Professional Documents
Culture Documents
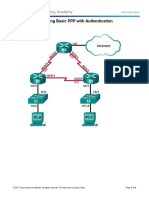
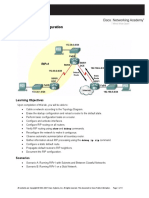
PT Activity 2.5.1: Basic PPP Configuration: Topology Diagram
PT Activity 2.5.1: Basic PPP Configuration: Topology Diagram
Uploaded by
Ayboo LocayonOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
PT Activity 2.5.1: Basic PPP Configuration: Topology Diagram
PT Activity 2.5.1: Basic PPP Configuration: Topology Diagram
Uploaded by
Ayboo LocayonCopyright:
Available Formats
PT Activity 2.5.
1: Basic PPP Configuration
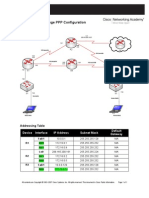
Topology Diagram
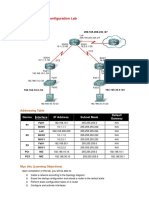
Addressing Table
Device R1 Interface Fa0/1 S0/0/0 Lo0 R2 S0/0/0 S0/0/1 R3 PC1 PC3 Fa0/1 S0/0/1 NIC NIC IP Address 192.168.10.1 10.1.1.1 209.165.200.225 10.1.1.2 10.2.2.1 192.168.30.1 10.2.2.2 192.168.10.10 192.168.30.10 Subnet Mask 255.255.255.0 255.255.255.252 255.255.255.224 255.255.255.252 255.255.255.252 255.255.255.0 255.255.255.252 255.255.255.0 255.255.255.0 Default Gateway N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A N/A 192.168.10.1 192.168.30.1
All contents are Copyright 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information.
Page 1 of 9
CCNA Exploration Accessing the WAN: PPP
PT Activity 2.5.1: Basic PPP Configuration
Learning Objectives
Configure OSPF routing on all routers. Configure PPP encapsulation on all serial interfaces. Intentionally break and restore PPP encapsulation. Configure PPP PAP and CHAP authentication. Intentionally break and restore PPP PAP and CHAP authentication.
Introduction
In this lab, you will learn how to configure PPP encapsulation on serial links using the network shown in the topology diagram. You will also learn how to restore serial links to their default HDLC encapsulation. Finally, you will configure PPP PAP authentication and PPP CHAP authentication.
Task 1: Configure OSPF on the Routers
Step 1. Enable OSPF routing on R1, R2, and R3. For all three routers, use cisco for the user EXEC password and class for the privileged EXEC password. Issue the router ospf command with a process ID of 1 to enter router configuration mode. For each router, advertise all the attached networks. R1(config)#router ospf 1 R1(config-router)#network 192.168.10.0 0.0.0.255 area 0 R1(config-router)#network 10.1.1.0 0.0.0.3 area 0 R1(config-router)# R2(config)#router ospf 1 R2(config-router)#network 10.1.1.0 0.0.0.3 area 0 R2(config-router)#network 10.2.2.0 0.0.0.3 area 0 R2(config-router)#network 209.165.200.224 0.0.0.31 area 0 R2(config-router)# R3(config)#router ospf 1 R3(config-router)#network 10.2.2.0 0.0.0.3 area 0 R3(config-router)#network 192.168.30.0 0.0.0.255 area 0 R3(config-router)# Step 2. Verify that you have full network connectivity. Use the show ip route and ping commands to verify connectivity. R1#show ip route <output omitted> 10.0.0.0/30 is subnetted, 2 subnets 10.1.1.0 is directly connected, Serial0/0/0 10.2.2.0 [110/128] via 10.1.1.2, 00:02:22, Serial0/0/0 192.168.10.0/24 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/1 192.168.30.0/24 [110/129] via 10.1.1.2, 00:00:08, Serial0/0/0 209.165.200.0/32 is subnetted, 1 subnets 209.165.200.225 [110/65] via 10.1.1.2, 00:02:22, Serial0/0/0
C O C O O
R1#ping 192.168.30.1 Type escape sequence to abort.
All contents are Copyright 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 2 of 9
CCNA Exploration Accessing the WAN: PPP
PT Activity 2.5.1: Basic PPP Configuration
Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 192.168.30.1, timeout is 2 seconds: !!!!! Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 32/32/32 ms R1# R2#show ip route <output omitted> 10.0.0.0/30 is subnetted, 2 subnets 10.1.1.0 is directly connected, Serial0/0/0 10.2.2.0 is directly connected, Serial0/0/1 192.168.10.0/24 [110/65] via 10.1.1.1, 00:02:31, Serial0/0/0 192.168.30.0/24 [110/65] via 10.2.2.2, 00:00:20, Serial0/0/1 209.165.200.0/27 is subnetted, 1 subnets 209.165.200.224 is directly connected, Loopback0
C C O O C
R2#ping 192.168.30.1 Type escape sequence to abort. Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 192.168.30.1, timeout is 2 seconds: !!!!! Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 16/16/16 ms R2#ping 192.168.10.1 Type escape sequence to abort. Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 192.168.10.1, timeout is 2 seconds: !!!!! Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 16/16/16 ms R2# R3#show ip route <output omitted> 10.0.0.0/30 is subnetted, 2 subnets 10.1.1.0 [110/128] via 10.2.2.1, 00:00:34, Serial0/0/1 10.2.2.0 is directly connected, Serial0/0/1 192.168.10.0/24 [110/129] via 10.2.2.1, 00:00:34, Serial0/0/1 192.168.30.0/24 is directly connected, FastEthernet0/1 209.165.200.0/32 is subnetted, 1 subnets 209.165.200.225 [110/65] via 10.2.2.1, 00:00:34, Serial0/0/1
O C O C O
R3#ping 209.165.200.225 Type escape sequence to abort. Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 209.165.200.225, timeout is 2 seconds: !!!!! Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 16/16/16 ms R3#ping 192.168.10.1 Type escape sequence to abort. Sending 5, 100-byte ICMP Echos to 192.168.10.1, timeout is 2 seconds: !!!!! Success rate is 100 percent (5/5), round-trip min/avg/max = 32/32/32 ms R3#
All contents are Copyright 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information.
Page 3 of 9
CCNA Exploration Accessing the WAN: PPP
PT Activity 2.5.1: Basic PPP Configuration
Task 2: Configure PPP Encapsulation on Serial Interfaces
Step 1. Use the show interface command to check whether HDLC is the default serial encapsulation. The default serial encapsulation on Cisco routers is HDLC. Use the show interface command on any of the serial interfaces to view the current encapsulation. R1#show interface serial0/0/0 Serial0/0/0 is up, line protocol is up Hardware is GT96K Serial Internet address is 10.1.1.1/30 MTU 1500 bytes, BW 128 Kbit, DLY 20000 usec, reliability 255/255, txload 1/255, rxload 1/255 Encapsulation HDLC, loopback not set <output omitted> If you check all the active serial interfaces, the encapsulation will be set to HDLC. Step 2. Change the encapsulation of the serial interfaces from HDLC to PPP. Change the encapsulation type on the link between R1 and R2, and observe the effects. R1(config)#interface serial 0/0/0 R1(config-if)#encapsulation ppp R1(config-if)# *Aug 17 19:02:53.412: %OSPF-5-ADJCHG: Process 1, Nbr 209.165.200.225 on Serial0/0/0 from F ULL to DOWN, Neighbor Down: Interface down or detached R1(config-if)# R2(config)#interface serial 0/0/0 R2(config-if)#encapsulation ppp R2(config-if)# What happens when one end of the serial link is encapsulated with PPP and the other end of the link is encapsulated with HDLC? What happens when PPP encapsulation is configured on each end of the serial link? Step 3. Change the encapsulation from HDLC to PPP on both ends of the serial link between R2 and R3. R2(config)#interface serial0/0/1 R2(config-if)#encapsulation ppp R2(config-if)# *Aug 17 20:02:08.080: %OSPF-5-ADJCHG: Process 1, Nbr 192.168.30.1 on Serial0/0/1 from FULL to DOWN, Neighbor Down: Interface down or detached *Aug 17 20:02:13.080: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Serial0/0/1, changed state to down *Aug 17 20:02:58.564: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Serial0/0/1, changed state to up *Aug 17 20:03:03.644: %OSPF-5-ADJCHG: Process 1, Nbr 192.168.30.1 on Serial0/0/1 from LOAD ING to FULL, Loading Done *Aug 17 20:03:46.988: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Serial0/0/1, changed
All contents are Copyright 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 4 of 9
CCNA Exploration Accessing the WAN: PPP
PT Activity 2.5.1: Basic PPP Configuration
state to down R3(config)#interface serial 0/0/1 R3(config-if)#encapsulation ppp R3(config-if)# *Aug 17 20:04:27.152: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Serial0/0/1, changed state to up *Aug 17 20:04:30.952: %OSPF-5-ADJCHG: Process 1, Nbr 209.165.200.225 on Serial0/0/1 from L OADING to FULL, Loading Done When does the line protocol on the serial link come up and the OSPF adjacency is restored? Step 4. Verify that PPP is now the encapsulation on the serial interfaces. R1#show interface serial0/0/0 Serial0/0/0 is up, line protocol is up Hardware is GT96K Serial Internet address is 10.1.1.1/30 MTU 1500 bytes, BW 128 Kbit, DLY 20000 usec, reliability 255/255, txload 1/255, rxload 1/255 Encapsulation PPP, LCP Open Open: CDPCP, IPCP, loopback not set <output omitted> R2#show interface serial 0/0/0 Serial0/0/0 is up, line protocol is up Hardware is GT96K Serial Internet address is 10.1.1.2/30 MTU 1500 bytes, BW 128 Kbit, DLY 20000 usec, reliability 255/255, txload 1/255, rxload 1/255 Encapsulation PPP, LCP Open Open: CDPCP, IPCP, loopback not set <output omitted> R2#show interface serial 0/0/1 Serial0/0/1 is up, line protocol is up Hardware is GT96K Serial Internet address is 10.2.2.1/30 MTU 1500 bytes, BW 128 Kbit, DLY 20000 usec, reliability 255/255, txload 1/255, rxload 1/255 Encapsulation PPP, LCP Open Open: CDPCP, IPCP, loopback not set <output omitted> R3#show interface serial 0/0/1 Serial0/0/1 is up, line protocol is up Hardware is GT96K Serial Internet address is 10.2.2.2/30 MTU 1500 bytes, BW 128 Kbit, DLY 20000 usec, reliability 255/255, txload 1/255, rxload 1/255 Encapsulation PPP, LCP Open Open: CDPCP, IPCP, loopback not set <output omitted>
All contents are Copyright 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information.
Page 5 of 9
CCNA Exploration Accessing the WAN: PPP
PT Activity 2.5.1: Basic PPP Configuration
Task 3: Break and Restore PPP Encapsulation
Step 1. Return both serial interfaces on R2 to their default HDLC encapsulation. R2(config)#interface serial 0/0/0 R2(config-if)#encapsulation hdlc R2(config-if)# *Aug 17 20:36:48.432: %OSPF-5-ADJCHG: Process 1, Nbr 192.168.10.1 on Serial0/0/0 from FULL to DOWN, Neighbor Down: Interface down or detached *Aug 17 20:36:49.432: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Serial0/0/0, changed state to down R2(config-if)# *Aug 17 20:36:51.432: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Serial0/0/0, changed state to up R2(config-if)#interface serial 0/0/1 *Aug 17 20:37:14.080: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Serial0/0/0, changed state to down R2(config-if)#encapsulation hdlc R2(config-if)# *Aug 17 20:37:17.368: %OSPF-5-ADJCHG: Process 1, Nbr 192.168.30.1 on Serial0/0/1 from FULL to DOWN, Neighbor Down: Interface down or detached *Aug 17 20:37:18.368: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Serial0/0/1, changed state to down *Aug 17 20:37:20.368: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Serial0/0/1, changed state to up *Aug 17 20:37:44.080: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Serial0/0/1, changed state to down Why is it useful to intentionally break a configuration? ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ Why do both serial interfaces go down, come back up, and then go back down? ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ Can you think of another way to change the encapsulation of a serial interface from PPP to the default HDLC encapsulation other than using the encapsulation hdlc command? (Hint: It has to do with the no command.) ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________
All contents are Copyright 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information.
Page 6 of 9
CCNA Exploration Accessing the WAN: PPP
PT Activity 2.5.1: Basic PPP Configuration
Step 2. Return both serial interfaces on R2 to PPP encapsulation. R2(config)#interface s0/0/0 R2(config-if)#encapsulation ppp *Aug 17 20:53:06.612: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Serial0/0/0, changed state to up R2(config-if)#interface s0/0/1 *Aug 17 20:53:10.856: %OSPF-5-ADJCHG: Process 1, Nbr 192.168.10.1 on Serial0/0/0 from LOAD ING to FULL, Loading Done R2(config-if)#encapsulation ppp *Aug 17 20:53:23.332: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Serial0/0/1, changed state to up *Aug 17 20:53:24.916: %OSPF-5-ADJCHG: Process 1, Nbr 192.168.30.1 on Serial0/0/1 from LOAD ING to FULL, Loading Done R2(config-if)#
Task 4: Configure PPP Authentication
Step 1. Configure PPP PAP authentication on the serial link between R1 and R2. R1(config)#username R2 password cisco R1(config)#int s0/0/0 R1(config-if)#ppp authentication pap R1(config-if)# *Aug 22 18:58:57.367: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Serial0/0/0, changed state to down *Aug 22 18:58:58.423: %OSPF-5-ADJCHG: Process 1, Nbr 209.165.200.225 on Serial0/0/0 from F ULL to DOWN, Neighbor Down: Interface down or detached R1(config-if)#ppp pap sent-username R1 password cisco What happens when PPP PAP authentication is only configured on one end of the serial link? ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ R2(config)#username R1 password cisco R2(config)#interface Serial0/0/0 R2(config-if)#ppp authentication pap R2(config-if)#ppp pap sent-username R2 password cisco R2(config-if)# *Aug 23 16:30:33.771: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Serial0/0/0, changed state to up *Aug 23 16:30:40.815: %OSPF-5-ADJCHG: Process 1, Nbr 192.168.10.1 on Serial0/0/0 from LOAD ING to FULL, Loading Done What happens when PPP PAP authentication is configured on both ends of the serial link? ____________________________________________________________________________________
All contents are Copyright 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information.
Page 7 of 9
CCNA Exploration Accessing the WAN: PPP
PT Activity 2.5.1: Basic PPP Configuration
Step 2. Configure PPP CHAP authentication on the serial link between R2 and R3. In PAP authentication, the password is not encrypted. While this is certainly better than no authentication at all, it is still highly preferable to encrypt the password that is being sent across the link. CHAP encrypts the password. R2(config)#username R3 password cisco R2(config)#int s0/0/1 R2(config-if)#ppp authentication chap R2(config-if)# *Aug 23 18:06:00.935: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Serial0/0/1, changed state to down R2(config-if)# *Aug 23 18:06:01.947: %OSPF-5-ADJCHG: Process 1, Nbr 192.168.30.1 on Serial0/0/1 from FULL to DOWN, Neighbor Down: Interface down or detached R2(config-if)# R3(config)#username R2 password cisco *Aug 23 18:07:13.074: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Serial0/0/1, changed state to up R3(config)#int s0/0/1 R3(config-if)# *Aug 23 18:07:22.174: %OSPF-5-ADJCHG: Process 1, Nbr 209.165.200.225 on Serial0/0/1 from L OADING to FULL, Loading Done R3(config-if)#ppp authentication chap R3(config-if)# Notice that the line protocol on interface serial 0/0/1 changes state to UP even before the interface is configured for CHAP authentication. Can you guess why this is the case? ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________
Task 5: Intentionally Break and Restore PPP CHAP Authentication
Step 1. Break PPP CHAP authentication. On the serial link between R2 and R3, change the authentication protocol on interface serial 0/0/1 to PAP. R2#conf t Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. R2(config)#int s0/0/1 R2(config-if)#ppp authentication pap R2(config-if)#^Z R2# *Aug 24 15:45:47.039: %SYS-5-CONFIG_I: Configured from console by console R2#copy run start Destination filename [startup-config]? Building configuration... [OK] R2#reload Does changing the authentication protocol to PAP on interface serial 0/0/1 break authentication between R2 and R3? ____________________________________________________________________________________
All contents are Copyright 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information. Page 8 of 9
CCNA Exploration Accessing the WAN: PPP
PT Activity 2.5.1: Basic PPP Configuration
Step 2. Restore PPP CHAP authentication on the serial link. Notice that it is not necessary to reload the router for this change to take effect. R2#conf t Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. R2(config)#int s0/0/1 R2(config-if)#ppp authentication chap R2(config-if)# *Aug 24 15:50:00.419: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Serial0/0/1, changed state to up R2(config-if)# *Aug 24 15:50:07.467: %OSPF-5-ADJCHG: Process 1, Nbr 192.168.30.1 on Serial0/0/1 from LOAD ING to FULL, Loading Done R2(config-if)# Step 3. Intentionally Break PPP CHAP authentication by changing the password on R3. R3#conf t Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. R3(config)#username R2 password ciisco R3(config)#^Z R3# *Aug 24 15:54:17.215: %SYS-5-CONFIG_I: Configured from console by console R3#copy run start Destination filename [startup-config]? Building configuration... [OK] R3#reload After reloading, what is the status of the line protocol on serial 0/0/1? ____________________________________________________________________________________ Step 4. Restore PPP CHAP authentication by changing the password on R3. R3#conf t Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z. R3(config)#username R2 password cisco R3(config)# *Aug 24 16:11:10.679: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Serial0/0/1, changed state to up R3(config)# *Aug 24 16:11:19.739: %OSPF-5-ADJCHG: Process 1, Nbr 209.165.200.225 on Serial0/0/1 from LOADING to FULL, Loading Done R3(config)# Note that the link has come back up. Test connectivity by pinging from PC1 to PC3.
All contents are Copyright 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved. This document is Cisco Public Information.
Page 9 of 9
You might also like
- Compete With Zscaler Battlecard v3 0Document4 pagesCompete With Zscaler Battlecard v3 0DC ExpertNo ratings yet
- 2.4.1.5 Lab - Troubleshooting Basic PPP With AuthenticationDocument8 pages2.4.1.5 Lab - Troubleshooting Basic PPP With AuthenticationVianey LopezNo ratings yet
- CCNA Whiteboard Study ToolDocument4 pagesCCNA Whiteboard Study ToolmxNo ratings yet
- Cisco CCNA Command Guide: An Introductory Guide for CCNA & Computer Networking Beginners: Computer Networking, #3From EverandCisco CCNA Command Guide: An Introductory Guide for CCNA & Computer Networking Beginners: Computer Networking, #3No ratings yet
- 2.3.2.7 Lab - Configuring Basic PPP With AuthenticationDocument17 pages2.3.2.7 Lab - Configuring Basic PPP With AuthenticationTony Blanco100% (1)
- CN v6 Instructor Packet Tracer ManualDocument118 pagesCN v6 Instructor Packet Tracer ManualLongo LaurisNo ratings yet
- 3.4.1.5 Lab - Troubleshooting Basic PPP With Authentication - ILMDocument23 pages3.4.1.5 Lab - Troubleshooting Basic PPP With Authentication - ILMvincent67% (3)
- 3.6.1.2 Packet Tracer - Skills Integration Challenge - ILMDocument6 pages3.6.1.2 Packet Tracer - Skills Integration Challenge - ILMElectronica EdwinNo ratings yet
- 4.3.3.4 Lab - Configure HSRPDocument7 pages4.3.3.4 Lab - Configure HSRPLeo Leo17% (6)
- Lab 4 Basic PPP Configuration Lab: Topology DiagramDocument6 pagesLab 4 Basic PPP Configuration Lab: Topology DiagramDat LCNo ratings yet
- Basic PPP ConfigurationDocument16 pagesBasic PPP ConfigurationEngku PuteraNo ratings yet
- Lab 8.5.1: Troubleshooting Enterprise Networks 1: Topology DiagramDocument12 pagesLab 8.5.1: Troubleshooting Enterprise Networks 1: Topology DiagrambusmaniakNo ratings yet
- IMTC-191 Lab 3Document13 pagesIMTC-191 Lab 3Alex 1001No ratings yet
- 6.2.7 Lab - Configure Automated Security FeaturesDocument11 pages6.2.7 Lab - Configure Automated Security FeaturesHani GoytomNo ratings yet
- 6.2.7 Lab Configure Automated Security FeaturesDocument11 pages6.2.7 Lab Configure Automated Security FeaturesCesar Lazo DiazNo ratings yet
- 6.2.7 Lab - Configure Automated Security FeaturesDocument11 pages6.2.7 Lab - Configure Automated Security FeaturesntutaNo ratings yet
- Lab 8.5.1Document12 pagesLab 8.5.1Gianluca PorcarelliNo ratings yet
- 10.2.3.4 Lab - Troubleshooting Advanced Single-Area OSPFv2Document6 pages10.2.3.4 Lab - Troubleshooting Advanced Single-Area OSPFv2Andres Carlos Rodriguez RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Lab 8.5.3: Troubleshooting Enterprise Networks 3: Topology DiagramDocument11 pagesLab 8.5.3: Troubleshooting Enterprise Networks 3: Topology DiagrambusmaniakNo ratings yet
- 16.1.4 Lab - Configure Route Redistribution Using BGP - ILMDocument26 pages16.1.4 Lab - Configure Route Redistribution Using BGP - ILMAndrei Petru PârvNo ratings yet
- 6.3.6 Lab - Basic Device Configuration and OSPF AuthenticationDocument7 pages6.3.6 Lab - Basic Device Configuration and OSPF AuthenticationGISTSalehuddinNo ratings yet
- 4.4.7 Lab - Configure Secure Administrative AccessDocument11 pages4.4.7 Lab - Configure Secure Administrative AccessJesús EnriqueNo ratings yet
- 4.4.7 Lab Configure Secure Administrative AccessDocument10 pages4.4.7 Lab Configure Secure Administrative AccessHector De Jesus Tapia GorgonioNo ratings yet
- 4.4.7 Lab - Configure Secure Administrative Access - ILMDocument22 pages4.4.7 Lab - Configure Secure Administrative Access - ILMRony Schäfer JaraNo ratings yet
- Lab: Basic RIP Configuration: Topology DiagramDocument11 pagesLab: Basic RIP Configuration: Topology DiagramFarhan AhmadNo ratings yet
- 2.4.1.5 Lab - Troubleshooting Basic PPP With Authentication - ILMDocument23 pages2.4.1.5 Lab - Troubleshooting Basic PPP With Authentication - ILMchristyan leonNo ratings yet
- EWAN Lab 2 5 2 AnswerDocument13 pagesEWAN Lab 2 5 2 AnswerLekan MulanaNo ratings yet
- Lab 3: Basic EIGRP Configuration Lab: Topology DiagramDocument4 pagesLab 3: Basic EIGRP Configuration Lab: Topology DiagramDat LCNo ratings yet
- 6.3.6 Lab - Basic Device Configuration and OSPF Authentication - ILMDocument11 pages6.3.6 Lab - Basic Device Configuration and OSPF Authentication - ILMRony Schäfer JaraNo ratings yet
- 10.1.3.4 Packet Tracer - Configuring OSPF Advanced FeaturesDocument2 pages10.1.3.4 Packet Tracer - Configuring OSPF Advanced FeaturesCarlos Beltran0% (1)
- 10.1.3.4 Packet Tracer - Configuring OSPF Advanced FeaturesDocument2 pages10.1.3.4 Packet Tracer - Configuring OSPF Advanced Featuressebastian ruizNo ratings yet
- 2.3.2.6 Packet Tracer - Configuring PAP and CHAP Authentication - ILMDocument3 pages2.3.2.6 Packet Tracer - Configuring PAP and CHAP Authentication - ILMElectronica EdwinNo ratings yet
- HRRPDocument7 pagesHRRPJavier CastilloNo ratings yet
- 10.1.3.4 Packet Tracer - Configuring OSPF Advanced FeaturesDocument3 pages10.1.3.4 Packet Tracer - Configuring OSPF Advanced FeaturesSean VillacortaNo ratings yet
- 10.1.3.5 Lab - Configuring OSPFv2 Advanced FeaturesDocument7 pages10.1.3.5 Lab - Configuring OSPFv2 Advanced FeaturesdboNo ratings yet
- Lab 01 - Securing The Router For Administrative AccessDocument39 pagesLab 01 - Securing The Router For Administrative AccessespolieeeNo ratings yet
- 10.1.3.4 Packet Tracer - Configuring OSPF Advanced Features - ILMDocument2 pages10.1.3.4 Packet Tracer - Configuring OSPF Advanced Features - ILMSergio TejedorNo ratings yet
- 11.1.2 Lab - Implement eBGP For IPv4 - ILMDocument22 pages11.1.2 Lab - Implement eBGP For IPv4 - ILMlokuras de la vidaNo ratings yet
- PT6433 v2 CompletedDocument3 pagesPT6433 v2 Completedlorel17157No ratings yet
- 11.1.2 Lab - Implement eBGP For IPv4Document16 pages11.1.2 Lab - Implement eBGP For IPv4Deux AmisNo ratings yet
- Lab 3.5.1: Basic Frame RelayDocument24 pagesLab 3.5.1: Basic Frame RelaychipomaNo ratings yet
- 10.1.3.5 Lab - Configuring OSPFv2 Advanced Features ELEISER HEBER ZELAYA CONDORIDocument8 pages10.1.3.5 Lab - Configuring OSPFv2 Advanced Features ELEISER HEBER ZELAYA CONDORIHeber Eleiser Zelaya Condori100% (2)
- 2.5.3 Packet Tracer - Propagate A Default Route in OSPFv2Document2 pages2.5.3 Packet Tracer - Propagate A Default Route in OSPFv2-- JokerNo ratings yet
- 7.3.2.7 Lab - Testing Network Connectivity With Ping and TracerouteDocument16 pages7.3.2.7 Lab - Testing Network Connectivity With Ping and TracerouteRaja Dang Jalernpan100% (6)
- 2.2.2.5 Lab - Configuring IPv4 Static and Default RoutesDocument15 pages2.2.2.5 Lab - Configuring IPv4 Static and Default Routesbalvinder singh50% (6)
- 2.3.2.6 Packet Tracer - Configuring PAP and CHAP AuthenticationDocument3 pages2.3.2.6 Packet Tracer - Configuring PAP and CHAP AuthenticationLayla KettlewellNo ratings yet
- Packet Tracer - Skills Integration Challenge: TopologyDocument11 pagesPacket Tracer - Skills Integration Challenge: TopologyUTM SOE-161No ratings yet
- 2.4.3.4 Lab - Configuring HSRP and GLBP - ILMDocument16 pages2.4.3.4 Lab - Configuring HSRP and GLBP - ILMرافد البركيNo ratings yet
- 4.3.3.4 Lab - Configure HSRPDocument7 pages4.3.3.4 Lab - Configure HSRPjb100% (1)
- Midterm Lab 2-Testing-Network-Connectivity-with-Ping-and-Traceroute (20240505124030)Document15 pagesMidterm Lab 2-Testing-Network-Connectivity-with-Ping-and-Traceroute (20240505124030)getalon57No ratings yet
- Lab - Configure A Branch ConnectionDocument9 pagesLab - Configure A Branch Connectionratacle57% (7)
- 2.6.1.2 Lab - Securing The Router For Administrative Access PDFDocument38 pages2.6.1.2 Lab - Securing The Router For Administrative Access PDFAAANo ratings yet
- Practica7 - Configuring OSPFv2 Advanced FeaturesDocument9 pagesPractica7 - Configuring OSPFv2 Advanced FeaturesOctavio KuriNo ratings yet
- Lab - Securing The Router For Administrative Access: IntegrantesDocument59 pagesLab - Securing The Router For Administrative Access: IntegrantesAlex Fernando GarcesNo ratings yet
- Network with Practical Labs Configuration: Step by Step configuration of Router and Switch configurationFrom EverandNetwork with Practical Labs Configuration: Step by Step configuration of Router and Switch configurationNo ratings yet
- CISCO PACKET TRACER LABS: Best practice of configuring or troubleshooting NetworkFrom EverandCISCO PACKET TRACER LABS: Best practice of configuring or troubleshooting NetworkNo ratings yet
- LEARN MPLS FROM SCRATCH PART-B: A Beginners guide to next level of networkingFrom EverandLEARN MPLS FROM SCRATCH PART-B: A Beginners guide to next level of networkingNo ratings yet
- WAN TECHNOLOGY FRAME-RELAY: An Expert's Handbook of Navigating Frame Relay NetworksFrom EverandWAN TECHNOLOGY FRAME-RELAY: An Expert's Handbook of Navigating Frame Relay NetworksNo ratings yet
- Exploring BeagleBone: Tools and Techniques for Building with Embedded LinuxFrom EverandExploring BeagleBone: Tools and Techniques for Building with Embedded LinuxRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2)
- CCST Cisco Certified Support Technician Study Guide: Networking ExamFrom EverandCCST Cisco Certified Support Technician Study Guide: Networking ExamNo ratings yet
- Pds - Manual 1 To 11Document19 pagesPds - Manual 1 To 11xxxNo ratings yet
- Modul Praktik NetworkDocument74 pagesModul Praktik Network10. Hasna Fatharani Athaqiya. TMB 13No ratings yet
- CloudGuard Auto Scaling For AWSDocument25 pagesCloudGuard Auto Scaling For AWSSharib NomaniNo ratings yet
- HCIP-Datacom-WAN Planning and Deployment V1.0 Training MaterialDocument701 pagesHCIP-Datacom-WAN Planning and Deployment V1.0 Training MaterialPius YeoNo ratings yet
- Quectel BG96 TCP (IP) AT Commands Manual V1.0Document43 pagesQuectel BG96 TCP (IP) AT Commands Manual V1.0Alex BaranciraNo ratings yet
- Assigment 2 (Hisyamuddin) CiscoDocument7 pagesAssigment 2 (Hisyamuddin) CiscohisyamuddinNo ratings yet
- Network Engineer Job Interview Technical Questions..: by pp2Document5 pagesNetwork Engineer Job Interview Technical Questions..: by pp2Vishnu PandeyNo ratings yet
- Variable Length Subnet Mask (VLSM) Subnetting: By: Fritzie S. EstradaDocument29 pagesVariable Length Subnet Mask (VLSM) Subnetting: By: Fritzie S. EstradaAntonetteNo ratings yet
- Ccna and Mcse Interview QuestionsDocument54 pagesCcna and Mcse Interview QuestionsMir Farhan Ali AbediNo ratings yet
- Lab NetworkDocument9 pagesLab NetworkPro NebyuNo ratings yet
- Deep WebDocument2 pagesDeep WebProsper AlikizangNo ratings yet
- Lab Exercises 2Document21 pagesLab Exercises 2arivsNo ratings yet
- Quizzes 11Document16 pagesQuizzes 11Petter PNo ratings yet
- SPv3 SampleDocument116 pagesSPv3 SampleNoelia BaleronNo ratings yet
- Presentation 2Document20 pagesPresentation 2Adithya narayanNo ratings yet
- Fscil NFSC Fscin PS Afct Ansin: PS Asmin: Asm Fsmin: NFSM Sigil: SGSGP 600-1 Mgtil: AfctDocument12 pagesFscil NFSC Fscin PS Afct Ansin: PS Asmin: Asm Fsmin: NFSM Sigil: SGSGP 600-1 Mgtil: AfctkmalNo ratings yet
- Networking PDFDocument10 pagesNetworking PDFHariNo ratings yet
- Internet Service Providers Association of Bangladesh (ISPAB) Primary Voter List - 2021-2022, 2022-2023, PallabiDocument3 pagesInternet Service Providers Association of Bangladesh (ISPAB) Primary Voter List - 2021-2022, 2022-2023, Pallabiakbor powernet100% (1)
- W4 Network Access - PresentationDocument57 pagesW4 Network Access - PresentationNaih イ ۦۦNo ratings yet
- Activity No. 1 RIP v.2Document4 pagesActivity No. 1 RIP v.2secretNo ratings yet
- Best Mobile Broadband Devices in Pakistan: Jazz Super 4G Devices For Seamless Internet ConnectivityDocument3 pagesBest Mobile Broadband Devices in Pakistan: Jazz Super 4G Devices For Seamless Internet Connectivityshahid rasoolNo ratings yet
- Access Control Lists John Mowry: © 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All Rights Reserved. Cisco Confidential Presentation - IDDocument34 pagesAccess Control Lists John Mowry: © 2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All Rights Reserved. Cisco Confidential Presentation - IDdeepank singhNo ratings yet
- RFC 9297Document13 pagesRFC 9297elracoNo ratings yet
- History of Internet Protocol:: What Is IP?Document25 pagesHistory of Internet Protocol:: What Is IP?Amrit Razz ShresthaNo ratings yet
- ADD A TITLE SLI-WPS OfficeDocument30 pagesADD A TITLE SLI-WPS Officenur asirahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 v8.02Document151 pagesChapter 3 v8.02Mazhar AbbasNo ratings yet
- Configuration Script CSG - ATN910C-B.HUIZUCAR - PHEONIX.01Document5 pagesConfiguration Script CSG - ATN910C-B.HUIZUCAR - PHEONIX.01AlexNo ratings yet
- CCNP Switch V7.1 Quiz - Chapter 5: Intervlan Routing and DHCPDocument8 pagesCCNP Switch V7.1 Quiz - Chapter 5: Intervlan Routing and DHCPjohnNo ratings yet