Professional Documents
Culture Documents
03 - Estimation of Blood Glucose Using Glucose Oxidase
03 - Estimation of Blood Glucose Using Glucose Oxidase
Uploaded by
Chitti ThanujaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
03 - Estimation of Blood Glucose Using Glucose Oxidase
03 - Estimation of Blood Glucose Using Glucose Oxidase
Uploaded by
Chitti ThanujaCopyright:
Available Formats
TITLE: Estimation of Blood Glucose Using Glucose Oxidase AIMS AND OBJECTIVES: To understand the importance of measuring blood
od glucose level. To understand the principles of enzymatic estimation of glucose. Enzymatic method yields maximum specificity for glucose estimation. Glucose can be measured by its reaction with glucose oxidase, in which gluconic acid and hydrogen peroxide are formed. Hydrogen peroxide than reacts with an oxygen acceptor, such as ortho-dianisidine, phenylamine-phenazone or any other chromogenic oxygen acceptors, in a reaction catalysed by peroxidase to form a colour. One of the advantages of enzymatic method is its specificity. This enables the estimation of glucose even in a complex mixture. Thus, this method is widely used in the field of clinical chemistry and for food analysis. In clinical chemistry, the enzymatic analysis of glucose in blood and urine has been modified as dipstick test. However in the present practical, the conventional enzymatic method shall be used. METHOD: 1. SAMPLES TEST: a. The following substances are added in the tube. i. 1.8 ml sodium sulphate-zink sulphate ii. 0.1 ml blood iii. 0.1 ml NaOH (0.1M) b. Mix carefully. c. d. Centrifuge at 3000 RPM for 5 min. Transfer the supernatant into new test tube.
INTRODUCTION
Note: The glucose concentration in the supernatant is 1/20 of the concentration in the blood sample.
2.
BLANK & STANDARD: a. b. Glucose standards 12 mg/dl are provided. Preparing concentration glucose standard point. CONCENTRATION (mg/dL) GLUCOSE STANDARD (mL) M1V1 : M2V2 WATER (mL) H2O = 2.0 ml 0.5 mL = 1.5 mL H2O = 2.0 ml 1.0 mL = 1.0 mL H2O = 2.0 ml 1.5 mL = 0.5 mL H2O = 2.0 ml 2.0 mL = 0 mL 2.0 mL 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0 2.0 TOTAL mL PER TUBE
TUBES
3.0
(12)V1: 3.0 (2.0 ) V1 : 0.5 mL M1V1 : M2V2
6.0
(12)V1: 6.0 (2.0 ) V1 : 1.0 mL M1V1 : M2V2
9.0
(12)V1: 9.0 (2.0 ) V1 : 1.5 mL M1V1 : M2V2
12.0
(12)V1: 12.0 (2.0 ) V1 : 2.0 mL
BLANK
c.
Then, add 5 ml ortho-tolidine mixture where consisting; i. 1% ortho-tolidine 12.5 mg (500 units) glucose oxidase in 100 ml phosphate buffer, pH 7.0. MINUTE ADDED ORTHO-TOLIDINE 2 4 6 8 10 12 iv. Mix quickly. v. The time is staggered every 2 minutes when adding the ortho-tolidine solution as shown table above. vi. Incubate the tubes at room temperature for exactly 10 min. vii. Then, measure at absorbance 625nm. Notes: 2 ORTHO-TOLIDINE mL 5.0 5.0 5.0 5.0 5.0 5.0 TOTAL mL PER TUBE 7.0 7.0 7.0 7.0 7.0 7.0 ii. 4mg (100 units) peroxidase iii.
TUBES BLANK 1 2 3 4 SAMPLE
Ensure that each tubes absorbance is read exactly after 10 min. If the absorbance reading for the sample is too high, dilute the supernatant which was obtained earlier, (2x) with water and repeat the subsequent steps.
RESULTS: GLUCOSE CONCENTRATION (mg/dL) 0 3.0 6.0 9.0 12.0 SAMPLE DISCUSSION: On this experiment, blood glucose is estimated by using enzymes glucose oxidase. Where Ortho-toluidine is use as chemical for exploited to quantitative carbohydrates molecules to form Schiff bases with aromatic amines. Ortho-tolidine in a hot acidic solution will yield a colored compound with absorbance maxima at 625 nm. ABSORBANCE READING (nm) 0.000 0.181 0.120 0.006 0.005 0.045
GLUCOSE OXIDASE Glucose + O2 + H2O H2O2 + Reduced chromogen
Glucose Oxidase
Gluconic Acid + H2O2 Oxidized chromogen + H2O
Peroxidase
Glucose oxidase is the most specific enzyme reacting with only D-glucose and glucose oxidase converts D-glucose to gluconic acid. Added Mutarose to the reaction can facilitate the conversion of D-glucose to D-Glucose. Oxygen is consumed and hydrogen peroxide is produced. The reaction is measured based on rate of disappearance of oxygen. Spectrophotometer is used for read absorbance, where it proportional to the amount of glucose presents in the sample. However, on this experiment, the absorbance reading for concentration reading is not expected as well and it fully incorrect. Because the absorbance reading supposedly from the lower thru high value. But, on another hand for comparison with other group shown that the results reading are correct and accordingly as table below.
GLUCOSE CONCENTRATION (mg/dL) 0 3.0 6.0 9.0 12.0 The problems that can be come across are shown in table below;
ABSORBANCE READING (nm) 0.000 0.056 0.160 0.225 0.225
CAUSES 1.
DESCRPTION Pipetting sample or chemical solution inappropriate. Taken wrong sample reading. Unclean Cuvettes. Mislabeling or not label sample. Chemical are already expired. Improper making the chemical solution. Increase levels of uric acid, bilirubin, and ascorbic acid can cause falsely decreased values as a result of these substances being oxidized by peroxidase, which prevents the oxidation and detection of the chromogen. Galactose, an aldohexose, and mannose, an aldopentose, will also react with Orthotoluidine and produce a colored compound that can interfere with the reaction.
HUMAN ERROR
2. 3. 4. 1. 2. 1.
MATERIAL
SUBSTANCES
1. CHEMICAL
CALCULATION: Calculation concentration of blood glucose is not valid because the absorbance reading is to low to plot at the graph. But, as for example, the calculation shown; o 8.8 mg/dL (From plot graph) X 20 (times dilution) = 176 mg/dl If converted to unit mmol/L o 176 mg / dL X 1 dL/100 mL X 1000 mL/ L X 1 mmol/180 mg (gmw glucose :180) = 9.7 mmol/L
QUESTION: 1.What are the advantages of glucose oxidase method in comparison to various other methods of glucose analysis? 1. ADVANTAGES OF GLUCOSE OXIDASE This method most specific enzymatic than other method such as; reduction of cupric to cuprous salts, and reduction of ferricyanide to ferrocyanide method. 2. The reaction can be monitored polarographically either by measuring the rate of disappearance of oxygen. 2.Discuss the principles of the enzymatic assay method. PRINCIPLES OF THE ENZYMATIC ASSAY 4
1. 2. 3.
Glucose oxidase reacts specifically to D-glucose, where it converts to gluconic acid. The hydrogen peroxide is used to oxidize a dye compound. Two commonly used chromogens are 3-methyl-2-benzothiazolinone hydrazone and N,Ndimethylaniline. The principle reaction as shown below; Glucose + O2 + H2O
Glucose Oxidase
4.
Gluconic Acid + H2O2 Oxidized chromogen + H2O
H2O2 + Reduced chromogen
Peroxidase
CONCLUSION: 1. 2. The blood glucose level is not applicable on this test because value is too small. However, on the experiment the glucose oxidase method is more specific test for determination the glucose than other method. 3. Glucose test is useful in monitoring of hyperglycemia or hypoglycemia thru patient.
You might also like
- LAB REPORT HESS'S LAW (Final)Document7 pagesLAB REPORT HESS'S LAW (Final)Arhaan SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Lab Report Exp 2 Plasmid ExtractionDocument8 pagesLab Report Exp 2 Plasmid ExtractionAmeera ShahirahNo ratings yet
- Enzyme Lab ReportDocument9 pagesEnzyme Lab ReportG100% (1)
- Laboratory Report CHM 213 (Physical Chemistry)Document6 pagesLaboratory Report CHM 213 (Physical Chemistry)Muhd Mirza HizamiNo ratings yet
- Sample Lab ReportDocument24 pagesSample Lab ReportDarkhens71% (7)
- Lab Report Beer S LawDocument16 pagesLab Report Beer S LawRhema Mohabul100% (2)
- Lab Bio 3Document5 pagesLab Bio 3Nada Nabila63% (8)
- Chemistry Lab ReportDocument8 pagesChemistry Lab ReportLutendo Assurance Madzivhaa100% (2)
- Techniques in Microbiology I PDFDocument16 pagesTechniques in Microbiology I PDFMohd Izwan67% (3)
- Chem 230L Laboratory Report Reactivity of Some Alkyl HalidesDocument5 pagesChem 230L Laboratory Report Reactivity of Some Alkyl HalidesDrJigsaw33% (6)
- Odors of Santity Distinctions of The Holy in Early Christianity and IslamDocument13 pagesOdors of Santity Distinctions of The Holy in Early Christianity and Islamkiedd_04100% (1)
- Lab ReportDocument7 pagesLab ReportJasz Azliey AzzamNo ratings yet
- Agarose Gel Electrophoresis (Full Report)Document10 pagesAgarose Gel Electrophoresis (Full Report)El LisNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Substrate Concentration On The Activity of EnzymesDocument7 pagesThe Effect of Substrate Concentration On The Activity of Enzymesjosephine100% (1)
- 4 Microbiology Lab Report Practical 3 PDFDocument10 pages4 Microbiology Lab Report Practical 3 PDFNurul IzzahNo ratings yet
- Estimation of Total Protein in Serum &Document22 pagesEstimation of Total Protein in Serum &Nada hasanNo ratings yet
- Osmotic Fragility of Red Blood CellsDocument3 pagesOsmotic Fragility of Red Blood Cellschaudhry umar farooqNo ratings yet
- Lab 3 Biuret Protein AssayDocument9 pagesLab 3 Biuret Protein Assayapi-384770852No ratings yet
- Study of Plant Cells - PlasmolysisDocument2 pagesStudy of Plant Cells - PlasmolysisMonika Mehan81% (16)
- Lab Report Prepare and Standardize A 0.1 M NaOH SolutionsDocument8 pagesLab Report Prepare and Standardize A 0.1 M NaOH Solutionsrodneyperu100% (2)
- Determination of Blood CholesterolDocument5 pagesDetermination of Blood Cholesterolkiedd_04100% (3)
- Bradford Protein-Determination of Milk ProteinDocument3 pagesBradford Protein-Determination of Milk Proteinanitram yo50% (2)
- Lab ReportDocument15 pagesLab ReportValentinoDullSatin100% (1)
- Laboratory Report CHM 213 (Physical Chemistry) : 1. Muhammad Mirza Hizami Bin RajieiDocument6 pagesLaboratory Report CHM 213 (Physical Chemistry) : 1. Muhammad Mirza Hizami Bin RajieiMuhd Mirza Hizami100% (2)
- Cell PhysiologyDocument61 pagesCell Physiologykiedd_04100% (4)
- Direct Agglutination AssayDocument6 pagesDirect Agglutination Assaykiedd_04100% (4)
- Estimation of Glucose by Folin Wu MethodDocument3 pagesEstimation of Glucose by Folin Wu MethodJeff LinksNo ratings yet
- Analytical Chemistry Lab Report Exp 4Document18 pagesAnalytical Chemistry Lab Report Exp 4Muhammad Zaim Hakeem100% (1)
- Lab Report 4 LipidDocument8 pagesLab Report 4 Lipidapi-384857069100% (2)
- Calibration of 25-Ml PipetteDocument6 pagesCalibration of 25-Ml PipetteBadrisiah BalqeesNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Protein Analysis (Bradford's Assay)Document3 pagesQuantitative Protein Analysis (Bradford's Assay)Sean Herman100% (1)
- Lab 4 Polyphenol OxidaseDocument2 pagesLab 4 Polyphenol OxidaseKarabo Yuval TsheoleNo ratings yet
- Lab Report chm256Document8 pagesLab Report chm256Wahida Amalin sofeaNo ratings yet
- Enyzmatic Activity of Salivary AmylaseDocument6 pagesEnyzmatic Activity of Salivary AmylaseGio Punsalan50% (2)
- Lab Poster Mic260Document1 pageLab Poster Mic260Nawar SallNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Volhard's MethodDocument9 pagesAnalysis of Volhard's MethodKingsley WongNo ratings yet
- Mic254 Lab Report Exp 2Document17 pagesMic254 Lab Report Exp 2NUR SABRINA MOHD SHAHNo ratings yet
- Preparing Buffers and Buffer CapacityDocument7 pagesPreparing Buffers and Buffer CapacityAndreaKatovic100% (1)
- Lab Report CHM260 (Exp 2)Document19 pagesLab Report CHM260 (Exp 2)Nur AthirahNo ratings yet
- Lab Report Exp 5Document5 pagesLab Report Exp 5api-384913960No ratings yet
- Practical ImmunoelectrophoresisDocument3 pagesPractical Immunoelectrophoresisvyastrupti150% (2)
- The Biuret AssayDocument6 pagesThe Biuret AssayvictorNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Analysis of Vitamin C Contained in FoodsDocument8 pagesQuantitative Analysis of Vitamin C Contained in FoodsCleve Hines100% (1)
- Titration of Amino Acids and PeptidesDocument4 pagesTitration of Amino Acids and PeptidesKatrina Miral100% (1)
- Lab Report 4 sbl1023Document7 pagesLab Report 4 sbl1023api-3850387010% (1)
- Gram Staining Lab ReportDocument3 pagesGram Staining Lab ReportAkash MehtaNo ratings yet
- Meiosis ReportDocument6 pagesMeiosis ReportDaizLee Ahmad71% (7)
- PW2. Preparation of SolutionsDocument5 pagesPW2. Preparation of SolutionsHeisenbonux100% (1)
- Lab Report 2 Food MicrobiologyDocument9 pagesLab Report 2 Food MicrobiologyLee Yann Lynn100% (3)
- CHM 256 Exp1 Standarization of HCL Solution With Na2CO3 Primary StandardDocument3 pagesCHM 256 Exp1 Standarization of HCL Solution With Na2CO3 Primary StandardZaiful AlifNo ratings yet
- Lab ReportDocument4 pagesLab Reportfwagner1100% (3)
- sbl1023 Lab 3 SpectrophotometerDocument6 pagessbl1023 Lab 3 Spectrophotometerapi-385146128No ratings yet
- Laboratory Experiment No. 11 - Transport Across MembranesDocument4 pagesLaboratory Experiment No. 11 - Transport Across MembranesMary Rose CatalbasNo ratings yet
- Enzymes Lab ReportDocument7 pagesEnzymes Lab ReportMemorie BrownNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 5 Protein Solubility and PHDocument3 pagesLab Report 5 Protein Solubility and PHDan Floyd FernandezNo ratings yet
- sbl1023 Lab 7 Human PhysiologyDocument8 pagessbl1023 Lab 7 Human Physiologyapi-385146128No ratings yet
- Experiment 4 Preparation of Standardized SolutionsDocument10 pagesExperiment 4 Preparation of Standardized SolutionsJohn Dy100% (1)
- Serial DilutionDocument8 pagesSerial DilutionRiyanNo ratings yet
- Experiment 3Document13 pagesExperiment 3Iqmal Hafidz100% (1)
- Bio 320 Exp 1Document5 pagesBio 320 Exp 1MuhammadAsyrafNo ratings yet
- Methods for Analysis of Carbohydrate Metabolism in Photosynthetic Organisms: Plants, Green Algae and CyanobacteriaFrom EverandMethods for Analysis of Carbohydrate Metabolism in Photosynthetic Organisms: Plants, Green Algae and CyanobacteriaNo ratings yet
- Exp 1Document9 pagesExp 1Amirul Ramlan100% (1)
- From The Bodies of Bees Classical and Christian Echoes in Surah Al-NahlDocument25 pagesFrom The Bodies of Bees Classical and Christian Echoes in Surah Al-Nahlkiedd_04No ratings yet
- Iklan Jabatan Pengajian Tinggi (Permohonan Kemasukan Tevt & Ilka) Sesi 2011/2012Document2 pagesIklan Jabatan Pengajian Tinggi (Permohonan Kemasukan Tevt & Ilka) Sesi 2011/2012kiedd_04No ratings yet
- The Place For Others in IslamDocument27 pagesThe Place For Others in Islamkiedd_04No ratings yet
- "Traditional" Exegeses of Q 4:34Document15 pages"Traditional" Exegeses of Q 4:34kiedd_04No ratings yet
- SYNAPSEDocument35 pagesSYNAPSEkiedd_04100% (3)
- Microbiology Colour Plate No.9Document1 pageMicrobiology Colour Plate No.9kiedd_04No ratings yet
- Refleks ArcsDocument34 pagesRefleks Arcskiedd_04100% (1)
- Microbiology Colour Plate No.6Document1 pageMicrobiology Colour Plate No.6kiedd_04No ratings yet
- Fadhilat Surah at TakwirDocument1 pageFadhilat Surah at Takwirkiedd_04No ratings yet
- Microbiology Colour Plate No.7Document1 pageMicrobiology Colour Plate No.7kiedd_04No ratings yet
- Microbiology Colour Plate No.8Document1 pageMicrobiology Colour Plate No.8kiedd_04No ratings yet
- API® CoryneDocument4 pagesAPI® Corynekiedd_04No ratings yet
- Microbiology Colour Plate No.5Document1 pageMicrobiology Colour Plate No.5kiedd_04No ratings yet
- Mitigation Potential and Costs Land-Use OptionsDocument9 pagesMitigation Potential and Costs Land-Use Optionskiedd_04No ratings yet
- Microbiology Colour Plate No.4Document1 pageMicrobiology Colour Plate No.4kiedd_04No ratings yet
- Microbiology Colour Plate No.2Document1 pageMicrobiology Colour Plate No.2kiedd_04No ratings yet
- Microbiology Colour Plate No.3Document1 pageMicrobiology Colour Plate No.3kiedd_04No ratings yet
- Microbiology Colour Plate No.1Document1 pageMicrobiology Colour Plate No.1kiedd_04No ratings yet
- Philosophical Consolation in Christianity and Islam Boethious and Al-KindiDocument10 pagesPhilosophical Consolation in Christianity and Islam Boethious and Al-Kindikiedd_04No ratings yet
- Carnitine DeficiencyDocument21 pagesCarnitine Deficiencykiedd_04100% (1)
- Mitigation of Climate ChangeDocument41 pagesMitigation of Climate Changekiedd_04No ratings yet
- Advance Diagnostic Medical Laboratory: The AP 20E® For Identification of BacteriaDocument1 pageAdvance Diagnostic Medical Laboratory: The AP 20E® For Identification of Bacteriakiedd_04100% (1)
- Mitigation of Climate ChangeDocument25 pagesMitigation of Climate Changekiedd_04No ratings yet
- Oxidase TestDocument1 pageOxidase Testkiedd_04100% (1)
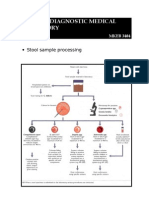
- Stool Sample ProcessingDocument1 pageStool Sample Processingkiedd_04No ratings yet
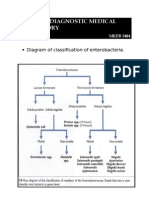
- Diagram of Classification of EnterobacteriaDocument1 pageDiagram of Classification of Enterobacteriakiedd_04100% (1)