneumatics Basic Level TP201 012002 294Avtomatika Kole Nehtenin100% (1)
- A Project Report ON - " ": Automatic Street LightDocument8 pagesA Project Report ON - " ": Automatic Street LightPranjal Babar 25100% (1)
- Felipe Calderon Integrated High SchoolDocument3 pagesFelipe Calderon Integrated High SchoolRafaiza ManoNo ratings yet
- Conceptual Integrated Science 2nd Edition Hewitt Solutions Manual DownloadDocument4 pagesConceptual Integrated Science 2nd Edition Hewitt Solutions Manual DownloadSteve Duncan100% (25)
- Lecture 1 PDFDocument46 pagesLecture 1 PDFLin Xian XingNo ratings yet
- 7KM31201BA011EA0 Datasheet enDocument6 pages7KM31201BA011EA0 Datasheet enNIKINo ratings yet
- Lebanese International University School of EngineeringDocument12 pagesLebanese International University School of EngineeringHassan RashedNo ratings yet
- Insulation Resistance Test - Factors Affecting Test ResultsDocument2 pagesInsulation Resistance Test - Factors Affecting Test Resultstenk_manNo ratings yet
- Catalogue Vacuum Circuit Breaker 3ah4 enDocument36 pagesCatalogue Vacuum Circuit Breaker 3ah4 enspctin100% (1)
- Chapter 2 OvervoltageDocument11 pagesChapter 2 OvervoltageCaliNo ratings yet
- DTOcean - Optimal Design Tools For Ocean Energy ArraysDocument94 pagesDTOcean - Optimal Design Tools For Ocean Energy ArraysWilson NevesNo ratings yet
- Digital Filmmaking: The Ultimate Guide to Web Video Production for Beginners and Non-Professionals, Learn Useful Tips and Advice on How You Can Create, Film and Edit Your VideosFrom EverandDigital Filmmaking: The Ultimate Guide to Web Video Production for Beginners and Non-Professionals, Learn Useful Tips and Advice on How You Can Create, Film and Edit Your VideosRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- The Innovators: How a Group of Hackers, Geniuses, and Geeks Created the Digital RevolutionFrom EverandThe Innovators: How a Group of Hackers, Geniuses, and Geeks Created the Digital RevolutionRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (543)
- Multiplexed Networks for Embedded Systems: CAN, LIN, FlexRay, Safe-by-Wire...From EverandMultiplexed Networks for Embedded Systems: CAN, LIN, FlexRay, Safe-by-Wire...No ratings yet
- Programming the Raspberry Pi, Third Edition: Getting Started with PythonFrom EverandProgramming the Raspberry Pi, Third Edition: Getting Started with PythonRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- 2022 Adobe® Premiere Pro Guide For Filmmakers and YouTubersFrom Everand2022 Adobe® Premiere Pro Guide For Filmmakers and YouTubersRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Electrical Engineering 101: Everything You Should Have Learned in School...but Probably Didn'tFrom EverandElectrical Engineering 101: Everything You Should Have Learned in School...but Probably Didn'tRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (27)
- Retro Gaming with Raspberry Pi: Nearly 200 Pages of Video Game ProjectsFrom EverandRetro Gaming with Raspberry Pi: Nearly 200 Pages of Video Game ProjectsNo ratings yet
- Empires of Light: Edison, Tesla, Westinghouse, and the Race to Electrify the WorldFrom EverandEmpires of Light: Edison, Tesla, Westinghouse, and the Race to Electrify the WorldRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (87)
- Power System Control and ProtectionFrom EverandPower System Control and ProtectionB. Don RussellRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (11)
- Conquering the Electron: The Geniuses, Visionaries, Egomaniacs, and Scoundrels Who Built Our Electronic AgeFrom EverandConquering the Electron: The Geniuses, Visionaries, Egomaniacs, and Scoundrels Who Built Our Electronic AgeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (10)
- Practical Electrical Wiring: Residential, Farm, Commercial, and IndustrialFrom EverandPractical Electrical Wiring: Residential, Farm, Commercial, and IndustrialRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- INCOSE Systems Engineering Handbook: A Guide for System Life Cycle Processes and ActivitiesFrom EverandINCOSE Systems Engineering Handbook: A Guide for System Life Cycle Processes and ActivitiesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Guide to the IET Wiring Regulations: IET Wiring Regulations (BS 7671:2008 incorporating Amendment No 1:2011)From EverandGuide to the IET Wiring Regulations: IET Wiring Regulations (BS 7671:2008 incorporating Amendment No 1:2011)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- The Innovators: How a Group of Hackers, Geniuses, and Geeks Created the Digital RevolutionFrom EverandThe Innovators: How a Group of Hackers, Geniuses, and Geeks Created the Digital RevolutionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (331)
- Hacking Electronics: An Illustrated DIY Guide for Makers and HobbyistsFrom EverandHacking Electronics: An Illustrated DIY Guide for Makers and HobbyistsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Teach Yourself Electricity and Electronics, 6th EditionFrom EverandTeach Yourself Electricity and Electronics, 6th EditionRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (15)
- Build Your Own Electronics WorkshopFrom EverandBuild Your Own Electronics WorkshopRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)