Professional Documents
Culture Documents
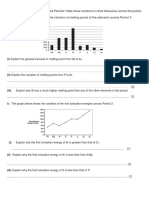
5.3 Transition Metals HW Part I
5.3 Transition Metals HW Part I
Uploaded by
su966Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
5.3 Transition Metals HW Part I
5.3 Transition Metals HW Part I
Uploaded by
su966Copyright:
Available Formats
A2 LEVEL CHEMISTRY
5.3 TRANSITION METALS
PART I
ASSESSED HOMEWORK
Answer all questions
Max 114 marks
Name
..
Mark
../114
Paddington Academy
....%
Grade
1.
Mercury forms two ions, Hg22+ and Hg2+. The table shows the electronic configuration
of mercury in these ions.
ion
electronic configuration
Hg22+
[Xe]4f145d106s1
Hg2+
[Xe]4f145d10
Use the electronic configurations to explain why mercury is not a transition element.
.................................................................................................................................
.................................................................................................................................
[Total 1 mark]
2.
Iron forms several complex ions in which the oxidation state of iron is +3.
(i)
Complete the electronic configuration for an iron(Ill) ion, Fe3+.
1s22s22p6 .......................................................................................................
[1]
(ii)
Explain, using electronic configuration, why iron is a transition element.
........................................................................................................................
........................................................................................................................
[1]
[Total 2 marks]
3.
A moss killer contains iron(II) sulphate.
Some of the iron(II) sulphate gets oxidised to form iron(III) sulphate. During the
oxidation iron(II) ions, Fe2+, react with oxygen, O2, and hydrogen ions to make water
and iron(III) ions, Fe3+.
(a)
Complete the electronic configuration for Fe3+ and use it to explain why iron is a
transition element.
Fe3+:1s22s22p6 ................................................................................................
........................................................................................................................
........................................................................................................................
[2]
Paddington Academy
(b)
State two typical properties of compounds of a transition element.
1 .....................................................................................................................
2 .....................................................................................................................
[2]
(c)
Describe how aqueous sodium hydroxide can be used to distinguish between
aqueous iron(II) sulphate and aqueous iron(III) sulphate.
........................................................................................................................
........................................................................................................................
........................................................................................................................
[2]
(d)
Construct the equation for the oxidation of acidified iron(II) ions by oxygen.
........................................................................................................................
[2]
[Total 8 marks]
4.
Iron forms several complex ions in which the oxidation state of iron is +3.
Excess aqueous sodium hydroxide is added to an aqueous solution containing Fe3+
(aq).
(i)
Describe what you would see happen.
........................................................................................................................
[1]
(ii)
Write an ionic equation, including state symbols, for the reaction that takes place.
........................................................................................................................
[2]
[Total 3 marks]
5.
The compound FeSO4.7H2O can be used to kill moss in grass. Iron(II) ions in a
solution of FeSO4.7H2O are slowly oxidised to form iron(III) ions.
Describe a test to show the presence of iron(III) ions in a solution of FeSO4.7H2O.
.................................................................................................................................
.................................................................................................................................
[Total 1 mark]
Paddington Academy
6.
Iron forms several complex ions in which the oxidation state of iron is +3.
One of these complex ions is [Fe(CN)6]3. This is called the hexacyanoferrate(III) ion.
In the hexacyanoferrate(III) ion the cyanide ions, CN, act as ligands.
(i)
Suggest why a cyanide ion can act as a ligand.
........................................................................................................................
........................................................................................................................
[1]
(ii)
Draw the expected shape for the complex ion [Fe(CN)6]3. Include bond angles
and the name of the shape.
[2]
[Total 3 marks]
7.
Cobalt readily forms complex ions in which the cobalt has an oxidation state of +2.
One complex ion of cobalt is the hexaaquocobalt(II) ion [Co(H2O)6]2+.
(i)
What is the co-ordination number of Co2+ in this complex ion?
........................................................................................................................
[1]
(ii)
Water is acting as a ligand. Explain the meaning of the term ligand.
........................................................................................................................
........................................................................................................................
........................................................................................................................
[2]
[Total 3 marks]
Paddington Academy
8.
Ammonia is a simple molecule. The HNH bond angle in an isolated ammonia
molecule is 107.
The diagram shows part of the [Cu(NH3)4(H2O)2]2+ ion and the HNH bond angle in
the ammonia ligand.
H
Cu
2+
N 1 0 9 .5
H
Explain why the HNH bond angle in the ammonia ligand is 109.5 rather than
107.
.................................................................................................................................
.................................................................................................................................
.................................................................................................................................
.................................................................................................................................
[Total 3 marks]
9.
Water is a simple molecule. The HOH bond angle in an isolated water molecule is
104.5.
The diagram shows part of the [Cu(H2O)6]2+ ion and the HOH bond angle in the
water ligand.
H
C u 2+
107
H
Explain why the HOH bond angle in the water ligand is 107 rather than 104.5.
.................................................................................................................................
.................................................................................................................................
.................................................................................................................................
.................................................................................................................................
[Total 3 marks]
Paddington Academy
10.
Artists between the 13th and the 19th Centuries used a green pigment called verdigris.
The artists made the pigment by hanging copper foil over boiling vinegar.
A sample of verdigris has the formula [(CH3COO)2Cu]2.Cu(OH)2.xH2O.
Analysis of the sample shows that it contains 16.3% water by mass.
Calculate the value of x in the formula.
answer ...................................................
[Total 3 marks]
Paddington Academy
11.
In this question, one mark is available for the quality of use and organisation of
scientific terms.
Copper and iron are typical transition elements. One of the characteristic properties of
a transition element is that it can form complex ions.
Explain in terms of electronic configuration why copper is a transition element.
Give an example of a complex ion that contains copper. Draw the three
dimensional shape of the ion and describe the bonding within this complex ion.
Transition elements show typical metallic properties. Describe three other typical
properties of transition elements. Illustrate each property using copper or iron or
their compounds.
[11]
Quality of Written Communication [1]
[Total 12 marks]
Paddington Academy
12.
Dilute aqueous copper(II) sulphate contains [Cu(H2O)6]2+ ions.
(a)
Concentrated hydrochloric acid is added drop by drop to a small volume of dilute
aqueous copper(II) sulphate. The equation for the reaction taking place is as
follows.
[CuCl ]2(aq) + 6H O(l)
[Cu(H2O)6]2+(aq) + 4Cl(aq)
4
2
(i)
Describe the observations that would be made during the addition of the
concentrated hydrochloric acid.
...............................................................................................................
[1]
(ii)
Describe the bonding within the complex ion, [CuCl4]2.
...............................................................................................................
...............................................................................................................
...............................................................................................................
[2]
(b)
Concentrated aqueous ammonia is added drop by drop to aqueous copper(II)
sulphate until present in excess. Two reactions take place, one after the other, to
produce the complex ion [Cu(NH3)4(H2O)2]2+(aq).
Describe the observations that would be made during the addition of
concentrated aqueous ammonia.
........................................................................................................................
........................................................................................................................
........................................................................................................................
[2]
[Total 5 marks]
13.
The Co2+ ion can form complexes with two different co-ordination numbers.
(a)
What is meant by the co-ordination number of a complex ion?
........................................................................................................................
........................................................................................................................
[1]
Paddington Academy
(b)
The following equilibrium is readily established.
[Co(H2O)6]2+ + 4Cl
(i)
[CoCl4]2 + 6H2O
In the boxes below, draw the shape of each complex ion.
[Co(H2O)6]2+
[CoCl4]2
[2]
(ii)
What colour change would you expect to see when an excess of Cl is
added to [Co(H2O)6]2+?
from ............................................... to ..................................................
[2]
(iii)
Describe how you would move the position of this equilibrium to the left.
...............................................................................................................
[1]
[Total 6 marks]
14.
The ethanedioate ion, C2O42, can act as a bidentate ligand when it forms complex
ions with a transition metal ion. The structure of the ethanedioate ion is shown below.
O
O
C
(a)
C
O
What do you understand by the term bidentate ligand?
........................................................................................................................
........................................................................................................................
[2]
Paddington Academy
(b)
The ethanedioate ion readily forms an octahedral complex ion with Cr3+.
Show the structure and charge of this complex ion.
[3]
[Total 5 marks]
15.
The edta4 ion forms complex ions with Ni2+(aq).
(a)
Complete the electronic configuration of the Ni2+ ion.
Is22s22p6 ........................................................................................................
[1]
(b)
The edta4 ion has the following structure.
O
O
O
O
C
(i)
C H
H 2C
N
C
C H
C H
C H
N
H 2C
O
O
C
O
Put a ring around two different types of atom in the edta4 ion that are
capable of forming a dative covalent bond with the Ni2+ ion.
[2]
(ii)
What feature of these atoms allows them to form a bond with Ni2+?
...............................................................................................................
[1]
[Total 4 marks]
Paddington Academy
10
16.
Stereoisomerism is very common in transition metal complexes. Some complexes have
found an important use in the treatment of cancer.
(i)
Name a transition metal complex used in the treatment of cancer.
........................................................................................................................
[1]
(ii)
Describe how this complex helps in the treatment of cancer.
........................................................................................................................
........................................................................................................................
........................................................................................................................
[2]
[Total 3 marks]
17.
(a)
Co2+ forms the complex [Co(NH3)4Cl2]. This complex exists as two
stereoisomers.
(i)
Draw diagrams to show the two isomeric forms of this complex.
[2]
(ii)
What type of stereoisomerism is shown by this complex?
...............................................................................................................
[1]
(b)
Cobalt also forms a complex with the formula [Co(H2NCH2CH2NH2)2Cl2]. This
complex shows the same kind of isomerism as [Co(NH3)4Cl2] but it also shows a
different type of stereoisomerism.
Draw diagrams to show the two isomers of this different type of stereoisomerism.
[2]
[Total 5 marks]
Paddington Academy
11
18.
(a)
A common ligand which combines with a number of transition metal ions is
ethane-1,2-diamine, H2NCH2CH2NH2. This is a bidentate ligand.
Explain the meaning of the term bidentate.
........................................................................................................................
........................................................................................................................
[1]
(b)
The complex [CoCl2(H2NCH2CH2NH2)2] is a neutral molecule. It shows two types
of stereoisomerism. Use this molecule to explain what you understand by the
term stereoisomerism. Your answer should include diagrams to show clearly the
structures of the different isomers in both types of stereoisomerism.
........................................................................................................................
........................................................................................................................
........................................................................................................................
........................................................................................................................
........................................................................................................................
........................................................................................................................
........................................................................................................................
........................................................................................................................
........................................................................................................................
[7]
[Total 8 marks]
Paddington Academy
12
19.
Platinum forms complexes with a co-ordination number of 4.
(a)
(i)
Explain the term co-ordination number.
...............................................................................................................
...............................................................................................................
[1]
(ii)
State the shape of these platinum complexes.
...............................................................................................................
[1]
(b)
The tetrachloroplatinate(II) ion readily undergoes the following reaction.
[PtCl4]x + 2NH3
(i)
[Pt(NH3)2Cl2]y + 2Cl
What type of reaction is this?
...............................................................................................................
[1]
(ii)
Suggest values for x and y in the equation.
x =
y =
[2]
Paddington Academy
13
(c)
The complex [Pt(NH3)2Cl2]y exists in two isomeric forms.
(i)
Draw diagrams to show the structure of these isomers.
[2]
(ii)
What type of isomerism is this?
...............................................................................................................
[1]
(iii)
One of the isomers of [Pt(NH3)2Cl2]y is an important drug used in the
treatment of cancer.
How does this drug help in the treatment of cancer?
...............................................................................................................
...............................................................................................................
...............................................................................................................
...............................................................................................................
[2]
[Total 10 marks]
Paddington Academy
14
20.
Ruthenium (Ru) is a metal in the second transition series. It forms complex ions with
the following formulae.
(a)
= [Ru(H2O)6]3+
= [Ru(H2O)5Cl]2+
= [Ru(H2O)4Cl2]+
(i)
What is the oxidation number of ruthenium in B?
oxidation number of ruthenium = .........................................................
[1]
(ii)
One of the complex ions, A, B or C, shows stereoisomerism.
Draw diagrams to show the structures of the two isomers.
[2]
(iii)
Name this type of stereoisomerism.
...............................................................................................................
[1]
(b)
The complex ion [Ru(H2O)6]3+ can be converted into [Ru(H2O)5Cl]2+.
(i)
Suggest a suitable reagent for this conversion.
...............................................................................................................
[1]
(ii)
What type of reaction is this?
...............................................................................................................
[1]
[Total 6 marks]
Paddington Academy
15
21.
This question looks at the chemistry of transition elements.
(a)
(i)
Explain what is meant by the terms transition element, complex ion and
ligand,
(ii)
Discuss, with examples, equations and observations, the typical reactions
of transition elements.
In your answer you should make clear how any observations provide
evidence for the type of reaction discussed.
[11]
Paddington Academy
16
(b)
Describe, using suitable examples and diagrams, the different shapes and
stereoisomerism shown by complex ions.
In your answer you should make clear how your diagrams illustrate the type of
stereoisomerism involved.
[9]
[Total 20 marks]
Paddington Academy
17
You might also like
- Topical Questions For ElectrolysisDocument6 pagesTopical Questions For Electrolysisokguserfucker idontgiveashitNo ratings yet
- Transition III QuestionsDocument12 pagesTransition III QuestionsRahul SinghNo ratings yet
- I6 Reactions of Ions in Aqueous SolutionDocument16 pagesI6 Reactions of Ions in Aqueous Solution/ “Nu” /No ratings yet
- Topic 3 BondingDocument23 pagesTopic 3 Bondingnaturecore9No ratings yet
- 5070 Mock 1 P2 - 2024Document10 pages5070 Mock 1 P2 - 2024ShamsaNo ratings yet
- Balanced Equations & Associated Calc's 10 QPDocument8 pagesBalanced Equations & Associated Calc's 10 QPjade.davis0019No ratings yet
- t2 Chem Revision Ex 22 - Answer SchemeDocument20 pagest2 Chem Revision Ex 22 - Answer SchemeNicholas Ow50% (2)
- Shingai Study Centre A-Level Chemistry Test: 1) Which Property Decreases Down Group 7 in The Periodic Table?Document9 pagesShingai Study Centre A-Level Chemistry Test: 1) Which Property Decreases Down Group 7 in The Periodic Table?TubocurareNo ratings yet
- Unit QuestionsDocument155 pagesUnit QuestionsSanya KhanNo ratings yet
- General Properties of Transition Metals 1 QPDocument10 pagesGeneral Properties of Transition Metals 1 QPaanammanaNo ratings yet
- 4.1 Reactivity of Metals 3 QPDocument16 pages4.1 Reactivity of Metals 3 QPDumpsterFireGamingNo ratings yet
- Bonding Qs CombinedDocument29 pagesBonding Qs CombinedJainam MehtaNo ratings yet
- Igcse Electrochemistry Review PDFDocument7 pagesIgcse Electrochemistry Review PDFbilly ogadaNo ratings yet
- BondingDocument14 pagesBondingMuizzudin AzaliNo ratings yet
- Bonding - Structuce 3 QPDocument14 pagesBonding - Structuce 3 QPtertianerima101No ratings yet
- Metal p4 Ws 4Document10 pagesMetal p4 Ws 4NonnoonoNo ratings yet
- Physical ChemDocument160 pagesPhysical ChemAbdul AahadNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table 2 QPDocument12 pagesPeriodic Table 2 QPChibale Mchere BandaNo ratings yet
- t2 Chem Revision Ex 22Document19 pagest2 Chem Revision Ex 22Nicholas OwNo ratings yet
- Mixed Topic Revision 1 DiffusionDocument23 pagesMixed Topic Revision 1 DiffusionYaakkwNo ratings yet
- Exam Style QuestionsDocument4 pagesExam Style QuestionsGulnurNo ratings yet
- RedoxDocument19 pagesRedoxHamna BilalNo ratings yet
- Reversible ReactionDocument17 pagesReversible ReactionNavyaa SinghNo ratings yet
- Cons. of Mass, Chemical Measurements - Eqns 2 QPDocument18 pagesCons. of Mass, Chemical Measurements - Eqns 2 QPHusain KamaliNo ratings yet
- My TestDocument10 pagesMy TestMarin PesicNo ratings yet
- Electricity & Chemistry 2 QPDocument10 pagesElectricity & Chemistry 2 QPValerine VictoriaNo ratings yet
- TransitionDocument39 pagesTransitioniratuzipacifique2No ratings yet
- Practice PDFDocument20 pagesPractice PDFMartin LayneNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table QPDocument8 pagesPeriodic Table QPUnknown SAJNo ratings yet
- Edexcel Chemistry Topic 3Document11 pagesEdexcel Chemistry Topic 3locopocpNo ratings yet
- Structure and BondingDocument34 pagesStructure and BondingmalakNo ratings yet
- 5.3.1 Transition MetalsDocument37 pages5.3.1 Transition MetalsMalak AlqaidoomNo ratings yet
- Bond Polarity 1 QP AS ChemistryDocument8 pagesBond Polarity 1 QP AS ChemistryBabueNo ratings yet
- 1.4 TestDocument5 pages1.4 TestdfghjNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 Term 1 Chemistry RevisionDocument7 pagesGrade 9 Term 1 Chemistry Revisionsiddloves.snowNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structuure and BondingDocument6 pagesAtomic Structuure and BondingHarshika Prasanganie Abeydeera100% (1)
- Nitrogen 240128 145942Document11 pagesNitrogen 240128 145942omarkbkb2007suiNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Assessment International Education Practice QuestionsDocument11 pagesCambridge Assessment International Education Practice QuestionslNo ratings yet
- Electrochemical Cells 1 QPDocument11 pagesElectrochemical Cells 1 QPOrangesPlzNo ratings yet
- P7 Oxidation Reduction and RedoxDocument42 pagesP7 Oxidation Reduction and Redox/ “Nu” /No ratings yet
- Tutorial 2 Electrochem A2Document9 pagesTutorial 2 Electrochem A2Nur Dinah Alesha Mohd Ali ZarNo ratings yet
- C2 Representing Reactions HigherDocument11 pagesC2 Representing Reactions HigherdownendscienceNo ratings yet
- As NNNNDocument10 pagesAs NNNN4language4allNo ratings yet
- Reaction Rates - Equilibrium 2 QPDocument18 pagesReaction Rates - Equilibrium 2 QPKeerthy verNo ratings yet
- Electrolysis PPDocument12 pagesElectrolysis PPshamsur.rehman.khatriNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table, Group 2 and The Halogens 2 QPDocument14 pagesPeriodic Table, Group 2 and The Halogens 2 QPmalakNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: CHEMISTRY 0620/42Document12 pagesCambridge IGCSE: CHEMISTRY 0620/42taimurmalik5562100% (1)
- Worksheet of Amount of SubstanceDocument33 pagesWorksheet of Amount of SubstanceTai PanNo ratings yet
- Electricity & Chemistry 1 QPDocument11 pagesElectricity & Chemistry 1 QPValerine VictoriaNo ratings yet
- C2 Useful Products IntermediateDocument13 pagesC2 Useful Products IntermediatedownendscienceNo ratings yet
- Periodic Table, Group 2 and The Halogens 1 QPDocument13 pagesPeriodic Table, Group 2 and The Halogens 1 QPmalakNo ratings yet
- t2 Chem Revision Ex 9Document23 pagest2 Chem Revision Ex 9Nicholas OwNo ratings yet
- Unit f326 Practical Skills in Chemistry 2 Evaluative Task SpecimenDocument14 pagesUnit f326 Practical Skills in Chemistry 2 Evaluative Task Specimenlockedup123No ratings yet
- Nitrogen & Fertilisers 1 QPDocument10 pagesNitrogen & Fertilisers 1 QPwembley1629No ratings yet
- Metals mj2020Document6 pagesMetals mj2020FenNo ratings yet
- AlkanesDocument9 pagesAlkanesyahvip07No ratings yet
- 2.4 2.5 2.6 Assessed HomeworkDocument7 pages2.4 2.5 2.6 Assessed HomeworkRabia Rafique100% (1)
- Unusual Structures and Physical Properties in Organometallic ChemistryFrom EverandUnusual Structures and Physical Properties in Organometallic ChemistryNo ratings yet
- Volumetric Analysis 12Document3 pagesVolumetric Analysis 12vijay kumar100% (2)
- pl-23-154 Technische Productfiche Power-Buds enDocument2 pagespl-23-154 Technische Productfiche Power-Buds enMax ImeNo ratings yet
- Project Report On Bakery Gel (Transulucent Semi Solid Paste)Document4 pagesProject Report On Bakery Gel (Transulucent Semi Solid Paste)EIRI Board of Consultants and PublishersNo ratings yet
- Inorganic Reaction Mechanisms-Part IIDocument44 pagesInorganic Reaction Mechanisms-Part IIUsama El-AyaanNo ratings yet
- 14.hydroxyl Compounds Lecture NotesDocument22 pages14.hydroxyl Compounds Lecture Notesgeoboom12100% (4)
- Recent Developments in The Chemistry of Halogen-Free Flame Retardant PolymersDocument52 pagesRecent Developments in The Chemistry of Halogen-Free Flame Retardant PolymersThinh Dang100% (1)
- Genetics Analysis: Integrated ApproachDocument18 pagesGenetics Analysis: Integrated ApproachJeanne JacksonNo ratings yet
- Extraction of Organic Analytes From FoodsDocument409 pagesExtraction of Organic Analytes From FoodsBoyana RatchevaNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrate Polymers: Sara R. Labafzadeh, Kashmira Vyavaharkar, Jari S. Kavakka, Alistair W.T. King, Ilkka KilpeläinenDocument7 pagesCarbohydrate Polymers: Sara R. Labafzadeh, Kashmira Vyavaharkar, Jari S. Kavakka, Alistair W.T. King, Ilkka KilpeläinenAbiCorreaNo ratings yet
- Plant Cell Culture Extract of Cirsium EriophorumDocument11 pagesPlant Cell Culture Extract of Cirsium EriophorumNguyễn Hữu Bảo MinhNo ratings yet
- Cc1 Lab Uric Acid Determination - CuenoDocument6 pagesCc1 Lab Uric Acid Determination - CuenoShyne ReyesNo ratings yet
- Determination of Phosphate in Sugarcane JuicesDocument8 pagesDetermination of Phosphate in Sugarcane Juicessha2salaNo ratings yet
- Ozone Depletion Potential (ODP) and Global Warming Potential (GWP)Document4 pagesOzone Depletion Potential (ODP) and Global Warming Potential (GWP)Justin MercadoNo ratings yet
- MARKLUND Et Al-1974-European Journal of Biochemistry PDFDocument6 pagesMARKLUND Et Al-1974-European Journal of Biochemistry PDFMartina PinkNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S2949750723000433 MainDocument10 pages1 s2.0 S2949750723000433 MainFlames ShoppingNo ratings yet
- Wax Characterisation by Instrumental Analysis PDFDocument132 pagesWax Characterisation by Instrumental Analysis PDFCarlotta C.100% (1)
- LCAricestrawDocument11 pagesLCAricestrawShrikant DeshmukhNo ratings yet
- Clinical Chemistry II - EnzymologyDocument9 pagesClinical Chemistry II - EnzymologyWynlor AbarcaNo ratings yet
- Summative Test #4 Gen BioDocument1 pageSummative Test #4 Gen BioKennedy Fieldad VagayNo ratings yet
- F Solution INCHO 2010 Solution of Previous Year Question Papers of Indian National Chemistry Olympiad (INChO)Document14 pagesF Solution INCHO 2010 Solution of Previous Year Question Papers of Indian National Chemistry Olympiad (INChO)Akshay Pandey100% (2)
- Corrected Organic and Inorganic Pollutants in WaterDocument23 pagesCorrected Organic and Inorganic Pollutants in WaterBhalmung KnightNo ratings yet
- Bioremediation: Case Studies in Central AlbertaDocument8 pagesBioremediation: Case Studies in Central Albertamarcomac2000No ratings yet
- Cs HN 0007Document2 pagesCs HN 0007DanielLêNo ratings yet
- Quality of Sewage QsDocument15 pagesQuality of Sewage Qsjonathan190710001019No ratings yet
- Development of Bio-Pesticides From Bio-Oil of OilDocument8 pagesDevelopment of Bio-Pesticides From Bio-Oil of OilHafizul HisyamNo ratings yet
- Chem Workshop - Question Paper CompilationDocument197 pagesChem Workshop - Question Paper Compilations1672snehil6353No ratings yet
- Boron Reagents in Process ChemistryDocument34 pagesBoron Reagents in Process ChemistryAnonymous Gb9EyWNo ratings yet
- Bio1TC2 Chromatography QA 2013Document3 pagesBio1TC2 Chromatography QA 2013teahockNo ratings yet
- Mold ResurfacingDocument34 pagesMold ResurfacinghollabackcockNo ratings yet
- NYJC 2021 H2 Chemistry 9729 P2Document20 pagesNYJC 2021 H2 Chemistry 9729 P2Allison KhooNo ratings yet