Professional Documents
Culture Documents
JDBC Concepts: Statement Object
JDBC Concepts: Statement Object
Uploaded by
querysiva6410Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
JDBC Concepts: Statement Object
JDBC Concepts: Statement Object
Uploaded by
querysiva6410Copyright:
Available Formats
JDBC
JDBC concepts
JDBC is a Java API and a standard part of the Java class libraries that control basic functions for Java application development. The SQL capabilities that JDBC provides are similar to those of ODBC and dynamic SQL. The following sequence of events is typical of a JDBC application: 1 Create a Connection object call the getConnection( ) static method of the
DriverManager class to create a Connection object. This establishes a
database connection. 2 Generate a Statement object use the Connection object to generate a Statement object. 3 Pass a SQL statement to the Statement object if the statement is a query, this action returns a ResultSet object. The ResultSet object contains the data returned from the SQL statement, but provides it one row at a time (similar to the way a cursor works). 4 Loop over the rows of the results set call the next( ) method of the ResultSet object to: Advance the current row (the row in the result set that is being exposed through the ResultSet object) by one row. Return a Boolean value (true/false) to indicate whether there is a row to advance to. 5 For each row, retrieve the values for columns in the ResultSet object use the getInt( ), getString( ), or similar method to identify either the name or position of the column.
Differences between client- and server-side JDBC
The difference between JDBC on the client and in the database server is in how a connection is established with the database environment. When you use client-side or server-side JDBC, you call the
Drivermanager.getConnection() method to establish a connection to the server.
For client-side JDBC, you use the Sybase jConnect JDBC driver, and call the Drivermanager.getConnection() method with the identification of the server. This establishes a connection to the designated server.
You might also like
- JDBC in 5 Minutes:: Code-FlowDocument10 pagesJDBC in 5 Minutes:: Code-FlowSamrat singhNo ratings yet
- DBC Questions What Is The JDBC?Document11 pagesDBC Questions What Is The JDBC?Satish BabuNo ratings yet
- Introduction To JDBCDocument3 pagesIntroduction To JDBCSasi S INDIANo ratings yet
- Object Oriented CH1Document47 pagesObject Oriented CH1Dawit WoldemichaelNo ratings yet
- JDBC SessionDocument25 pagesJDBC SessionYatin NimeshNo ratings yet
- JDBC ArchitectureDocument3 pagesJDBC ArchitectureAtinderpal SinghNo ratings yet
- Chapter Six Introduction To JDBC ProgrammingDocument34 pagesChapter Six Introduction To JDBC ProgrammingFasika TafaNo ratings yet
- 2484Document44 pages2484Ankita SharmaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 JDBCDocument16 pagesUnit 1 JDBCroshnibijuNo ratings yet
- JAVA Module 4Document13 pagesJAVA Module 4SreejithNo ratings yet
- AJP Chapter 5 DatabaseDocument10 pagesAJP Chapter 5 DatabaseAayush ChalkeNo ratings yet
- Java Unit IVDocument16 pagesJava Unit IVSreejithNo ratings yet
- Interacting With DatabaseDocument31 pagesInteracting With DatabaseAyushi JapsareNo ratings yet
- What Is JDBC?: Java Database Connectivity Api Allows Us To Work With RelationalDocument7 pagesWhat Is JDBC?: Java Database Connectivity Api Allows Us To Work With RelationalSomenath MajhiNo ratings yet
- Database JavaDocument31 pagesDatabase Javaprerana sheteNo ratings yet
- JDBCDocument8 pagesJDBCPratap Singh RathoreNo ratings yet
- JDBC Basics - Java Database Connectivity StepsDocument6 pagesJDBC Basics - Java Database Connectivity StepsPrashant KumarNo ratings yet
- 5-JDBC Final - 2014ec (7) - 1Document26 pages5-JDBC Final - 2014ec (7) - 1Teshale SiyumNo ratings yet
- Java Unit IIIDocument29 pagesJava Unit IIILALITH MOHANNo ratings yet
- Oracle Applications Using Java & JDBCDocument82 pagesOracle Applications Using Java & JDBCvenkatNo ratings yet
- JDBC - Java Database ConnectivityDocument17 pagesJDBC - Java Database ConnectivitynavecNo ratings yet
- JDBC - Java Database ConnectivityDocument17 pagesJDBC - Java Database ConnectivityPuspala ManojkumarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 JDBCDocument43 pagesChapter 5 JDBCervesdrNo ratings yet
- Java Database ConnectivityDocument25 pagesJava Database ConnectivityRajivNo ratings yet
- Java JDBC TutorialDocument3 pagesJava JDBC TutorialbyprasadNo ratings yet
- JDBCDocument1 pageJDBCanarki417No ratings yet
- Unit 1: JDBC (Java Database Connectivity)Document7 pagesUnit 1: JDBC (Java Database Connectivity)Waseem ShaikhNo ratings yet
- EC-Unit 1B Enterprise FoundationsDocument29 pagesEC-Unit 1B Enterprise Foundationsbala0302No ratings yet
- Chapter 7-Java Database ConnectivityDocument44 pagesChapter 7-Java Database ConnectivityHabiteneh EndaleNo ratings yet
- JDBC NewDocument14 pagesJDBC NewBanasthali StudentNo ratings yet
- Database Connectivity Pages DeletedDocument35 pagesDatabase Connectivity Pages DeletedGULAB SINGHNo ratings yet
- Java Notes Unit-5Document4 pagesJava Notes Unit-5Vaishnavi MittalNo ratings yet
- Java Database ConnectivityDocument42 pagesJava Database ConnectivityAmandeep singhNo ratings yet
- JDBCDocument31 pagesJDBCImtiyaz ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - 2016-Java Database Connectivity With JDBCDocument22 pagesChapter 3 - 2016-Java Database Connectivity With JDBCBeka BekoNo ratings yet
- Object Oriented Programming: Prof. Varsha DangeDocument8 pagesObject Oriented Programming: Prof. Varsha DangeWAGHULE SHUBHAMNo ratings yet
- Java Database ConnectivityDocument47 pagesJava Database ConnectivityPushp SainiNo ratings yet
- Java Database ConnectivityDocument6 pagesJava Database Connectivityridhi guptaNo ratings yet
- JDBC DriversDocument8 pagesJDBC Driversshahidss743886No ratings yet
- JDBC - Java Database ConnectivityDocument28 pagesJDBC - Java Database ConnectivityirfanexpNo ratings yet
- Architecture Design of JDBCDocument6 pagesArchitecture Design of JDBCshobyscmsNo ratings yet
- JDBCDocument24 pagesJDBCbahaaalhusainyNo ratings yet
- JDBC Introduction To JDBC: 1. Java - Sql. 2. Javax - Sql.Document7 pagesJDBC Introduction To JDBC: 1. Java - Sql. 2. Javax - Sql.mrcopy xeroxNo ratings yet
- JDBC Basics - Java Database Connectivity StepsDocument11 pagesJDBC Basics - Java Database Connectivity Stepsarsv55No ratings yet
- Database and JDBCDocument13 pagesDatabase and JDBCHassan YassinNo ratings yet
- JDBCDocument37 pagesJDBCshubhamNo ratings yet
- JDBC Chapter 1Document45 pagesJDBC Chapter 1kassahunNo ratings yet
- Components of JDBCDocument3 pagesComponents of JDBCwesternrailwayNo ratings yet
- What Is JDBC?: Core Java Programming SQL or Mysql DatabaseDocument11 pagesWhat Is JDBC?: Core Java Programming SQL or Mysql DatabaseKARANAM SANTOSHNo ratings yet
- JDBC SlidesDocument45 pagesJDBC Slidesapi-3758996100% (2)
- Slide Chương 12 PtitDocument60 pagesSlide Chương 12 PtitKiên VũNo ratings yet
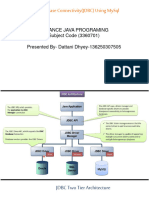
- Advanced Java Programming (22517) : Program - Computer Technology Semester-5Document31 pagesAdvanced Java Programming (22517) : Program - Computer Technology Semester-5Ashlesha AdhatraoNo ratings yet
- JDBC Word DocumentDocument12 pagesJDBC Word DocumentGone HarikrishnaNo ratings yet
- Database Connectivity To Mysql: Informatics Practices Class Xii By-Deepak Bhinde PGT Comp. SCDocument27 pagesDatabase Connectivity To Mysql: Informatics Practices Class Xii By-Deepak Bhinde PGT Comp. SCrohan rajNo ratings yet
- Java JDBC SlideshareDocument24 pagesJava JDBC Slidesharekavita.mittalNo ratings yet
- JDBC ArchitectureDocument8 pagesJDBC ArchitecturemsukumarbtechNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6-DatabaseConnectivity FinalDocument36 pagesChapter 6-DatabaseConnectivity FinalGhanshyam SharmaNo ratings yet
- JDBCDocument14 pagesJDBCMahendiran AlagappanNo ratings yet
- 02 JDBCDocument30 pages02 JDBCFuadNaserAl-deenNo ratings yet
- JSP-Servlet Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be AskedFrom EverandJSP-Servlet Interview Questions You'll Most Likely Be AskedNo ratings yet