Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Nursing 194 CONCEPT MAP: Goal Met
Nursing 194 CONCEPT MAP: Goal Met
Uploaded by
Leigh Foster WilkinsOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Nursing 194 CONCEPT MAP: Goal Met
Nursing 194 CONCEPT MAP: Goal Met
Uploaded by
Leigh Foster WilkinsCopyright:
Available Formats
Nursing 194 CONCEPT MAP
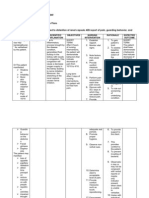
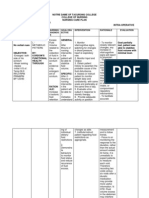
Acute pain r/t bladder hemorrhaging amb bladder spasms 1. Medicate with antispasmodics or analgesics as prescribed. Document pain relief obtained, using pain scale. 2. If patient is losing urine around catheter, check catheter and drainage tubing for evidence of obstruction. 3. Encourage intake of fluids to 2-3L/day to help reduce spasms. A.F. Admitted 5/28/12 83yr old female Admitting Diagnosis: Bladder Cancer Allergies: Penicillin 1. Monitor for and report abdominal cramps, diarrhea, colic, irritability, nausea, or muscle weakness. 2. Monitor mental orientation and signs of disorientation. 3. Assess vital signs for decreasing BP, changes in LOC, tachycardia, tachypnea, thready pulse. Goal met Fluid Volume Deficit r/t to active fluid volume loss secondary to hemorrhaging amb bleeding and decreased hgb
Goal met
Goal- Within 1 hr of intervention, patient's subject perception of discomfort decreases, as documented by a pain scale.
Chronic pain r/t bladder cancer aeb patient stating she aches after chemo.
Goal-Patient is normovolemic and free of signs of shock and electrolyte imbalance.
RBC@10 .4 HCT@33 .1
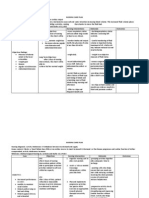
1.
Administer opioid and non opioid analgesics in correct dose, at correct frequency, and via correct route. Assess for signs and symptoms of tolerance, and when it occurs, discuss treatment with health care provider. Use nonpharmacologic approaches, such as acupressure, biofeedback, relaxation therapy, application heat or cold, and massage.
2.
3.
Goal-Patient participates in a prescribed regimen and reports that pain and side effects associated with the prescribed therapy are reduced to a level of 3 or less within 1-2 hours of intervention.
Goal met.
You might also like
- Orthopedic Inpatient Protocols: A Guide to Orthopedic Inpatient RoundingFrom EverandOrthopedic Inpatient Protocols: A Guide to Orthopedic Inpatient RoundingNo ratings yet
- Ms Flash CardsDocument15 pagesMs Flash CardsMia MalazoNo ratings yet
- Gi Exam2016Document28 pagesGi Exam2016Andrea BroccoliNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument10 pagesNursing Care PlanGinel Laquiores100% (1)
- Abdominal Aortic AneurysmDocument3 pagesAbdominal Aortic AneurysmyabaeveNo ratings yet
- NCP ConstipationDocument3 pagesNCP ConstipationNkk Aqnd Mgdngl100% (4)
- NCPDocument22 pagesNCPMaricris S. Sampang100% (1)
- NCPsDocument13 pagesNCPsRocel DevillesNo ratings yet
- Case Study Multiple Organ Dysfunction and ShockDocument3 pagesCase Study Multiple Organ Dysfunction and ShockJrBong SemaneroNo ratings yet
- Peptic UlcerDocument53 pagesPeptic UlcerHoney Lyn AlebioNo ratings yet
- Case AnalysisDocument25 pagesCase AnalysisGerly LagutingNo ratings yet
- Assessment Needs Nursing Diagnos IS Goal/Obj Ective Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument10 pagesAssessment Needs Nursing Diagnos IS Goal/Obj Ective Intervention Rationale EvaluationApol Pen67% (3)
- Decreased Cardiac OutputDocument9 pagesDecreased Cardiac OutputChinita Sangbaan75% (4)
- NCPDocument11 pagesNCPzharienabNo ratings yet
- Client Information Sheet (CIS)Document10 pagesClient Information Sheet (CIS)Christine RombawaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study and NCP!Document8 pagesDrug Study and NCP!Abegail Abaygar100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan For Benign Prostatic Hypertrophy NCPDocument9 pagesNursing Care Plan For Benign Prostatic Hypertrophy NCPderic88% (8)
- Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesNursing Care PlanCristina L. JaysonNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan - Using NandaDocument16 pagesNursing Care Plan - Using NandaWardinatul ImanNo ratings yet
- Myocardial InfarctionDocument5 pagesMyocardial InfarctionDharline Abbygale Garvida AgullanaNo ratings yet
- Gi NclexDocument14 pagesGi NclexYoke W Khoo100% (3)
- Cellulitis Care PlanDocument6 pagesCellulitis Care PlanNaya Kayala0% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan: DiagnosisDocument11 pagesNursing Care Plan: DiagnosisCharmaine100% (1)
- NCPDocument11 pagesNCPJaziel Remo100% (1)
- Assessment Nsg. Diagnosis Sci. Explanation Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument6 pagesAssessment Nsg. Diagnosis Sci. Explanation Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationRoMarie AbainzaNo ratings yet
- Case ScenarioDocument40 pagesCase ScenarioDave Michael GeliNo ratings yet
- SDVSSDVSVDocument2 pagesSDVSSDVSVGovind Narayan PandeyNo ratings yet
- Health Teaching Plan - Lateral Neck Mass Probably MalignantDocument5 pagesHealth Teaching Plan - Lateral Neck Mass Probably MalignantRene John FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Gallbladder-Liver and Pancreatic DisordersDocument7 pagesGallbladder-Liver and Pancreatic DisordersHasan A AsFourNo ratings yet
- Parenteral Nutrition Basic IVT Nov 2008Document53 pagesParenteral Nutrition Basic IVT Nov 2008Crystal Mae Castrodes DaquipilNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan 1: Group 1Document9 pagesNursing Care Plan 1: Group 1Danieal NeymarNo ratings yet
- Clinical Abstract (2nd Sem 1st Rotation)Document3 pagesClinical Abstract (2nd Sem 1st Rotation)Michael Gino SarenasNo ratings yet
- NCP CalculiDocument8 pagesNCP CalculihailleyannNo ratings yet
- MS QuestionsDocument53 pagesMS QuestionsHoney Lyn AlebioNo ratings yet
- Case Study #1 (NCM116RC)Document4 pagesCase Study #1 (NCM116RC)Dexel Lorren ValdezNo ratings yet
- Diabetic KetoacidosisDocument5 pagesDiabetic KetoacidosisJamie IllmaticNo ratings yet
- Nursing Management of Patient With Upper Gastrointestinal BleedingDocument10 pagesNursing Management of Patient With Upper Gastrointestinal BleedingVia Katherine PanganibanNo ratings yet
- Conceptmaptext For EpDocument9 pagesConceptmaptext For Epapi-272402391No ratings yet
- Acute Abdominal-WPS OfficeDocument3 pagesAcute Abdominal-WPS OfficeA HNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Rationale Planning Nursing Interventio N Rationale EvaluationDocument16 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Rationale Planning Nursing Interventio N Rationale EvaluationKatrina Mae RamirezNo ratings yet
- Fdar For Abdominal Pain Related To Acute AppendicitisDocument1 pageFdar For Abdominal Pain Related To Acute AppendicitisArki ObusanNo ratings yet
- Peforated Peptic UlcerDocument19 pagesPeforated Peptic Ulcertecklor SiakamwiNo ratings yet
- Med Name: Mechanism of Action: Dosage: 10 MG Daily Priority Med Specific Patient TeachingDocument6 pagesMed Name: Mechanism of Action: Dosage: 10 MG Daily Priority Med Specific Patient TeachingBrittany BennettNo ratings yet
- Guidelines For The Management of Malignant Ascites ST Peters Hospice, BristolDocument6 pagesGuidelines For The Management of Malignant Ascites ST Peters Hospice, Bristoldrakarion itizinNo ratings yet
- Practical Nursing Diploma Program Pre-Clinical Nursing Care Research Assignment "Prep and Plan"Document7 pagesPractical Nursing Diploma Program Pre-Clinical Nursing Care Research Assignment "Prep and Plan"Jeremy ThomasNo ratings yet
- Drug Indication Action Side Effects and Adverse Reaction Nursing ConsiderationDocument8 pagesDrug Indication Action Side Effects and Adverse Reaction Nursing Considerationkier khierNo ratings yet
- NCP2 - DengueDocument4 pagesNCP2 - DengueSummer SuarezNo ratings yet
- NCP PROPER Pain and Decreased Cardiac OutputDocument3 pagesNCP PROPER Pain and Decreased Cardiac OutputErienne Lae Manangan - CadalsoNo ratings yet
- VIII. Nursing Care PlanDocument12 pagesVIII. Nursing Care PlanNefre Dayap DarrocaNo ratings yet
- NCP and DStudyDocument8 pagesNCP and DStudyJessica Rosan Hewald ManapatNo ratings yet
- Complicarions Ward ClassDocument29 pagesComplicarions Ward ClassRoeder CuerdaNo ratings yet
- Medicine Ward NCPDocument11 pagesMedicine Ward NCPKimsha ConcepcionNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument8 pagesNCPJose Benit DelacruzNo ratings yet
- HypertensionDocument30 pagesHypertension123cj456No ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument8 pagesNursing Care PlanAngela SweetNo ratings yet
- ConceptmapcareplanDocument4 pagesConceptmapcareplanapi-316030498No ratings yet
- Ncp'sDocument8 pagesNcp'sDuchess Kleine RafananNo ratings yet
- Accesory OrganDocument12 pagesAccesory OrganTrisha SuazoNo ratings yet