Professional Documents
Culture Documents
PBL Eye
Uploaded by
SpencerOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
PBL Eye
Uploaded by
SpencerCopyright:
Available Formats
[1].Enlarged jugulodigastric lymph nodes are also commonly found in tonsillitis.
Hyperaemia or hyperemia describes the increase of blood flow to different tissue s in the body. It can have medical implications, but is also a regulatory respon se, allowing change in blood supply to different tissues through vasodilation. C linically, hyperaemia in tissues manifest as erythema, because of the engorgemen t of vessels with oxygenated blood.[1] Hyperaemia can also occur due to a fall i n atmospheric pressure outside the body. Peritonsillar abscess is a complication of tonsillitis. It is most often caused by a type of bacteria called group A beta-hemolytic streptococcus. Peritonsillar abscess is usually a disease of older children, adolescents, and y oung adults. It has become uncommon with the use of antibiotics to treat tonsill itis. Infectious mononucleosis occurs with infection by the Epstein Barr virus.[15] [16] The infection is spread via saliva, and has an incubation period of four to seve n weeks.[17] Symptoms usually persist for two to three weeks,[18] but fatigue is often more prolonged.[4] most contagious period is thought to last about six weeks after the onset of sym ptoms. Some studies indicate a person can spread the infection for many months a fter the symptoms are completely gone, with one particular study indicating as l ong as 18 months.[19] The virus replicates first within epithelial cells in the pharynx (which causes pharyngitis, or sore throat), and later primarily within B cells (which are inva ded via their CD21). The host immune response involves cytotoxic (CD8-positive) T cells against infected B lymphocytes, resulting in enlarged, atypical lymphocy tes (Downey cells).[20][21] When the infection is acute (recent onset, instead of chronic), heterophile anti bodies are produced.[11]
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- USMLE Road Map Gross Anatomyi PDFDocument258 pagesUSMLE Road Map Gross Anatomyi PDFSpencerNo ratings yet
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Jefferson - Aoa USMLE Step 1Document12 pagesJefferson - Aoa USMLE Step 1Mc Ase100% (1)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Answers For NBME 5 and 6Document2 pagesAnswers For NBME 5 and 6Håvard Jenssen100% (1)
- 2017 Monthly Us Holidays CalendarDocument12 pages2017 Monthly Us Holidays CalendarKhairul RizalNo ratings yet
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- FA 2017 Changes PDFDocument38 pagesFA 2017 Changes PDFrsimranjitNo ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- 1 Bridging Anticoag Primum Non NocereDocument12 pages1 Bridging Anticoag Primum Non NocereSpencerNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- 2017 Monthly Calendar Landscape 04Document12 pages2017 Monthly Calendar Landscape 04SpencerNo ratings yet
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- First Aid Q&A PDFDocument764 pagesFirst Aid Q&A PDFStephanie Williams100% (9)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- 1 Bridging Anticoag Primum Non NocereDocument12 pages1 Bridging Anticoag Primum Non NocereSpencerNo ratings yet
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Antro Choanal PolypDocument16 pagesAntro Choanal PolypSpencer100% (1)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- PFT Class NotesDocument7 pagesPFT Class NotesFajar AgNo ratings yet
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Presentation Diagnosis of Diabetes Mellitus: Presented by Kanwal AmjadDocument29 pagesPresentation Diagnosis of Diabetes Mellitus: Presented by Kanwal AmjadSpencerNo ratings yet
- QUESTION BANK 2007 From UT HoustonDocument44 pagesQUESTION BANK 2007 From UT HoustonMindy Lee80% (5)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Chronic Pharyngitis FinalDocument27 pagesChronic Pharyngitis FinalSpencerNo ratings yet
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- An Insight Into Step 3Document4 pagesAn Insight Into Step 3SpencerNo ratings yet
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
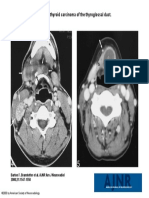
- AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2000 Sep 21 (8) 1547-50, Fig 4Document1 pageAJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2000 Sep 21 (8) 1547-50, Fig 4SpencerNo ratings yet
- MCQs on Biochemical Cardiac Markers for AMI DetectionDocument2 pagesMCQs on Biochemical Cardiac Markers for AMI DetectionSyed Usama Rashid50% (2)
- Acute Otitis MediaDocument27 pagesAcute Otitis MediaSpencerNo ratings yet
- 2017 Monthly Us Holidays CalendarDocument12 pages2017 Monthly Us Holidays CalendarSpencerNo ratings yet
- Erratum Notice: O Level First Language Urdu Syllabus 3247 Paper 2: Texts Prescribed Texts For Examination in 2009Document1 pageErratum Notice: O Level First Language Urdu Syllabus 3247 Paper 2: Texts Prescribed Texts For Examination in 2009SpencerNo ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Derma McqsDocument3 pagesDerma McqsSyed Usama Rashid100% (1)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- 2017 Monthly Calendar Landscape 04Document12 pages2017 Monthly Calendar Landscape 04SpencerNo ratings yet
- CNS Flashcards Study SetDocument2 pagesCNS Flashcards Study SetSpencerNo ratings yet
- Genital UlcerDocument64 pagesGenital UlcerSpencerNo ratings yet
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Fetal SurveilanceDocument34 pagesFetal SurveilanceSpencerNo ratings yet
- Anatomy MS WristJointSGDDocument24 pagesAnatomy MS WristJointSGDSpencerNo ratings yet
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)