Professional Documents
Culture Documents
16 Dinamika Fluida
Uploaded by
Alkautsar Permana0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
41 views14 pagesOriginal Title
16 DINAMIKA FLUIDA
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
41 views14 pages16 Dinamika Fluida
Uploaded by
Alkautsar PermanaCopyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 14
DINAMIKA FLUIDA
ARIF BUDIMAN, M.Si
Physics 111: Lecture 24, Pg 2
DINAMIKA FLUIDA = ALIRAN FLUIDA
(STREAMLINE)
Physics 111: Lecture 24, Pg 3
l Aliran fluida steady (mantap):
Kecepatan aliran fluida tidak bergantung pada waktu,
kebalikannya aliran fluida non steady (tak mantap).
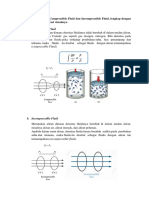
l Aliran fluida compressible (termampatkan):
Densitas fluida bergantung pada tekanan (gas),
kebalikannya aliran fluida incompressible (tak
termampatkan), contohnya zat cair.
l Aliran fluida Rotational:
Partikel fluida mempunyai momentum sudut. Untuk
mendeteksi aliran ini dapat meletakan kincir ke dalam
aliran tsb, apabila kincir berputar maka aliran disebut aliran
fluida Rotational. kebalikannya aliran fluida Irrotational.
JENIS-JENIS ALIRAN FLUIDA
Physics 111: Lecture 24, Pg 4
l Aliran fluida viscous (kental):
Kecepatan masing-masing fluida berkurang secara
seragam dari lapisan paling atas ke lapisan paling bawah.
Kebalikannya aliran fluida non viscous (tak kental/encer).
Physics 111: Lecture 24, Pg 5
PERSAMAAN KONTINUITAS
l Aliran fluida bersifat: non steady, incompressibel, irrotasianal
dan non viscous.
l Berlaku hukum kekekalan massa.
Am
1
Am
2
( ) ( )
konst Av
v A v A
t
x A
t
x A
t
V
t
V
t
m
t
m
=
=
A
A
=
A
A
A
A
=
A
A
A
A
=
A
A
2 2 1 1
2 2 1 1
2 1
2 1
Physics 111: Lecture 24, Pg 6
PERSAMAAN BERNOULLI
l Aliran fluida bersifat: non steady, incompressibel, irrotasianal
dan non viscous.
l Teorema Kerja Energi Mekanik
Am
1
Am
2
Physics 111: Lecture 24, Pg 7
( ) ( ) | |
2 2 1 1
2 2 2 1 1 1
2 1
V P V P W
x A P x A P W
W W W
A A =
A + A =
+ =
( ) ( )
( ) ( )
( ) ( )
1 1 2 2
2
1 1 2
1
2
2 2 2
1
1 1 2 2
2
1 1 2
1
2
2 2 2
1
1 2 1 2
gy V gy V v V v V W
gy m gy m v m v m W
U U K K W
U K W
A A + A A =
A A + A A =
+ =
A + A =
( ) ( )
( ) ( )
konst gy v P
gy v P gy v P
gy v gy v P P
V gy v V gy v V P V P
gy V gy V v V v V V P V P
= + +
+ + = + +
+ + =
A + + A = A A
A A + A A = A A
2
2
1
2
2
2 2
1
2 1
2
1 2
1
1
2 2
2
2 2
1
1
2
1 2
1
2 1
2 2 2
2
2 2
1
1 1
2
1 2
1
2 2 1 1
1 1 2 2
2
1 1 2
1
2
2 2 2
1
2 2 1 1
Physics 111: Lecture 24, Pg 8
VENTURIMETER
Alat ukur laju aliran fluida dalam pipa
Physics 111: Lecture 24, Pg 9
TABUNG PITOT
Alat ukur laju aliran gas
Physics 111: Lecture 24, Pg 10
VISKOSITAS
l Rasio shear stress dan strain dalam fluida disebut koefisien
viskositas q.
Physics 111: Lecture 24, Pg 11
l Jika diasumsikan lapisan atas mempunyai laju v dan
lapisan mempunyai laju v = 0, maka dv/dy = v/D.
l Satuan SI viskositas adalah N.s/m
2
dan satuan cgs
dyne.s/cm
2
disebut poise (yang diambil dari nama ahli
Fisika Prancis Jean-Louis-Marie Poiseuille, orang pertama
yang mengamati aliran fluida kental dalam tabung).
l 1 poise = 0.1 N.s/m
2
.
Physics 111: Lecture 24, Pg 12
VISKOSITAS BEBERAPA FLUIDA
Physics 111: Lecture 24, Pg 13
HUKUM STOKES
l Jika sebuah bola pejal berjari-jari r bergerak dengan laju v dalam
fluida viscous dan steady yang diam, menurut Sir George
Stokes bola tersebut akan mendapat gaya gesekan (gaya
Stokes) sebesar
F
ges
= 6 t q r v
l Pernyataan di atas dikenal dengan Hukum Stokes
B
W
F
ges
a
( ) ( ) ( ) a r rv g r g r
ma F B W
ma F
ges
tot
' 6 '
3
3
4
3
3
4
3
3
4
t tq t t =
=
=
l = massa jenis bola
l = massa jenis fluida
Physics 111: Lecture 24, Pg 14
l Karena gaya Stokes berbanding lurus dengan kecepatan
maka kecepatan bola akan bertambah dengan percepatan
yang makin berkurang sehingga akhirnya kecepatan tetap
(a = 0), kecepatan ini disebut kecepatan akhir atau terminal
yaitu
( ) ( )
( )
q
tq t t
=
=
'
0 6 '
2
9
2
3
3
4
3
3
4
g r
v
rv g r g r
You might also like
- Mek Fluida & Hidrolika - MomentumDocument39 pagesMek Fluida & Hidrolika - MomentumDebby Steven RachmanNo ratings yet
- Statika Dan Dinamika FluidaDocument29 pagesStatika Dan Dinamika FluidaIRVAN CHAIRUMANNo ratings yet
- Tugas Review Handbook Transport Phenomena - Ulfa Meila Anggriani..Document10 pagesTugas Review Handbook Transport Phenomena - Ulfa Meila Anggriani..Ulfa Meila AnggrianiNo ratings yet
- HidrolikaDocument16 pagesHidrolikaLambok SitinjakNo ratings yet
- Laporan Resmi Aliran Fluida - Augie Davin Siagian - 012100003Document18 pagesLaporan Resmi Aliran Fluida - Augie Davin Siagian - 012100003Agnia AnwarNo ratings yet
- 3-Prayoga Arya Wicaksono-1304620069-ViskositasDocument38 pages3-Prayoga Arya Wicaksono-1304620069-ViskositasPrayoga AryaNo ratings yet
- Mekanika Fluida 2Document120 pagesMekanika Fluida 2sodo purwitoNo ratings yet
- RPP 3.8 JunDocument13 pagesRPP 3.8 JunJun HidayatNo ratings yet
- Julia Jasmin Rifka Hayati - 1302618060 - Kekentalan Zat Cair (Viskositas)Document23 pagesJulia Jasmin Rifka Hayati - 1302618060 - Kekentalan Zat Cair (Viskositas)Rahmah Khairunnisa QonitaNo ratings yet
- Fluida Statis - Tugas - FisikaDocument9 pagesFluida Statis - Tugas - FisikaRogiva Ghozi ModusaNo ratings yet
- Aliran Viskos Dalam PipaDocument39 pagesAliran Viskos Dalam PipaMuhammadHafizNo ratings yet
- Praktikum Fisika Dasar Koefisien KekentaDocument27 pagesPraktikum Fisika Dasar Koefisien KekentaRahmah Khairunnisa QonitaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 06Document9 pagesChapter 06Andrianto WahyuNo ratings yet
- Mekanika Fluida DasarrDocument102 pagesMekanika Fluida DasarrAhmad Amril Nurman100% (2)
- Mekanika Benda - Benda Yang Berubah BentukDocument22 pagesMekanika Benda - Benda Yang Berubah BentukHanifa Fitria0% (1)
- KELOMPOK 4 Dinamika FluidaDocument20 pagesKELOMPOK 4 Dinamika FluidaWayan WardaniNo ratings yet
- Hidrodinamika 1 Macam AliranDocument65 pagesHidrodinamika 1 Macam AliranPieter Abandon All ShipNo ratings yet
- 6 FluidaDocument34 pages6 Fluidaputri wulandari100% (1)
- 3 KinematikaGelombang 2021Document25 pages3 KinematikaGelombang 2021Yulia AnggrainiNo ratings yet
- Fluida DinamikDocument9 pagesFluida DinamikFramms2No ratings yet
- Revisi UTS MekFludDocument11 pagesRevisi UTS MekFludErpin HabibahNo ratings yet
- Kajian Teori Fisika Untuk Roket Air1Document3 pagesKajian Teori Fisika Untuk Roket Air1Chandra Prasetyo75% (4)
- Laporan Awal f1 SohpyaaaaDocument19 pagesLaporan Awal f1 SohpyaaaaIga MawarniNo ratings yet
- Makalah Hukum StokesDocument12 pagesMakalah Hukum Stokeseva0% (1)
- RheologiDocument47 pagesRheologin4dn4dNo ratings yet
- D081191046 Tugas#1Hidrodinamika B 2020Document7 pagesD081191046 Tugas#1Hidrodinamika B 2020Rizky and Rania toys play TuhareaNo ratings yet
- Si 21311parameterfisikfluidav02Document38 pagesSi 21311parameterfisikfluidav02Dita AmaliaNo ratings yet
- Aliran Fluida Tanpa GesekanDocument30 pagesAliran Fluida Tanpa Gesekanisanbale100% (1)
- Fisika Fluida DinamisDocument18 pagesFisika Fluida DinamisRafa Assidiq100% (1)
- Mekanika FluidaDocument8 pagesMekanika FluidaRio NNo ratings yet
- Bab1 Fluida Dan Sifat SifatnyaDocument7 pagesBab1 Fluida Dan Sifat Sifatnyaafwan89No ratings yet
- 10& 11 Fluida (Bu Oke)Document66 pages10& 11 Fluida (Bu Oke)Yudha Adi KusumaNo ratings yet
- Laporan Pendahuluan Aliran FluidaDocument13 pagesLaporan Pendahuluan Aliran FluidaIntanti Mulana PutriNo ratings yet
- LAPORAN PRAKTIKUM Tekanan HidrostatisDocument10 pagesLAPORAN PRAKTIKUM Tekanan Hidrostatisobay16100% (1)
- 01 Transportasi FluidaDocument80 pages01 Transportasi FluidaAnonymous 07ofRn1No ratings yet
- Laprak Akhir Mekflu Modul Osborn (BAB II)Document27 pagesLaprak Akhir Mekflu Modul Osborn (BAB II)Begini ? Begitu ?No ratings yet
- BAB 2 TekananDocument74 pagesBAB 2 TekananWahyudi HasanNo ratings yet
- Presentasi 2Document8 pagesPresentasi 2NaselaNo ratings yet
- Persamaan Energi Dan MomentumDocument13 pagesPersamaan Energi Dan MomentumIlma Kreka ZeolitaNo ratings yet
- Mekanika Fluida Perkuliahan 4Document14 pagesMekanika Fluida Perkuliahan 4iamnarayaNo ratings yet
- Penentuan Tegangan Permukaan Dengan Metode Berat TetesDocument23 pagesPenentuan Tegangan Permukaan Dengan Metode Berat TetesDesy Adtriani100% (1)
- Viskositas Dan Mekanisme Transfer MomentumDocument20 pagesViskositas Dan Mekanisme Transfer MomentumZulaikhaNo ratings yet
- Analisa HidrolikaDocument37 pagesAnalisa HidrolikamuharrierNo ratings yet
- 3929 - FG 4 LTK CL-1 FD Gravitasi, Fluida, OsilasiDocument48 pages3929 - FG 4 LTK CL-1 FD Gravitasi, Fluida, Osilasijki idNo ratings yet
- Viskositas Dan Mekanisme Transfer MomentumDocument20 pagesViskositas Dan Mekanisme Transfer MomentumGufron PaytrenNo ratings yet
- Mekanika Fluida After MidDocument97 pagesMekanika Fluida After MidRian AnshariNo ratings yet
- Tugas Instrumen KendaliDocument40 pagesTugas Instrumen KendaliissadNo ratings yet
- Aliran Fluida Dalam Pipa TertutupDocument11 pagesAliran Fluida Dalam Pipa Tertutupcelia hart elizabethNo ratings yet
- Pertemuan - 4: Mekanika FluidaDocument35 pagesPertemuan - 4: Mekanika FluidaDOPE MBAPPENo ratings yet
- Visikositas Dan Difusi Hukum FickDocument24 pagesVisikositas Dan Difusi Hukum Ficklisa andrianiNo ratings yet
- SI-2131 #1 Parameter Fisik FluidaDocument18 pagesSI-2131 #1 Parameter Fisik FluidaPojok SipilNo ratings yet
- Fluida StatikDocument15 pagesFluida StatikUsep KasmanNo ratings yet
- Aplikasi Digital MicroprocessorDocument13 pagesAplikasi Digital MicroprocessorAlkautsar PermanaNo ratings yet
- Tugas Pengolahan Sinyal DigitalDocument3 pagesTugas Pengolahan Sinyal DigitalAlkautsar PermanaNo ratings yet
- Tugas Sistem Transmisi Komunikasi (Analog)Document22 pagesTugas Sistem Transmisi Komunikasi (Analog)Alkautsar PermanaNo ratings yet
- Smith Chart1Document7 pagesSmith Chart1Alkautsar PermanaNo ratings yet
- SCADADocument15 pagesSCADAAlkautsar PermanaNo ratings yet
- Bab II Modulasi AmplitudoDocument19 pagesBab II Modulasi AmplitudoAnisa Ulya DarajatNo ratings yet