Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Heat and Mass Transfer Incropera 1-10
Uploaded by
Sung LeeCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Heat and Mass Transfer Incropera 1-10
Uploaded by
Sung LeeCopyright:
Available Formats
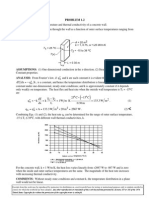
PROBLEM 1.10 KNOWN: Thickness, diameter and inner surface temperature of bottom of pan used to boil water.
Rate of heat transfer to the pan. FIND: Outer surface temperature of pan for an aluminum and a copper bottom. SCHEMATIC:
ASSUMPTIONS: (1) One-dimensional, steady-state conduction through bottom of pan. ANALYSIS: From Fouriers law, the rate of heat transfer by conduction through the bottom of the pan is
T T q = kA 1 2 L
Hence,
T1 = T2 + qL kA
where A = D 2 / 4 = ( 0.2m )2 / 4 = 0.0314 m 2 . Aluminum:
T1 = 110 C +
600W ( 0.005 m ) 240 W/m K 0.0314 m2
600W ( 0.005 m ) 390 W/m K 0.0314 m 2
)
)
= 110.40 C
< <
Copper:
T1 = 110 C +
= 110.24 C
COMMENTS: Although the temperature drop across the bottom is slightly larger for aluminum (due to its smaller thermal conductivity), it is sufficiently small to be negligible for both materials. To a good approximation, the bottom may be considered isothermal at T 110 C, which is a desirable feature of pots and pans.
Excerpts from this work may be reproduced by instructors for distribution on a not-for-profit basis for testing or instructional purposes only to students enrolled in courses for which the textbook has been adopted. Any other reproduction or translation of this work beyond that permitted by Sections 107 or 108 of the 1976 United States Copyright Act without the permission of the copyright owner is unlawful.
You might also like
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Heat and Mass Transfer Incropera 1-12Document1 pageHeat and Mass Transfer Incropera 1-12Sung Lee0% (1)
- Heat and Mass Transfer Incropera 1-11Document1 pageHeat and Mass Transfer Incropera 1-11Sung LeeNo ratings yet
- sm1 09Document1 pagesm1 09awoods12835No ratings yet
- Heat and Mass Transfer Incropera 1-7Document1 pageHeat and Mass Transfer Incropera 1-7Sung LeeNo ratings yet
- Heat and Mass Transfer Incropera 1-8Document1 pageHeat and Mass Transfer Incropera 1-8Sung LeeNo ratings yet
- Heat and Mass Transfer Incropera 1-4Document1 pageHeat and Mass Transfer Incropera 1-4Sung LeeNo ratings yet
- sm1 05Document1 pagesm1 05awoods12835No ratings yet
- sm1 06Document1 pagesm1 06awoods12835No ratings yet
- Heat Loss Through a Concrete Wall as a Function of Outside TemperatureDocument1 pageHeat Loss Through a Concrete Wall as a Function of Outside TemperatureHuma MaqsoodNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals - of - Heat - and - Mass - Transfer-Incropera-6th-solutions sm1 - 03Document1 pageFundamentals - of - Heat - and - Mass - Transfer-Incropera-6th-solutions sm1 - 03aegis414100% (1)
- Heat Transfer ch-1Document1 pageHeat Transfer ch-1Fawazil NawesNo ratings yet