Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ulcer Examination
Ulcer Examination
Uploaded by
Matyie SmkasOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ulcer Examination
Ulcer Examination
Uploaded by
Matyie SmkasCopyright:
Available Formats
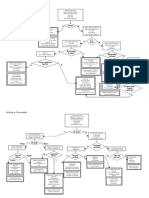
EXAMINATION OF AN ULCER Adequately expose the ulcer.
Describe: Intro: Site Size Tenderness Define: Shape Depth Edges: Sloping Punched out Undermined Rolled Everted Base: Healthy Sloughy Avascular Purulent Necrotic Underlying structures visible?
Surrounding Tissues: Erythema/cellulitis. Arterial & Venous & Neurological assessment. Offer as appropriate: Vascular examination Venous examination Neurological examination.
Make a Diagnosis: Is the ulcer painless? NO Are foot pulses present? YES ?Venous NO Probably ischaemic
YES Neurological Cause
NB: Beware of multiple pathologies, esp. in diabetic patients. (Peripheral Vascular Disease + Neurological Ulcers). Glossary-Describing the Edge: Flat Sloping Edge: healing ulcer, usually shallow, typical of a venous ulcer. Punched-out/Vertical Edge: rapid death and sloughing of the full thickness skin without attempt at repair. Typical of neuropathic/vasculitic ulcers. Historically Syphilitic Ulcers, -now rare. Undermined Edge: occur when infection supervenes in subcutaneous tissue, e.g. pressure sores. Historically caused by tuberculous ulcers. Rolled Edge: develops when there is slow growth of tissue at the edge of the ulcer. Almost pathognomonic of BCC. Everted/Heaped Edge: develops when tissue at the edge of the ulcer is growing quickly & spilling over normal skin. Usually SCC.
You might also like
- Pre-Op Case Protocol #4Document2 pagesPre-Op Case Protocol #4IC BNo ratings yet
- SurgeryDocument14 pagesSurgeryVinit ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Anaest CWU OTDocument15 pagesAnaest CWU OTHana Fauzi100% (1)
- 6.examination of Inguinal SwellingDocument4 pages6.examination of Inguinal SwellingMuvenn Kannan100% (1)
- AV Fistula ExamDocument4 pagesAV Fistula ExamKay BristolNo ratings yet
- Surgical History For ULCER & LumpDocument94 pagesSurgical History For ULCER & LumpAbdullah MatarNo ratings yet
- Neck Examination PDFDocument2 pagesNeck Examination PDFNizam Mischievous'Lovely Schremo BoyysNo ratings yet
- Examination of Inguinoscrotal SwellingDocument3 pagesExamination of Inguinoscrotal SwellingHumna YounisNo ratings yet
- OSCE Surgery Block PDFDocument31 pagesOSCE Surgery Block PDFanabanananNo ratings yet
- Basic Thyroid ExaminationDocument6 pagesBasic Thyroid ExaminationPalwasha MalikNo ratings yet
- Nephrotic Syndrome: Dinesh Kumar PDocument42 pagesNephrotic Syndrome: Dinesh Kumar PRiya Sweetsolitude100% (1)
- Thyroid SwellingDocument8 pagesThyroid SwellingDn Ezrinah Dn Esham50% (2)
- Anaest CWU ICUDocument13 pagesAnaest CWU ICUHana FauziNo ratings yet
- Systemic Surgery NuggetsDocument17 pagesSystemic Surgery NuggetsAhmad UsmanNo ratings yet
- Hernia Examination SchemeDocument4 pagesHernia Examination Schemeatribecalledquest20No ratings yet
- Long Case PUDDocument6 pagesLong Case PUDNadia SalwaniNo ratings yet
- Name: Wong Wai Kheong Matrix No: BMS12081154Document13 pagesName: Wong Wai Kheong Matrix No: BMS12081154myolie wuNo ratings yet
- Stoma Examination OSCE GuideDocument5 pagesStoma Examination OSCE GuideEssa AfridiNo ratings yet
- Comment On Dressing or Bandages and Take Them Down, Comment On ScarsDocument4 pagesComment On Dressing or Bandages and Take Them Down, Comment On ScarsGNo ratings yet
- CKD History TakingDocument2 pagesCKD History TakingNadia Salwani80% (5)
- Case History SurgeryDocument8 pagesCase History SurgeryMohamad Yusri100% (1)
- OSCE Checklist - Hernia Examination-1Document1 pageOSCE Checklist - Hernia Examination-1singhurvashi365No ratings yet
- Jaundice: Checklist For HistoryDocument17 pagesJaundice: Checklist For HistoryMustafa H. KadhimNo ratings yet
- Case Writeup Albert Labores 9.24.2010 StrokeDocument6 pagesCase Writeup Albert Labores 9.24.2010 StrokeAJ RegaladoNo ratings yet
- Stoma Examination - OSCE GuideDocument3 pagesStoma Examination - OSCE GuideAhmed AlkhaqaniNo ratings yet
- Gi Long CaseDocument8 pagesGi Long CaseNadia SalwaniNo ratings yet
- Lupus Case PresentationDocument48 pagesLupus Case PresentationRoscelie KhoNo ratings yet
- Obstructive JaundiceDocument13 pagesObstructive JaundiceJeevan VijayNo ratings yet
- Clinical ExDocument123 pagesClinical ExDeepti ChaharNo ratings yet
- Obstetrics History Taking in and Examination PowerpointDocument15 pagesObstetrics History Taking in and Examination Powerpointياسر كوثر هانيNo ratings yet
- Mass in Epigastrium-2Document37 pagesMass in Epigastrium-2brown_chocolate87643100% (1)
- Thyroid Examination and ThyroidectomyDocument9 pagesThyroid Examination and ThyroidectomyAhmadNo ratings yet
- Bleeding Per RectumeDocument35 pagesBleeding Per RectumetharakaNo ratings yet
- Surgery OSCE SpotsDocument1 pageSurgery OSCE SpotsAbdulNo ratings yet
- Prepared by Mary Ann A. Cubon, RN, RM, ManDocument35 pagesPrepared by Mary Ann A. Cubon, RN, RM, ManCarlaLuisaVillalunaNo ratings yet
- Breast Lump History: Opening The ConsultationDocument2 pagesBreast Lump History: Opening The ConsultationYoyoguyNo ratings yet
- Obstetric History & ExaminationDocument4 pagesObstetric History & ExaminationalifisallahNo ratings yet
- Case Presentation Lump Right HypochondriumDocument22 pagesCase Presentation Lump Right HypochondriumNANDAN RAINo ratings yet
- Hepatobiliary Notes 2.0Document18 pagesHepatobiliary Notes 2.0Sri VathanahNo ratings yet
- Malunion Delayed Union and Nonunion FracturesDocument31 pagesMalunion Delayed Union and Nonunion FracturesRasjad ChairuddinNo ratings yet
- Pediatrics 2 LaboratoryDocument40 pagesPediatrics 2 LaboratoryAmaetenNo ratings yet
- Preoperative EvaluationDocument4 pagesPreoperative EvaluationFadly Setiawirawan100% (1)
- Exam Technique, HNBreast, Thyroid&AbdomenDocument9 pagesExam Technique, HNBreast, Thyroid&AbdomenInsyirah Hatta100% (1)
- Upper GITDocument13 pagesUpper GITKiara Govender100% (1)
- Examination of A StomaDocument3 pagesExamination of A StomaChloe100% (1)
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease: DefinitionDocument4 pagesInflammatory Bowel Disease: Definitionkarl abiaadNo ratings yet
- Approach To A Child With Cough and Difficulty in BreathingDocument23 pagesApproach To A Child With Cough and Difficulty in BreathingKashif Burki100% (2)
- PRO 2012 Short Case (Surgical) CompilationDocument24 pagesPRO 2012 Short Case (Surgical) CompilationvijayaNo ratings yet
- History Taking OBS GYNDocument10 pagesHistory Taking OBS GYNzvkznhsw2tNo ratings yet
- Surgery BookDocument95 pagesSurgery BookKhaled Mahmud100% (1)
- 4 5820951304909882278 PDFDocument386 pages4 5820951304909882278 PDFMohamed HamoodNo ratings yet
- Fever Proforma and Assignment - 1Document48 pagesFever Proforma and Assignment - 1SivaNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular BigDocument37 pagesCardiovascular Bigfaiz nasirNo ratings yet
- Gyne Case COCDocument37 pagesGyne Case COCLian BaylosisNo ratings yet
- Management OF Breast Lump: Differential DiagnosisDocument4 pagesManagement OF Breast Lump: Differential DiagnosisMuhammad Azhar QureshiNo ratings yet
- Surgery CaseDocument43 pagesSurgery CaseAvni GuptaNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Examination: Preparation of The PatientDocument4 pagesCardiovascular Examination: Preparation of The PatientLolla SinwarNo ratings yet
- CASE PRESENTATION OF Obstructive JaundiceDocument25 pagesCASE PRESENTATION OF Obstructive JaundiceKhalid RizwanNo ratings yet
- Distal To Ligament of Treitz: CausesDocument8 pagesDistal To Ligament of Treitz: CausesKiara GovenderNo ratings yet
- Eob Osce Class of 2016Document4 pagesEob Osce Class of 2016HongMingNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Emergency Pocket GuideDocument2 pagesPediatric Emergency Pocket GuideHongMingNo ratings yet
- A Patient in The Observation WardDocument2 pagesA Patient in The Observation WardHongMingNo ratings yet
- Govt Hosp Listing As of Aug 2015 PahangDocument2 pagesGovt Hosp Listing As of Aug 2015 PahangHongMingNo ratings yet
- Doctor Patient RelationshipDocument1 pageDoctor Patient RelationshipHongMingNo ratings yet
- An Asthmatic PatientDocument2 pagesAn Asthmatic PatientHongMingNo ratings yet
- Confidence Intervals: Aka Interval Estimate Foo Wee Nee Kevin Kong Jun WaiDocument5 pagesConfidence Intervals: Aka Interval Estimate Foo Wee Nee Kevin Kong Jun WaiHongMingNo ratings yet
- Rovers Study ArticleDocument4 pagesRovers Study ArticleHongMingNo ratings yet
- Mild or Pricking Pain: Trauma? Y NDocument4 pagesMild or Pricking Pain: Trauma? Y NHongMingNo ratings yet
- Sexual AssaultDocument2 pagesSexual AssaultHongMingNo ratings yet
- Clinical Experience Sheet (Ces) and New End-Of-Rotation Assessment (Eora)Document3 pagesClinical Experience Sheet (Ces) and New End-Of-Rotation Assessment (Eora)HongMingNo ratings yet
- Student To Student Guide - IC 1 - 2014Document15 pagesStudent To Student Guide - IC 1 - 2014HongMingNo ratings yet
- REGUB Podcast 4Document3 pagesREGUB Podcast 4HongMingNo ratings yet
- Class of 2018 Course StructureDocument5 pagesClass of 2018 Course StructureHongMingNo ratings yet
- Epidemiology SlidesDocument30 pagesEpidemiology SlidesHongMingNo ratings yet