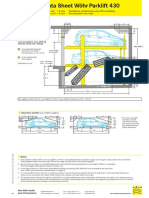
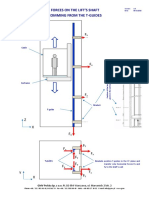
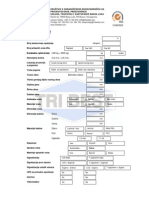
Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Catia FEM2
Uploaded by
Samira Adnan HalilovićCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Catia FEM2
Uploaded by
Samira Adnan HalilovićCopyright:
Available Formats
TOC
FEM Surface Preface Getting Started Basic Tasks Glossary Index
Dassault Systmes 1994-99. All rights reserved.
file:////Moyenne/users/cma/FMSDocCXR5/FmsEnglish/fmsug.doc/src/fmsugtoc.htm [09/26/2000 15:20:39]
Preface
Preface
CATIA - FEM Surface Version 5 Release 5 product allows you to rapidly generate a finite element model for complex surface parts. It provides users with automatic detail simplification without modifying the reference geometry. Using This Guide More Information
file:////Moyenne/users/cma/FMSDocCXR5/FmsEnglish/fmsug.doc/src/fmsugpr01.htm [09/26/2000 15:20:42]
Using This Guide
Using This Guide
This book is intended for the user who needs to quickly become familiar with CATIA - FEM Surface Version 5 Release 5. The user should be familiar with basic CATIA Version 5 concepts such as document windows, standard and view toolbars. To get the most out of this guide, we suggest you start reading and performing the step-by-step tutorial "Getting Started". This tutorial will show you how to analyse a part from scratch. The "Basic Tasks" section presents the main capabilities of the product. Each individual task is carefully defined and explained in detail. It may also be a good idea to take a look at the "Workbench Description" section, presenting the menus and toolbars. Finally, a "Glossary" has been provided to familiarise you with the terminology used in this guide.
file:////Moyenne/users/cma/FMSDocCXR5/FmsEnglish/fmsug.doc/src/fmsugpr02.htm [09/26/2000 15:20:44]
More Information
Where to Find More Information
Prior to reading this book, we recommend that you read the CATIA Version 5 Infrastructure User's Guide. CATIA - Part Design User's Guide may also prove useful. And you should view the Conventions used in this guide.
file:////Moyenne/users/cma/FMSDocCXR5/FmsEnglish/fmsug.doc/src/fmsugpr03.htm [09/26/2000 15:20:45]
Getting Started
Getting Started
The aim of the following tutorial is to give you an idea of what you can do with CATIA - FEM Surface. It provides a step-by-step scenario demonstrating how to use key capabilities. The main tasks proposed in this section are: Entering the Workbench Defining a New Mesh Setting Constraints Analysing Quality Re-meshing a Domain
Altogether, this scenario should take about 15 minutes to complete.
file:////Moyenne/users/cma/FMSDocCXR5/FmsEnglish/fmsug.doc/src/fmsuggs01.htm [09/26/2000 15:20:50]
Entering the Workbench
Entering the FEM Surface Workbench
This task demonstrates how to open a part and enter the FEM Surface Workbench. Before starting this scenario, you should be familiar with the basic commands common to all workbenches. You can use the Sample01.CATPart document from the samples directory for this task. 1. Select File -> Open, and select the desired .CATPart file. This opens a Part Design document containing the selected part. 2. Select Start -> Analysis & Simulation -> Advanced Meshing Tools. The New Analysis Case dialog box is displayed. 3. Select an Analysis Case type (Static or Frequency). Optionally, you can activate the "Keep as default starting analysis case" switch. Click OK to enter the workbench.
file:////Moyenne/users/cma/FMSDocCXR5/FmsEnglish/fmsug.doc/src/fmsuggs02.htm [09/26/2000 15:20:52]
Defining a New Mesh
Defining a New Mesh
This task demonstrates how to define a new mesh and it's global parameters on a single part. 1. Click the Surface Mesh icon 2. 3. . Select the geometry to be meshed by clicking on the part. In the Global parameters dialog box, we define the mesh parameters. In this example we: set the Mesh size to 5 mm set the Sag value to 1 mm activate the Details simplification set the Minimum size to 2 mm We leave the global method to quadrangle.
4.
Click the OK button. A new Smart Surfacic Mesh entity is created in the tree.
file:////Moyenne/users/cma/FMSDocCXR5/FmsEnglish/fmsug.doc/src/fmsuggs03.htm [09/26/2000 15:20:53]
Setting Constraints
Setting Constraints
This task demonstrates how to define constraints on nodes distributions. 1. Click the Add/remove constraints icon
2.
Select the edge to be constrained.
3.
Click the Ok button in the Add/Remove dialog box to end the constraints definition. At this stage, constraints are kept in the mesh definition.
4.
Click the Nodes distributions icon .
file:////Moyenne/users/cma/FMSDocCXR5/FmsEnglish/fmsug.doc/src/fmsuggs04.htm (1 of 3) [09/26/2000 15:20:55]
Setting Constraints
5.
Select the edge on which a new distribution will be set.
6.
In the Edit node distribution dialog box we define the parameters of the new distribution. Select the uniform distribution type and set the number of nodes to 10. Click the Ok button. The nodes distribution is created on the selected edge.
file:////Moyenne/users/cma/FMSDocCXR5/FmsEnglish/fmsug.doc/src/fmsuggs04.htm (2 of 3) [09/26/2000 15:20:55]
Setting Constraints
7.
In the Node distributions dialog box, click the Ok button to end the distributions definition.
At this stage, distributions are kept in the mesh definition.
file:////Moyenne/users/cma/FMSDocCXR5/FmsEnglish/fmsug.doc/src/fmsuggs04.htm (3 of 3) [09/26/2000 15:20:55]
Analysing Quality
Meshing and Analysing Quality
This task demonstrates how to generate the mesh and use some basic quality analysis functionalities. 1. Click the Mesh icon . The mesh is generated on the part and a little summary is provided in the Mesh update dialog box. The visualization is switched to quality mode so the user can see the quality of the generated mesh. 2. Click the Quality Analysis icon . The Quality Analysis dialog box lists the available quality specifications for visualizing the mesh. By selecting particular specifications, the user can decide how he wants to view the mesh. It also provides a set of functionalities for deeper analysis. Quality Analysis functionalities are available at all steps of the meshing process. See Quality Analysis for more detailed information.
file:////Moyenne/users/cma/FMSDocCXR5/FmsEnglish/fmsug.doc/src/fmsuggs05.htm (1 of 3) [09/26/2000 15:21:14]
Analysing Quality
3.
Click the Report icon
The Quality Report dialog box presents statistics for the selected quality specifications. Select the Mesh tab page to view mesh composition statistics.
4. Click the Single Analysis icon . You can select an element of the mesh and obtain a detailed view of it's quality in the Analyze Single pane. This allows you to check if any of your specifications have not been implemented.
file:////Moyenne/users/cma/FMSDocCXR5/FmsEnglish/fmsug.doc/src/fmsuggs05.htm (2 of 3) [09/26/2000 15:21:14]
Analysing Quality
5.
Click OK in the Quality Analysis dialog box to exit the Quality Analysis environment.
file:////Moyenne/users/cma/FMSDocCXR5/FmsEnglish/fmsug.doc/src/fmsuggs05.htm (3 of 3) [09/26/2000 15:21:14]
Re-meshing a Domain
Re-meshing a Domain
This task demonstrates how to re-mesh a domain with local specifications. 1. Click the re-mesh icon
2.
Select the domain to be re-meshed, as shown in the picture. We will try to remove the triangles by locally altering the mesh method.
3.
Set the parameters for the selected domain. To do this, you specify the: mesh method local size impact to neighbour domains. For this example, we will specify a mapped mesh and a size of 5 mm. And we specify that these domain specifications can affect neighbour domains. See Local Re-meshing for more detailed information.
file:////Moyenne/users/cma/FMSDocCXR5/FmsEnglish/fmsug.doc/src/fmsuggs06.htm (1 of 2) [09/26/2000 15:21:21]
Re-meshing a Domain
4.
Click OK to re-mesh the domain. The mesh is updated. The domain is now meshed with quadrangles only.
5.
To exit the meshing environment, click the exit icon
This completes the FEM Surface tutorial. Now, let's take a closer look at the application.
file:////Moyenne/users/cma/FMSDocCXR5/FmsEnglish/fmsug.doc/src/fmsuggs06.htm (2 of 2) [09/26/2000 15:21:21]
Basic Tasks
Basic Tasks
This section describes the basic tasks that allow you to complete the mesh of a part using CATIA - FEM Surface. These tasks include: Cleaning Geometry
file:////Moyenne/users/cma/FMSDocCXR5/FmsEnglish/fmsug.doc/src/fmsugbt0000.htm [09/26/2000 15:21:30]
Cleaning Geometry
Cleaning Geometry
Geometrical parts often present small holes or defects that should be ignored during the is intended to let the user specify which of these analysis. The clean geometry command details will be ignored by the mesher. It deals with three types of geometric problems:
Holes in the geometry.
Button hole - like gaps.
file:////Moyenne/users/cma/FMSDocCXR5/FmsEnglish/fmsug.doc/src/fmsugbt0200.htm [09/26/2000 15:21:32]
Removing Holes
Removing Holes
This first task shows you how to ignore holes in the geometry. You can use the Sample03.CATPart document from the samples directory for this task. 1. 2. Create a new Mesh on the part. Click the Remove Holes icon The diameter parameter is used to ignore all holes that are smaller than the given value.
3.
Set the diameter value to 10 mm and click Apply. See how the ignored holes are turned blue.
file:////Moyenne/users/cma/FMSDocCXR5/FmsEnglish/fmsug.doc/src/fmsugbt0201.htm (1 of 2) [09/26/2000 15:21:34]
Removing Holes
4.
Click a green hole. It is turned blue and will then be ignored by the mesher.
5.
Click a blue hole. It is reactivated and will be taken into account by the mesher.
file:////Moyenne/users/cma/FMSDocCXR5/FmsEnglish/fmsug.doc/src/fmsugbt0201.htm (2 of 2) [09/26/2000 15:21:34]
Removing Button Hole Gaps
Removing Button Hole Gaps
This task demonstrates how to configure the mesher to ignore button hole gaps. You can use the Sample02.CATPart document from the samples directory for this task. 1. Create a new Mesh on the part. Button hole gaps are automatically detected by the program and are displayed in magenta on the part.
2.
Click the Remove Holes . icon You can configure the mesher to ignore button hole gaps by simply clicking on the magenta contours. Now, they will be ignored by the mesher. In fact, the facing edges of the gap will be merged and the
3.
file:////Moyenne/users/cma/FMSDocCXR5/FmsEnglish/fmsug.doc/src/fmsugbt0202.htm (1 of 2) [09/26/2000 15:21:38]
Removing Button Hole Gaps
result will be considered as a standard edge.
file:////Moyenne/users/cma/FMSDocCXR5/FmsEnglish/fmsug.doc/src/fmsugbt0202.htm (2 of 2) [09/26/2000 15:21:38]
Glossary
Glossary C
crack A geometry defect that occurs when two adjacent faces, near the free edges, are not topologically linked.
G
global size The target size for element edges.
M
minimum size Minimum size of an edge of an element. When the detail elimination option is active, the mesher does not generate elements with edges shorter than the minimum size.
P
part A 3D entity obtained by combining different features in the Part Design workbench. Please see CATIA - Part Design User's Guide for further information.
file:////Moyenne/users/cma/FMSDocCXR5/FmsEnglish/fmsug.doc/src/fmsuggl.htm [09/26/2000 15:21:46]
Index
Index C
cleaning geometry
R
removing holes button hole gaps
file:////Moyenne/users/cma/FMSDocCXR5/FmsEnglish/fmsug.doc/src/fmsugix.htm [09/26/2000 15:21:50]
You might also like
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (589)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5796)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1091)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- MAN Diesel: Multi Purpose ControllerDocument13 pagesMAN Diesel: Multi Purpose ControllerŞansal Dikmener100% (2)
- CCNA Security Chapter 2 PowerpointDocument14 pagesCCNA Security Chapter 2 PowerpointEric NapholzNo ratings yet
- Oltp Vs Datawarehouse DSSDocument2 pagesOltp Vs Datawarehouse DSSriteshkumar2kNo ratings yet
- Cold Bending DIN 6935 (Eng)Document3 pagesCold Bending DIN 6935 (Eng)Samira Adnan HalilovićNo ratings yet
- Tower 7 Uputstvo SRBDocument1,041 pagesTower 7 Uputstvo SRBcipsicc100% (4)
- Electrical: Installation CalculationsDocument23 pagesElectrical: Installation CalculationsSamira Adnan HalilovićNo ratings yet
- Iphone 3G SchematicDocument31 pagesIphone 3G Schematicidedn1No ratings yet
- Instruction ManualDocument88 pagesInstruction ManualSamira Adnan Halilović100% (1)
- SavijanjeDocument76 pagesSavijanjeSamira Adnan HalilovićNo ratings yet
- Industry in Focus 2010: Lift and Escalator Industry AssociationDocument12 pagesIndustry in Focus 2010: Lift and Escalator Industry AssociationSamira Adnan HalilovićNo ratings yet
- Single Unit 2 Cars Suitable For Condominium and Office Buildings. Double Unit 4 Cars For Permanent Use Only!Document6 pagesSingle Unit 2 Cars Suitable For Condominium and Office Buildings. Double Unit 4 Cars For Permanent Use Only!Samira Adnan HalilovićNo ratings yet
- Forces From T-GuidesDocument1 pageForces From T-GuidesSamira Adnan HalilovićNo ratings yet
- RAL KartaDocument6 pagesRAL KartaSamira Adnan HalilovićNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Cylinders Series Ȋ.1: Ȋ.1 Type Dimensions (MM)Document1 pageHydraulic Cylinders Series Ȋ.1: Ȋ.1 Type Dimensions (MM)Samira Adnan HalilovićNo ratings yet
- Vxf2aidrDocument132 pagesVxf2aidrSamira Adnan HalilovićNo ratings yet
- Upitnik Za LiftDocument1 pageUpitnik Za LiftSamira Adnan HalilovićNo ratings yet
- GET-20087 - RPV311 Out of ServiceDocument2 pagesGET-20087 - RPV311 Out of ServiceJuvvyNo ratings yet
- TAC Time Aug 2016 v4Document38 pagesTAC Time Aug 2016 v4nunomgtorresNo ratings yet
- Query Processing and Optimization in Oracle RDB: Gennady Antoshenkov, Mohamed ZiauddinDocument9 pagesQuery Processing and Optimization in Oracle RDB: Gennady Antoshenkov, Mohamed ZiauddinEbaybookNo ratings yet
- The Glass House - A Photoshop Tutorial SketchUp 3D Rendering Tutorials by SketchUpArtistsDocument16 pagesThe Glass House - A Photoshop Tutorial SketchUp 3D Rendering Tutorials by SketchUpArtistsAbel FleitasNo ratings yet
- Angular 4 IntoductionDocument4 pagesAngular 4 IntoductionVillageSchool FoundationNo ratings yet
- Tecnos PDFDocument12 pagesTecnos PDFplovbaNo ratings yet
- HLR New in This ReleaseDocument11 pagesHLR New in This Releasenaloufijalal_1597142No ratings yet
- 2017 Tech Fast500 Apac Ranking ReportDocument13 pages2017 Tech Fast500 Apac Ranking ReportLisa GridnevaNo ratings yet
- Create App With Your Own SkillsDocument17 pagesCreate App With Your Own Skillsnaresh kolipakaNo ratings yet
- Stability Study With SAP Quality ManagementDocument48 pagesStability Study With SAP Quality ManagementRahulNo ratings yet
- MergedDocument393 pagesMergedRAVINo ratings yet
- HACKER AsmDocument21 pagesHACKER Asmkgrhoads100% (1)
- Project Report On Rich Internet Application For Automatic College Timetable Generation (24th March 2008)Document112 pagesProject Report On Rich Internet Application For Automatic College Timetable Generation (24th March 2008)Anitha Ganesh100% (1)
- Chapter 1 - Structures and PointersDocument2 pagesChapter 1 - Structures and PointershelolNo ratings yet
- Database Design Document OF Online Admission System: To Be Submitted in The Partial Fulfilment of B.E DegreeDocument8 pagesDatabase Design Document OF Online Admission System: To Be Submitted in The Partial Fulfilment of B.E DegreeAkaShGrOverNo ratings yet
- How To Bypass and Reset The ALOM Password For Sun V-Series and Netra Series - SAIFUL AZIZ's BLOGDocument6 pagesHow To Bypass and Reset The ALOM Password For Sun V-Series and Netra Series - SAIFUL AZIZ's BLOGzezycv6919No ratings yet
- React Developer ResumeDocument9 pagesReact Developer Resumesitoj1b1myv3100% (1)
- 3Document3 pages3jeancel carano-oNo ratings yet
- Actcut ENGDocument4 pagesActcut ENGSameer A AthaleyNo ratings yet
- How To Design Indexes Really - 0-2 PDFDocument72 pagesHow To Design Indexes Really - 0-2 PDFAgus BudionoNo ratings yet
- C and DS ContentDocument380 pagesC and DS ContentRavindra Reddy50% (2)
- GW90 ManualDocument616 pagesGW90 ManualEmil VivancoNo ratings yet
- PS360 BestPracticesforSpeechDocument10 pagesPS360 BestPracticesforSpeechRamskiNo ratings yet
- Chapter2 DarchivingDocument10 pagesChapter2 DarchivingDan MonrealNo ratings yet
- Dbms-Lab Assignment - 1: Name - VIKAS SINGH Roll No - 4257Document3 pagesDbms-Lab Assignment - 1: Name - VIKAS SINGH Roll No - 4257Vikas SinghNo ratings yet
- Oracle: Global Human Resources Cloud Implementing Global PayrollDocument296 pagesOracle: Global Human Resources Cloud Implementing Global PayrollShaik Riyaz PeerNo ratings yet