Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Laboratory Study (Urinalysis 0
Laboratory Study (Urinalysis 0
Uploaded by
Yasmeen Blair Ferrer MamaclayOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Laboratory Study (Urinalysis 0
Laboratory Study (Urinalysis 0
Uploaded by
Yasmeen Blair Ferrer MamaclayCopyright:
Available Formats
Laboratory Study (URINALYSIS)
Normal Findings
Result
Interpretation
Nursing responsibilities Before:
Color
pale to dark yellow or amber
Light yellow
Normal. A red or reddish-brown color could be from a food dye, consumption of beets, a drug, or the presence of either hemoglobin (from the breakdown of blood) or myoglobin (muscle breakdown)
Inform the client about the test to be done. Discuss the purpose and importance of the test. Secure a sterile specimen bottle. Instruct the patient on the proper procedure in obtaining a clean catch urine.
During: Transparency clear clear Normal. Urine is typically clear. A cloudy appearance may indicate an infection. Ensure that the patient obtains a clean urine
Maintain uncontaminated specimen to avoid alteration on the result
After: Albumin negative negative Normal. Urine protein levels are normally low and aren't detected by a dipstick test. Small increases in protein usually aren't a cause for concern. Larger amounts of protein in the urine may indicate a kidney problem. Normal. Normally the amount of sugar (glucose) in urine is too low to be detected. Any detection of sugar on this test usually calls for follow-up testing for diabetes. The pH level indicates the amount of acid in urine. Abnormal pH levels may indicate a kidney or urinary tract disorder. All urine specimens must be labeled with the patients name, time and date, they must also be refrigerated until they are given to the lab.
Sugar
negative
negative
pH
Slightly acidic
acidic
Specific Gravity
1.002 and 1.035
1.016
Normal. Higher than normal concentration often is a result of dehydration, rather than another underlying medical condition. But, it may indicate a kidney disorder.
Pus Cells
negative
2-4hpf
Presence of pus cells in urine may indicate an infection. A positive nitrite test indicates that bacteria may be present in significant numbers. Gram negative rods such as E. coli are more likely to give a positive test.
Morphous Urates
negative
positive
Bacteria
negative
positive
may indicate an infection
RBC
none
none
Normal. Blood in your urine requires additional testing, as it may be a sign of kidney damage, infection, kidney or bladder stones, kidney or bladder cancer or blood disorders, among other conditions
You might also like
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5813)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (844)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- Metered Dose Inhaler (Mdi)Document4 pagesMetered Dose Inhaler (Mdi)arn0ld21No ratings yet
- Quintos - 2nd Forensic Medicine AssignmentDocument5 pagesQuintos - 2nd Forensic Medicine AssignmentCharlene Joy Bumarlong QuintosNo ratings yet
- PrematurityDocument37 pagesPrematurityNishaThakuriNo ratings yet
- Research Presentation Script I. Background of The Study & Introduction of Research TitleDocument3 pagesResearch Presentation Script I. Background of The Study & Introduction of Research TitleSophia Adel RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Referensi SMT 4Document4 pagesReferensi SMT 4Afi YemaraNo ratings yet
- Burning Mouth SyndromeDocument3 pagesBurning Mouth SyndromeYohana RebeccaNo ratings yet
- Stress and Burnout Questionnaire GugDocument1 pageStress and Burnout Questionnaire GugGuransh SinghNo ratings yet
- Conservative Treatment of Early Postoperative Small Bowel Obstruction With Obliterative PeritonitisDocument10 pagesConservative Treatment of Early Postoperative Small Bowel Obstruction With Obliterative Peritonitisalemago90No ratings yet
- Asanas & Their Benefits, Limitations and Complementary AsanasDocument2 pagesAsanas & Their Benefits, Limitations and Complementary Asanassaurin.tailor425100% (1)
- Bed MakingDocument8 pagesBed MakingV_RN100% (1)
- Speech by Her Excellency Margaret Kenyatta, First Lady of The Republic of Kenya During The Official Opening Ceremony of the 10th Stop Cervical, Breast and Prostate Cancer in Africa (SCCA) Conference in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia on 25th July, 2016.Document4 pagesSpeech by Her Excellency Margaret Kenyatta, First Lady of The Republic of Kenya During The Official Opening Ceremony of the 10th Stop Cervical, Breast and Prostate Cancer in Africa (SCCA) Conference in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia on 25th July, 2016.First Lady KenyaNo ratings yet
- Hyperosmolar Hyperglycemic StateDocument10 pagesHyperosmolar Hyperglycemic StateMirko S. León RguezNo ratings yet
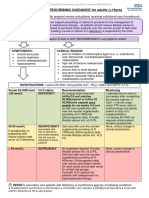
- VITAMIN D PRESCRIBING GUIDANCE For Adults ( 18yrs)Document3 pagesVITAMIN D PRESCRIBING GUIDANCE For Adults ( 18yrs)afifahNo ratings yet
- English Books BibliotekaDocument10 pagesEnglish Books BibliotekahazeemmegahedNo ratings yet
- ASDAS CalculatorDocument4 pagesASDAS CalculatorSthepany HuertasNo ratings yet
- Cefixime and DicloxacillinDocument3 pagesCefixime and DicloxacillinCurtis CrawfordNo ratings yet
- Trans SaVi Oto Lec 03 Diseases of The External and Middle EarDocument13 pagesTrans SaVi Oto Lec 03 Diseases of The External and Middle EarJoherNo ratings yet
- Label Nama ObatDocument20 pagesLabel Nama ObatRiza MutiNo ratings yet
- Instrument Introduction: Automatic Hematology Analyzer Seeing Beyond LimitDocument2 pagesInstrument Introduction: Automatic Hematology Analyzer Seeing Beyond LimitCarla YcoNo ratings yet
- Preconception CounsellingDocument22 pagesPreconception Counsellingapi-209383619No ratings yet
- Multiple and Mixed Valvular Heart DiseaseDocument13 pagesMultiple and Mixed Valvular Heart DiseaseВенцислав МирчевNo ratings yet
- Basic Lower Limb Assessment Flow SheetDocument2 pagesBasic Lower Limb Assessment Flow Sheetمحمد نعمة جياد100% (1)
- Drug Study2Document8 pagesDrug Study2zbestgurlNo ratings yet
- Genetic Screening, Prenatal DiagnosisDocument56 pagesGenetic Screening, Prenatal DiagnosisLunaLure100% (1)
- Motion To TravelDocument6 pagesMotion To TravelEdward V. ByrneNo ratings yet
- Associates of Applied Science Degree RequirementsDocument1 pageAssociates of Applied Science Degree Requirementsapi-608273689No ratings yet
- NCP 1Document3 pagesNCP 1itsmeayaNo ratings yet
- Final Care Coordination PlanDocument9 pagesFinal Care Coordination PlanEmmanuel InyanzaNo ratings yet
- First Aid GuideDocument5 pagesFirst Aid GuideAniruddha BagchiNo ratings yet
- PNLE IV For Psychiatric NursingDocument15 pagesPNLE IV For Psychiatric Nursinggeng gengNo ratings yet