Professional Documents
Culture Documents
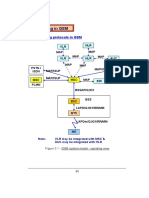
Figure 1 - GSM System Architecture With Essential Components
Uploaded by
anildhumeOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Figure 1 - GSM System Architecture With Essential Components
Uploaded by
anildhumeCopyright:
Available Formats
Figure 1 - GSM system architecture with essential components.
Figure 2 - GPRS system architecture
Figure 3 - GPRS system architecture and routing example
Probability for Table 1. Reliability classes. Class Lost Duplicat Out of packe ed sequence t packet packet Corrupted packet
1 109 109 109 109 128 2Class 104 byte 5packet 105 1024 byte 6 10 10 packet 2 5 5 3 10 10 10 102 Mean 95% Mean 95% delay delay delay delay 1 2 3 4 <0.5s <5s <50s <1.5s <25s <250s <2s < 15s <75s <7s <75s <375s
Best effort Best effort Best effort Best effort Table 2. Delay classes.
Figure 4 - PDP context activation.
Figure 5 - State model of a GPRS mobile station.
Figure 9 - Paging (mobile terminated packet transfer).
Figure 6 - Intra-SGSN routing area update.
Figure 7 - GSM carrier frequencies, duplexing, and TDMA frames.
Group Table 3. Logical channels in GPRS. Packet data traffic channel Packet broadcast control channel Packet common control channel (PCCCH)
Chann el PDTCH PBCCH PRACH PAGCH PPCH PNCH
Function Data traffic Broadcast control Random access Access grant Paging Notification Timing advance control
Directio n MS MS MS MS MS MS BSS BSS BSS BSS BSS BSS BSS BSS
Packet dedicated control channels
PACCH Associated control MS PTCCH MS
Figure 8 - Uplink channel allocation (mobile originated packet transfer); one or two steps
Figure 9 - Paging (mobile terminated packet transfer
Figure 10 - Multiframe structure with 52 frames.
Infobi Parit Tai Output Data ts Cod Table 4. Channel coding Coding Prey l conv Punctur rate e schemes for the logical schem cod. witho bits bit encode ed bits kbit/ e USF ut rate traffic chennels in GPRS. BC s r s USF CS-1 CS-2 CS-3 CS-4 3 6 6 12 181 268 312 428 40 16 16 16 4 4 4 456 588 676 456 0 132 220 1/2 ~2/3 ~3/4 1 9.05 13.4 15.6 21.4
Figure 11 - Encoding of GPRS data packets.
Figure 12 - Convolutional encoder.
1:CS-1 is equivalent to the coding of the GSM SACCH (see [5]). 2:For the PRACH a different coding is used.
Figure 13 - Transmission plane.
Figure 14 - Signaling plane: MSSGSN
Figure 15 - Signaling plane: SGSNHLR, SGSNEIR.
Figure 16 - Signaling plane: SGSN MSC/VLR.
Figure 17 - Protocols at the Gi IP interface
Figure 18 - Example of a GPRSInternet connection.
You might also like
- Call FlowsDocument103 pagesCall Flows742952100% (3)
- ZTE - GPRS Parameter SettingDocument70 pagesZTE - GPRS Parameter SettingPuneet YadavNo ratings yet
- Answers:: Ans: (B) (B) It Point To The Next InstructionDocument13 pagesAnswers:: Ans: (B) (B) It Point To The Next InstructionronyiutNo ratings yet
- 3rd Generation Systems: - Review of Cellular Wireless Networks - UmtsDocument39 pages3rd Generation Systems: - Review of Cellular Wireless Networks - Umtsselvadpm5No ratings yet
- GPRS Overview: Reference: OutlineDocument22 pagesGPRS Overview: Reference: OutlineHasnain HaiderNo ratings yet
- Map Call Flow ImportantDocument22 pagesMap Call Flow ImportantPham Thanh Tam100% (1)
- System Architecture Evolution (SAE) in 3GPPDocument24 pagesSystem Architecture Evolution (SAE) in 3GPPSamsher SinghNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Network Planning and Optimisation 2G/3G/4G: Evolution to 5GFrom EverandFundamentals of Network Planning and Optimisation 2G/3G/4G: Evolution to 5GNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Mobile Network Engineering: GSM, 3G-WCDMA, LTE and the Road to 5GFrom EverandIntroduction to Mobile Network Engineering: GSM, 3G-WCDMA, LTE and the Road to 5GNo ratings yet
- From GSM to LTE-Advanced Pro and 5G: An Introduction to Mobile Networks and Mobile BroadbandFrom EverandFrom GSM to LTE-Advanced Pro and 5G: An Introduction to Mobile Networks and Mobile BroadbandNo ratings yet
- EDGE OverviewDocument33 pagesEDGE OverviewJuan Pablo Calderon VarelaNo ratings yet
- GPRS PCU ImplementationDocument22 pagesGPRS PCU ImplementationAhmed MohamedNo ratings yet
- A) Signaling Protocols in GSMDocument29 pagesA) Signaling Protocols in GSMVarun TomarNo ratings yet
- WB1 1 Data Fundamentals RANDocument71 pagesWB1 1 Data Fundamentals RANankur_infoNo ratings yet
- Notes PDFDocument14 pagesNotes PDFShashank NaikNo ratings yet
- 2.1 GPRS Network Coverage Area: Information & Communications TechnologyDocument20 pages2.1 GPRS Network Coverage Area: Information & Communications TechnologyultimoridigNo ratings yet
- GSM, GPRS, Umts, Hsdpa and HSUPA Protocols and Call Flow by Kiran KoonaDocument103 pagesGSM, GPRS, Umts, Hsdpa and HSUPA Protocols and Call Flow by Kiran KoonaZin MaungNo ratings yet
- 1.3.1 GSMDocument181 pages1.3.1 GSMJosue FredesNo ratings yet
- Presentation: OF Base Station System (BSS)Document30 pagesPresentation: OF Base Station System (BSS)wakeonlanNo ratings yet
- Gprs CodingDocument4 pagesGprs CodingPuneet GuptaNo ratings yet
- E o SDHDocument28 pagesE o SDHrahulskdNo ratings yet
- EvolutionDocument15 pagesEvolution185534 ktr.ece.14No ratings yet
- General Packet Radio Service Physical-Layer Performance SimulationDocument6 pagesGeneral Packet Radio Service Physical-Layer Performance SimulationAdeeb HusnainNo ratings yet
- Curs 1 - GSM - NetworkDocument21 pagesCurs 1 - GSM - NetworkDarius DaKiddNo ratings yet
- GSM GPRS: Global System For Mobile CommunicationDocument55 pagesGSM GPRS: Global System For Mobile CommunicationArrul InsaniNo ratings yet
- Pilot and Data Aided Channel Estimation For Uplink MC-CDMA Mobile SystemsDocument5 pagesPilot and Data Aided Channel Estimation For Uplink MC-CDMA Mobile SystemsAnonymous BkmsKXzwyKNo ratings yet
- LTE PP SlidesDocument13 pagesLTE PP SlidesAnonymous VHXJw23L2l50% (2)
- GPRS For 2 Hours TrainingDocument105 pagesGPRS For 2 Hours Trainingh_hadidiNo ratings yet
- 2.5g Gprs HSCSD EdgeDocument24 pages2.5g Gprs HSCSD Edgeaamirnav123No ratings yet
- Radio Network GPRS/EDGE Concept and ParametersDocument73 pagesRadio Network GPRS/EDGE Concept and ParametersClive MangwiroNo ratings yet
- 3G Mobile CommunicationDocument27 pages3G Mobile CommunicationTechy GuyNo ratings yet
- Fast ARQ in High Speed Downlink Packet Access For WCDMA SystemsDocument7 pagesFast ARQ in High Speed Downlink Packet Access For WCDMA SystemsTorsion TesnorNo ratings yet
- GSM P&O Training Material For Skill Certificate-GPRS Parameter SettingDocument70 pagesGSM P&O Training Material For Skill Certificate-GPRS Parameter SettingRehanKhanNo ratings yet
- Sikomber Protokol Management JaringanDocument83 pagesSikomber Protokol Management JaringanIwan S SantosoNo ratings yet
- Evolution-Data Optimized: Standard RevisionsDocument5 pagesEvolution-Data Optimized: Standard Revisions185534 ktr.ece.14No ratings yet
- An Overview of GPRS: Navjot Kaur Lecturer in ECE, LPUDocument29 pagesAn Overview of GPRS: Navjot Kaur Lecturer in ECE, LPUShahid جنيدNo ratings yet
- TC & BSC OverviewDocument36 pagesTC & BSC OverviewVarun VarmaNo ratings yet
- Zigbee Body SensorDocument7 pagesZigbee Body SensorsunilsmcsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Data Services in GSM System: What GPRS IsDocument19 pagesChapter 2 Data Services in GSM System: What GPRS IsDavid JohnsNo ratings yet
- GPRS DimensionsDocument10 pagesGPRS Dimensionsyousef shabanNo ratings yet
- GPRS ExplainedDocument11 pagesGPRS ExplainedAhmed Hamed BadrNo ratings yet
- The GPRS Network: ContentsDocument13 pagesThe GPRS Network: ContentsChidhuro OwenNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Scheduling Framework On An RLC/MAC Layer For General Packet Radio ServiceDocument9 pagesDynamic Scheduling Framework On An RLC/MAC Layer For General Packet Radio ServiceAbdenago RoldanNo ratings yet
- TCP Ip NotesDocument14 pagesTCP Ip Notesjoshwaaa_hotmailcomNo ratings yet
- GSM BasesDocument9 pagesGSM BasesBasel wesamNo ratings yet
- SystemVue 2002AppNote PDFDocument6 pagesSystemVue 2002AppNote PDFCu BomNo ratings yet
- Korelasi Edge Dynamic Abis Pool (EDAP) Dengan Kecepatan Data Pada BSS Nokia PT. Telkomsel JakartaDocument9 pagesKorelasi Edge Dynamic Abis Pool (EDAP) Dengan Kecepatan Data Pada BSS Nokia PT. Telkomsel JakartaDave StephenNo ratings yet
- Upstream Channel BondingDocument13 pagesUpstream Channel BondingppNo ratings yet
- LCAS BenefitsDocument5 pagesLCAS BenefitsjwalantudesaiNo ratings yet
- Basic Call Set Up Pada GSMDocument46 pagesBasic Call Set Up Pada GSMfarazsaifNo ratings yet
- Digital Mobile Communications and the TETRA SystemFrom EverandDigital Mobile Communications and the TETRA SystemRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)