Professional Documents
Culture Documents
4.5 Enzyme
Uploaded by
limsi74Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
4.5 Enzyme
Uploaded by
limsi74Copyright:
Available Formats
4.5 Enzymes 1. Enzymes are that increase the rate of biochemical reaction. 2.
Enzymes enable biochemical reactions to take place in the cells. Example of biochemical reactions are of food, synthesis of substances, of muscles and respiration. 3. General Characteristics of Enzymes (a) Enzymes are produced by living cells. (b) The action of enzymes is highly (c) Enzymes the end of the reaction. (d) Enzymes are needed in . Each enzyme can only act on one substrate. or destroyed at
biochemical reactions but are not
amount to produce a large chemical change.
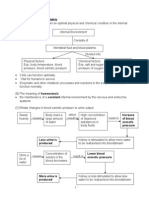
(e) Chemical reactions catalysed by enzymes are reactions. The enzymes can affect the reaction in both directions. amylase Starch + water Maltose (f) Enzymes are to temperature. At high temperature,(400C 600C), enzymes are . The activity of enzyme . At low temperature, enzymes are less . The temperature for most enzymes is 350C 400C. (g) Enzymes are sensitive to . Each enzyme has its own optimum pH. Most enzymes are active at . Some enzymes require condition (pH less than 7) or condition (pH more than 7). 4. Naming of Enzymes (a) The name of enzymes is formed by adding to the main part of the name of substrate. (b) Substrate Enzyme Maltose Sucrose lactose Protein lipids Examples of enzymes that are not named this way are pepsin, erepsin, and 5. The site for enzyme synthesis is located at the 6. cell. 7. The production of extracellular enzymes involves specific organelles in the cell. (a) Protein is produced in the . (b) The protein enters the lumen of the and is transported to the vesicles at the end of the endoplasmic reticulum. (c) These transport vesicles carry the protein to the . (d) Golgi apparatus modifies the protein into . (e) The enzyme is packed into of the Golgi apparatus and transported to the in the protoplasm of cells.
enzymes are enzymes produced in the cell and functions within the cells. enzymes are enzymes secreted out of the cell and functions outside the
(f) The secreting vesicle fuses with the plasma membrane to secrete the enzyme out of the cell.
You might also like
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (589)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (842)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5806)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1091)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Gozobiochem - Form 5 Biology Topic 1Document16 pagesGozobiochem - Form 5 Biology Topic 1Eunice TangNo ratings yet
- 3.4 HomeostasisDocument17 pages3.4 Homeostasislimsi74No ratings yet
- Pecutan Akhir Biology SPM: 15 November 2013Document43 pagesPecutan Akhir Biology SPM: 15 November 2013limsi74No ratings yet
- Topical Test Chapter 9 EssayDocument4 pagesTopical Test Chapter 9 Essaylimsi74No ratings yet
- Topical Test Chapter 6 Essay AnswerDocument5 pagesTopical Test Chapter 6 Essay Answerlimsi74No ratings yet