Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Metabolic Enzyme Regulation: Glycolysis
Uploaded by
BigBoostingOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Metabolic Enzyme Regulation: Glycolysis
Uploaded by
BigBoostingCopyright:
Available Formats
Metabolic Enzyme Regulation
General Notes * before regulator means enzyme is phosphorylated by a kinase (*PKA = Phosphorylated by Protein Kinase A) * after regulator means enzyme is dephosphorylated Ca2+ regulates by associating with calmodulin....Ca2+-Calmodulin complex mediates effects. Assume regulation by PKA is part of the Glucagon pathway.
ENZYME/PROTEIN
ACTIVATION GLYCOLYSIS
INHIBITION
COMMENTS
Hexokinase Glucokinase PFK-1 AMP F-2,6-BP
Glucose-6-P Glucose-6-P ATP Citrate PEP Low pH PEP Citrate *PKA ATP *PKA Lactate Pyruvate CoA / NAD+ / ADP Ca2+ / Mg2+ Acetyl CoA NADH ATP Cori Cycle (liver) Lactate-->Pyruvate KNOW MECHANISM Requires TPP, Lipoic Adic, FAD Regulated by PDH Kinase and PDH Phosphatase TCA CYLCLE Only in Liver Low pH - such as in anaerob. glycolysis (lactic acid) F-6-P <--> F-2,6-BP Not a Glycolytic Enzyme...Provides allosteric effector
PFK-2
AMP
Pyruvate Kinase
F-1,6-BP
LDH PDH
Citrate Synthase Isocitrate DH a-Ketoglutarate DH ADP Ca2+ Ca2+
Citrate NADH NADH
ENZYME/PROTEIN Malate DH
ACTIVATION
INHIBITION NADH
COMMENTS
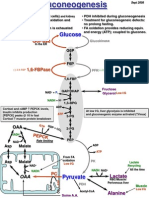
GLUCONEOGENESIS Pyruvate Carboxylase PEPCK Acetyl CoA Requires Biotin Induced by Glucagon OAA --> PEP (OAA exits mitochondria as either Asp or Malate) F-bis-Phospatase G-6-Phosphatase Citrate F-2,6-BP Induced by Glucagon Only in Liver Induced by Glucagon Deficiency - von Gierkes Disease GLYCOGEN SYTHESIS / DEGRADATION Glycogen Synthase Kinase Glycogen Synthase Protein Phosphatase* *PKB Inactivation by Insulin Pathway....leads to activation of Glycogen Synthase
*PKA Ca2+
Glycogen Phosphorylase Kinase Glycogen Phosphorylase
*PKA *Glycogen Phosphorylase Kinase AMP Ca2+
Protein Phosphatase* Protein Phosphatase*
FATTY ACID / TG SYNTHESIS Citrate Lyase Malic Enzyme Acetyl CoA Carboxylase Citrate Phosphatase* (Insulin Pathway) Palmitoyl CoA *AMP-activated Protein Kinase
ENZYME/PROTEIN FA Synthase Fatty Acyl CoA Synthetase CPT-I Glycerol Kinase LPL
ACTIVATION
INHIBITION
COMMENTS
Malonyl CoA
ApoCII
Recruited to apical surface of endothelial cells by Insulin
FATTY ACID OXIDATION HSL Fatty Acyl CoA Synthetase *PKA FA --> FAcyl CoA ATP-->AMP + 2P(i) (Loss of TWO high energy phosphates.... remember when calculating energy yield) B-Oxidation Spiral Enzymes NADH FAD(2H) 1) 2) 3) Acyl CoA DH Enoyl CoA Hydratase B-Hydroxy Acyl CoA DH 4) B-Keto Thiolase
KETONE BODY METABOLISM Thiolase HMG-CoA Sythase HMG-CoA Lyase B-Hydroxybutyrate DH Succinyl CoA : AACoA transferase
Sequence of Events Increased [FA] in cytosol [Malonyl CoA] decreased Increased import of FA into Mitochondria Increased B-Oxid. Increase ATP Increased NADH Build up of Acetyl CoA Acetyl CoA diverted from TCA to Ketone Bodies Lowering [FA] Reversal of <-------Previous
Basically, ketone bodies are formed in the mitochondrial matrix when acetyl CoA is being produced faster than it can be oxidized in the TCA cycle. So KBs can be correlated with high [FA] With restoration to normal [FA] ....KB synthesis stops because Acetyl CoA prefers to go to TCA cycle.
You might also like
- 11 - Carbohydrate MetabolismDocument68 pages11 - Carbohydrate MetabolismcheckmateNo ratings yet
- Enzymes Involved in Glycolysis, Fatty Acid and Amino Acid Biosynthesis: Active Site Mechanisms and InhibitionFrom EverandEnzymes Involved in Glycolysis, Fatty Acid and Amino Acid Biosynthesis: Active Site Mechanisms and InhibitionNo ratings yet
- Gluconeogenesis: Synthesizing Glucose from Non-Carbohydrate PrecursorsDocument31 pagesGluconeogenesis: Synthesizing Glucose from Non-Carbohydrate Precursorsemery100% (1)
- Glycolysis and Fermentation: Key Pathways and RegulationDocument14 pagesGlycolysis and Fermentation: Key Pathways and RegulationBONAVENTURA ALVINO DESMONDANo ratings yet
- Lect # 3 GluconeogenesisDocument40 pagesLect # 3 GluconeogenesisUbaid ur Rahman100% (1)
- 2021 CHO Metabolism 1Document48 pages2021 CHO Metabolism 1xb2k9gzkc9No ratings yet
- 13 - GluconeogenesisDocument23 pages13 - GluconeogenesischeckmateNo ratings yet
- Purines Pyrimidines: de Novo Pyrimidine and Purine SynthesisDocument44 pagesPurines Pyrimidines: de Novo Pyrimidine and Purine SynthesisKimber ManiulitNo ratings yet
- Metabolic RegulationDocument2 pagesMetabolic RegulationBigBoosting100% (1)
- GluconeogenesisDocument31 pagesGluconeogenesisRajakannanNo ratings yet
- Glycolysis "Sugar Splitting" 10 Reactions & Some Mechanisms Energy Enzymes Regulation Pyruvate Fate - Aerobic or Not?Document45 pagesGlycolysis "Sugar Splitting" 10 Reactions & Some Mechanisms Energy Enzymes Regulation Pyruvate Fate - Aerobic or Not?drnazzNo ratings yet
- ATP Production AEROBIC Metabolism: ST STDocument11 pagesATP Production AEROBIC Metabolism: ST STSiir Pwnsalot100% (1)
- Curs GluconeogenesisDocument25 pagesCurs GluconeogenesisOnofrei MariaNo ratings yet
- Gluconeogenesis + Evaluations 4/23/2003Document30 pagesGluconeogenesis + Evaluations 4/23/2003Ajay Pal NattNo ratings yet
- Lec Notes - Carbohydrates Metabolism II and Lipid MetabolismDocument12 pagesLec Notes - Carbohydrates Metabolism II and Lipid MetabolismyanNo ratings yet
- BIOCHEM (Glucogeniosis)Document30 pagesBIOCHEM (Glucogeniosis)Kara Kristine Tuano NarismaNo ratings yet
- Substrates&EnzymesDocument15 pagesSubstrates&EnzymesTanyaTouchéNo ratings yet
- Online Practice Tests, Live Classes, Tutoring, Study Guides Q&A, Premium Content and MoreDocument17 pagesOnline Practice Tests, Live Classes, Tutoring, Study Guides Q&A, Premium Content and MoreabctutorNo ratings yet
- BIOCHEMISTRY - Summary of PathwaysDocument8 pagesBIOCHEMISTRY - Summary of PathwaysWendy Mae100% (9)
- 5 RegulationDocument18 pages5 RegulationAli KesenNo ratings yet
- A 59-Year-Old Man With A History of Diabetes and Alcohol Abuse Is Brought To The Emergency Room in A Semiconscious and Minimally Responsive StateDocument43 pagesA 59-Year-Old Man With A History of Diabetes and Alcohol Abuse Is Brought To The Emergency Room in A Semiconscious and Minimally Responsive StateAnonymous eDD0YqzPMNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14Document23 pagesChapter 14nhocnho_1993No ratings yet
- Gluconeogenesis: The Pathway and RegulationDocument31 pagesGluconeogenesis: The Pathway and RegulationMunachande KanondoNo ratings yet
- Gluconeogenesis: An Overview of Glucose MetabolismDocument31 pagesGluconeogenesis: An Overview of Glucose MetabolismJavedNo ratings yet
- Carbo ChemDocument123 pagesCarbo ChemHan MichelNo ratings yet
- Collection of Importance in MBCHMDocument7 pagesCollection of Importance in MBCHMAnonymous vCXYXdv45No ratings yet
- Carbohydrate Metabolism Glycolysis: Biochemistry 2 Code (4131)Document24 pagesCarbohydrate Metabolism Glycolysis: Biochemistry 2 Code (4131)essaNo ratings yet
- PDH Complex REVIEW: DR Navin SDocument23 pagesPDH Complex REVIEW: DR Navin Svaseem1981No ratings yet
- Carbohydrate Metabolism Catabolism Blok 7 2018Document136 pagesCarbohydrate Metabolism Catabolism Blok 7 2018N A Anggriani WulandariNo ratings yet
- Glycolysis: DR Imran SiddiquiDocument13 pagesGlycolysis: DR Imran Siddiquiapi-19824406No ratings yet
- Glycogen metabolism and regulation enzymesDocument71 pagesGlycogen metabolism and regulation enzymesAzhar JirmandNo ratings yet
- MEH Review 2022Document36 pagesMEH Review 2022Moeed AliNo ratings yet
- GlycolysisDocument31 pagesGlycolysisrafea_naffa8326No ratings yet
- Carbohydrate Metabolism Week 2Document38 pagesCarbohydrate Metabolism Week 2shadaalnaas657No ratings yet
- Energy Metabolism of The Heart Under Different PathophysiologicalDocument27 pagesEnergy Metabolism of The Heart Under Different PathophysiologicalAmanuel MaruNo ratings yet
- F6P PFK-2 Fr. 2,6 BP FBP-2: Insulin Glucagon GlycolysisDocument4 pagesF6P PFK-2 Fr. 2,6 BP FBP-2: Insulin Glucagon GlycolysisKate TaylorNo ratings yet
- Glycolysis GluconeogenesisDocument66 pagesGlycolysis GluconeogenesisRahmad AllulNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Notes For BoardsDocument35 pagesBiochemistry Notes For BoardsUjjwal PyakurelNo ratings yet
- Integration of MetabolismDocument40 pagesIntegration of MetabolismririnNo ratings yet
- Chapter 31 - BiochemistryDocument4 pagesChapter 31 - Biochemistrydavetraf14No ratings yet
- Carbohydrate Metabolism Catabolism 2013Document108 pagesCarbohydrate Metabolism Catabolism 2013Anonymous nErkwtXnuS100% (1)
- Carbohydrate Metabolism 2Document41 pagesCarbohydrate Metabolism 2Shimmering MoonNo ratings yet
- Summarybioo Compressed PDFDocument3 pagesSummarybioo Compressed PDFHassan mohamad Al-bayateNo ratings yet
- CHO Met 2 Biochemistry 21-12-2018Document28 pagesCHO Met 2 Biochemistry 21-12-2018Abdii FiixeeNo ratings yet
- Lecture-4 On CHO MetabolismDocument27 pagesLecture-4 On CHO MetabolismMohammed ZeburNo ratings yet
- GlycolysisDocument35 pagesGlycolysisAastha SinhaNo ratings yet
- Lipid metabolism lecture 3 of 3: Fatty acid oxidationDocument43 pagesLipid metabolism lecture 3 of 3: Fatty acid oxidationKhalid OmarNo ratings yet
- Regulation of LipidsDocument13 pagesRegulation of LipidsNeha SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Gluconeogenesis: Preventing Hypoglycemia Through De Novo Glucose SynthesisDocument12 pagesGluconeogenesis: Preventing Hypoglycemia Through De Novo Glucose SynthesisDayledaniel SorvetoNo ratings yet
- GluconeogenesisDocument12 pagesGluconeogenesisRith Hengmeng (Study Smart)No ratings yet
- Liver Gluconeogenesis and Lactate Recycling ProcessDocument2 pagesLiver Gluconeogenesis and Lactate Recycling Processbigoldtruck38No ratings yet
- MetabolismDocument11 pagesMetabolismMituSamadderNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrate MetabolismDocument56 pagesCarbohydrate MetabolismPradini SugihartoNo ratings yet
- Gluco Neo GenesisDocument36 pagesGluco Neo GenesisAmalia DarwisNo ratings yet
- 10 GluconeogenesisDocument18 pages10 GluconeogenesiskulturewearzmNo ratings yet
- PDH Complex and TCA CycleDocument20 pagesPDH Complex and TCA CycleDarrion LouisNo ratings yet
- Glycolysis 3MD (3)Document48 pagesGlycolysis 3MD (3)gostrider0093sNo ratings yet
- Glycolysis and Gluconeogenesis: Instructor-RclDocument33 pagesGlycolysis and Gluconeogenesis: Instructor-RclNitish ShahNo ratings yet
- Glycolysis and Gluconeogenesis: Instructor-RclDocument33 pagesGlycolysis and Gluconeogenesis: Instructor-RclPrince Kyle R. DolosoNo ratings yet
- Guideline Watch: Practice Guideline For The Treatment of Patients With Bipolar Disorder, 2Nd EditionDocument9 pagesGuideline Watch: Practice Guideline For The Treatment of Patients With Bipolar Disorder, 2Nd EditionBigBoostingNo ratings yet
- The Mental Status ExaminationDocument16 pagesThe Mental Status Examinationeloisa.abcedeNo ratings yet
- GI NotesDocument19 pagesGI NotesBigBoostingNo ratings yet
- Obgyn Abbreviations For RotationDocument2 pagesObgyn Abbreviations For RotationBigBoostingNo ratings yet
- GI High YieldDocument1 pageGI High YieldBigBoostingNo ratings yet
- The Mirror Neuron System: Luigi Cattaneo, MD Giacomo Rizzolatti, MDDocument4 pagesThe Mirror Neuron System: Luigi Cattaneo, MD Giacomo Rizzolatti, MDBigBoostingNo ratings yet
- Psychosomatic MedicineDocument14 pagesPsychosomatic MedicineGiuseppe RutiglianiNo ratings yet
- Lectura 1 PDFDocument73 pagesLectura 1 PDFgroudon_18No ratings yet
- Neurologic Presentations of HIV/AIDSDocument23 pagesNeurologic Presentations of HIV/AIDSBigBoostingNo ratings yet
- Muscles NervesDocument3 pagesMuscles NervesBigBoostingNo ratings yet
- Psychiatric Genetics: Progress Amid Controversy: Margit Burmeister, Melvin G. Mcinnis and Sebastian ZöllnerDocument14 pagesPsychiatric Genetics: Progress Amid Controversy: Margit Burmeister, Melvin G. Mcinnis and Sebastian ZöllnerBigBoostingNo ratings yet
- Guideline Watch: Practice Guideline For The Treatment of Patients With Bipolar Disorder, 2Nd EditionDocument9 pagesGuideline Watch: Practice Guideline For The Treatment of Patients With Bipolar Disorder, 2Nd EditionBigBoostingNo ratings yet
- Triangles of The Neck Vertebral ArteryDocument6 pagesTriangles of The Neck Vertebral ArteryBigBoostingNo ratings yet
- Bone Cancer Chart 2012Document8 pagesBone Cancer Chart 2012BigBoostingNo ratings yet
- Cross Sections of Upper LimbDocument12 pagesCross Sections of Upper LimbBigBoostingNo ratings yet
- NervesDocument139 pagesNervesBigBoostingNo ratings yet
- Blue Boxes For MusculoskeletalDocument16 pagesBlue Boxes For MusculoskeletalBigBoostingNo ratings yet
- ProcarbazineDocument2 pagesProcarbazineBigBoostingNo ratings yet
- Neuro Phase Notes MS-1Document43 pagesNeuro Phase Notes MS-1BigBoostingNo ratings yet
- CNS PharmDocument16 pagesCNS PharmBigBoostingNo ratings yet
- Cranial Nerve TractsDocument2 pagesCranial Nerve TractsBigBoostingNo ratings yet
- Neoplasias TableDocument3 pagesNeoplasias TableBigBoostingNo ratings yet
- ThalidomideDocument2 pagesThalidomideBigBoostingNo ratings yet
- TretinoinDocument2 pagesTretinoinBigBoostingNo ratings yet
- RituximabDocument2 pagesRituximabBigBoosting100% (2)
- S Mechanism of Action: Inhibits Adenosine Deaminase (ADA) Which Leads To The AccumulationDocument2 pagesS Mechanism of Action: Inhibits Adenosine Deaminase (ADA) Which Leads To The AccumulationBigBoostingNo ratings yet
- VincristineDocument2 pagesVincristineBigBoostingNo ratings yet
- OfatumumabDocument2 pagesOfatumumabBigBoostingNo ratings yet
- MercaptopurineDocument2 pagesMercaptopurineBigBoostingNo ratings yet
- NilotinibDocument2 pagesNilotinibBigBoostingNo ratings yet