Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Zero Cross Detection
Uploaded by
Naser A SosiyCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Zero Cross Detection
Uploaded by
Naser A SosiyCopyright:
Available Formats
- -:
Zero Cross Detection
-:
-1 -2
2102/2102
Zero Cross Detection
it is clear that the frequency of the FM modulated signal can be found by means of the wavelength. The wavelength of the signal can be determined from the zero-crossing of the FM signal. A block diagram of ZC can be seen in figure 1. The principle of the ZC is to generate a pulse whenever a zero-crossing occurs. The generated pulses are then passed though a low pass filter and finally the signal is DC-blocked.
(a)
(b) Figure 1 : (a) Block diagram Zero-crossing Detection Demodulation Algorithm.(b) Basic circuit Zero Crossing Detector
Mathematic description
The pulse generator produces a pulse with fixed amplitude and a fixed duration each time a positive (or negative) going zero-crossing occurs. In most systems, the carrier frequency is much higher than the frequency of the message signal, thus negating the need for detecting both zero-crossings. The output of the pulse generator is a pulse train . If the pulse train is viewed over a short period seconds, where , the numbers of pulses in T can be calculated by (1)
where:
is the maximum frequency deviation. is the base band signal, with a maximum amplitude of 1.
[Hz]
Continuously integrating over frequency of the baseband signal, yields
second, where
is the maximum
(2)
(3)
Adding a DC-block yields (4)
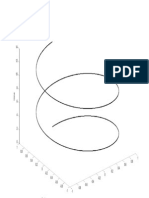
Figure 2 : zero Crossproces illustrates the zero-cross demodulation process.
You might also like
- Edit 888Document2 pagesEdit 888Naser A SosiyNo ratings yet
- AC55VDocument1 pageAC55VNaser A SosiyNo ratings yet
- Electrical PowerDocument20 pagesElectrical PowerNaser A SosiyNo ratings yet
- Types of MultiplexingDocument1 pageTypes of MultiplexingNaser A SosiyNo ratings yet
- 1 Power Spectral Density (PSD) of Communication Signals: S (T) S T) S T) V (T) eDocument4 pages1 Power Spectral Density (PSD) of Communication Signals: S (T) S T) S T) V (T) eNaser A SosiyNo ratings yet
- 1Document1 page1Naser A SosiyNo ratings yet
- 8085 MicroprocessorDocument23 pages8085 Microprocessorauromaaroot196% (55)
- SaturdayDocument7 pagesSaturdayNaser A SosiyNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)