Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Physical Examination
Uploaded by
Rodney Beltran SubaranOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Physical Examination
Uploaded by
Rodney Beltran SubaranCopyright:
Available Formats
Physical Examination Levels of Consciousness Alert- awake or easily aroused Lethargic- not fully alert, drifts off when
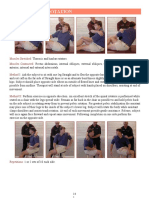
en not stimulated Obtunded- sleeps most times, difficult to arouse (loud noise, vigorous shaking or pain) Stupor- need persistent loud noise or pain for arousal; responds to stimuli Coma- no response (Jarvis CH 2) . A reflex 0 A reflex is defined as an immediate and involuntary response to a stimulus. Superficial reflexes. Stroke the skin with a hard object such as an applicator stick. What is felt is a superficial reflex 5 Ps Pain Pallor Pulses Paresthesia Paralysis There are five reflexes to check which include: Biceps: With the patient sitting, flex his arm at the elbow and rest his forearm on his thigh with the palm up. Place your thumb firmly on the biceps tendon in the antecubital fossa. Strike your thumb with the hammer. The elbow and forearm should flex, and the biceps muscle should contract. Triceps: The triceps tendon is tested with the patients arm flexed at a 90
angle. Supporting the arm with your hand, strike the triceps tendon on the posterior arm just above the elbow. The tendon should contract and the elbow extend. Brachioradialis: Have the patient rest his slightly flexed arm on his lap with the palm facing downward. Strike the posterior arm about two inches above the wrist on the thumb side. The forearm should rotate laterally and the palm turn upward. Patellar: Dangle the patients legs over the side of the bed. Place your hand on the patients thigh and strike the distal patellar tendon just below the kneecap. (If the patient must remain supine, flex each leg to a 45 angle and place your dominant hand behind his knee to support it.) The normal response is contraction of the quadriceps muscle with extension of the knee. Achilles: Have the patient dorsiflex (point downward) his foot slightly and lightly tap the Achilless tendon on the posterior ankle area. A slight jerking of the foot should be seen.
You might also like
- Paces 6 - Cns - Lower LimbDocument18 pagesPaces 6 - Cns - Lower LimbDrShamshad Khan100% (1)
- Reflex TestingDocument44 pagesReflex Testingsarguss14100% (7)
- Paces 7 - Cns - Upper LimbDocument11 pagesPaces 7 - Cns - Upper LimbDrShamshad KhanNo ratings yet
- Ex - Neuro ULDocument3 pagesEx - Neuro ULssNo ratings yet
- Examination of The ShoulderDocument33 pagesExamination of The ShoulderAnonymous 9QxPDpNo ratings yet
- Special TestsDocument12 pagesSpecial Testspfi_jenNo ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal SystemDocument160 pagesMusculoskeletal SystemAirene Aquino BusaniaNo ratings yet
- Neurological ExaminationDocument8 pagesNeurological Examinationg8048658No ratings yet
- Neurological Examination of The Limbs TextDocument8 pagesNeurological Examination of The Limbs Textvidur_talrejaNo ratings yet
- ReflexesDocument22 pagesReflexesgmpcbpzdysNo ratings yet
- KneeDocument11 pagesKneeArianne Mari BalingitNo ratings yet
- Introduction, Deep ReflexesDocument10 pagesIntroduction, Deep ReflexesQairul AzmanNo ratings yet
- Ortho PE NotesDocument35 pagesOrtho PE NotesSudesna Roy ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Neuro 1 and 2 LabDocument3 pagesNeuro 1 and 2 LabHardikPatelNo ratings yet
- Motor ExaminationDocument36 pagesMotor ExaminationKenneth DizonNo ratings yet
- Motor and Sensory Examination: Dr. Bandar Al Jafen, MD Consultant NeurologistDocument36 pagesMotor and Sensory Examination: Dr. Bandar Al Jafen, MD Consultant NeurologistJim Jose Antony100% (1)
- Hand ExaminationDocument16 pagesHand ExaminationRezaul KarimNo ratings yet
- 7) Muscle Palpation ArmDocument13 pages7) Muscle Palpation Armshahirah77No ratings yet
- HemiplegiaDocument11 pagesHemiplegiaFares EL DeenNo ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal Exam Teaching OutlineDocument12 pagesMusculoskeletal Exam Teaching OutlineAngeliki KostakiNo ratings yet
- MUSCULOSKELETAL Assessment ScripyDocument2 pagesMUSCULOSKELETAL Assessment ScripyKristinelou Marie N. ReynaNo ratings yet
- Lateral Epicondylitis: ST NDDocument2 pagesLateral Epicondylitis: ST NDMuhammad Ucuk100% (1)
- 5 Shoulder MovmentsDocument70 pages5 Shoulder Movmentsalinaziyad3No ratings yet
- PERIPHERAL JOINT MOBILIZATION - Lower Limbs (1) - 052048Document34 pagesPERIPHERAL JOINT MOBILIZATION - Lower Limbs (1) - 052048MUGISHA GratienNo ratings yet
- OMM NotesDocument16 pagesOMM NotesRednose55No ratings yet
- Ortho Neuro ExamsDocument0 pagesOrtho Neuro ExamsMaybs Palec Pamplona-ParreñoNo ratings yet
- Shoulder Pain and Dis FunctionDocument65 pagesShoulder Pain and Dis FunctionGunawan KurniadiNo ratings yet
- The HipsDocument2 pagesThe HipsReham QueNo ratings yet
- PNS Examination 15Document17 pagesPNS Examination 15NolanNo ratings yet
- Tendon ReflexDocument13 pagesTendon ReflexNurul Huda M ShahrinNo ratings yet
- Ortho VertDocument4 pagesOrtho VertfelixhartantoNo ratings yet
- Examination of The KneeDocument5 pagesExamination of The KneenushNo ratings yet
- Shoulder ExaminationDocument21 pagesShoulder ExaminationNgurah AndhikaNo ratings yet
- Special TestsDocument6 pagesSpecial Testschockulit100% (1)
- Neurological History and ExaminationDocument30 pagesNeurological History and ExaminationMaria Agatha100% (1)
- Sacroiliac Joint Dysfunction: Vahid - Marouf PTDocument40 pagesSacroiliac Joint Dysfunction: Vahid - Marouf PTvahidmaroufNo ratings yet
- Cranial Nerve AssessmentDocument5 pagesCranial Nerve AssessmentBAdz TanNo ratings yet
- MSK ExamDocument4 pagesMSK ExamRUDOLF YUSON BM20110052No ratings yet
- Upper & Lower Limb ExaminationDocument20 pagesUpper & Lower Limb Examinationcvmqx7yppd100% (1)
- Gonstead Ifec ProneDocument5 pagesGonstead Ifec ProneAurelien BoschatNo ratings yet
- MSK IV PracticalDocument10 pagesMSK IV Practicalroshanleung11No ratings yet
- Examination of The Peripheral Neurological SystemDocument2 pagesExamination of The Peripheral Neurological Systemkenners100% (12)
- Station 1: Nerve Tension TestsDocument8 pagesStation 1: Nerve Tension TestsRNo ratings yet
- Scapular Ax in NeuroDocument6 pagesScapular Ax in NeurolavanyaphdNo ratings yet
- Active Isolated Stretching The Mattes Method 151 184Document38 pagesActive Isolated Stretching The Mattes Method 151 184Nazareth Varas AlonsoNo ratings yet
- Hip MaitlandDocument14 pagesHip Maitlandakuphysio100% (1)
- Tugas Bedah HafizDocument43 pagesTugas Bedah HafizEmir Rasyid HafizNo ratings yet
- LymphaticDocument52 pagesLymphaticlemuel_queNo ratings yet
- Joint Mobilization - Upper ExtremityDocument11 pagesJoint Mobilization - Upper ExtremityRicha Mahajan50% (2)
- The Motor System ExaminationDocument42 pagesThe Motor System ExaminationHelend ChildDj100% (1)
- Physiotherapy - Stroke - Arm ExercisesDocument5 pagesPhysiotherapy - Stroke - Arm Exercisesayeshamumtazkakakhel322No ratings yet
- Manual Therapy Techniques For The ShoulderDocument12 pagesManual Therapy Techniques For The Shoulderubiktrash1492100% (1)
- Omm Exam 3 LGTDocument59 pagesOmm Exam 3 LGTSolomon Seth SallforsNo ratings yet
- Physioterapy SalveDocument45 pagesPhysioterapy SalveIkhar KeliobasNo ratings yet
- Special Tests For Elbow and ForearmDocument3 pagesSpecial Tests For Elbow and ForearmAllyza PenaNo ratings yet
- Clinical Examinations For PLAB 2Document12 pagesClinical Examinations For PLAB 2Mandeep KaurNo ratings yet
- MuscleDocument38 pagesMuscleAnonymous BzS0RF1qyNo ratings yet
- First Aid & Emergency Companions: First Aid & Emergencies at SeaFrom EverandFirst Aid & Emergency Companions: First Aid & Emergencies at SeaNo ratings yet