Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ec1269 - Microprocessors Applications
Uploaded by
Sourav DasCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ec1269 - Microprocessors Applications
Uploaded by
Sourav DasCopyright:
Available Formats
1. Differentiate Zener breakdown from avalanche breakdown? Zener Breakdown 1.
This occurs at junctions which being heavily doped have narrow depletion layers 2. This breakdown voltage sets a very strong electric field across this narrow layer. 3. Here electric field is very strong to rupture the covalent bonds thereby generating electronhole pairs. So even a small increase in reverse voltage is capable of producing large number of current carriers. ie why the junction has a very low resistance. This leads to Zener breakdown. Avalanche breakdown 1. This occurs at junctions which being lightly doped have wide depletion layers. 2. Here electric field is not strong enough to produce Zener breakdown. 3. Her minority carriers collide with semi conductor atoms in the depletion region, which breaks the covalent bonds and electron-hole pairs are generated. Newly generated charge carriers are accelerated by the electric field which results in more collision and generates avalanche of charge carriers. This results in avalanche breakdown.
2. State the principle of operation of SCR? A silicon controlled rectifier is a semi conductor device that acts as a true electronic switch. It can change alternating current in to direct current and at the same time it can control the amount of power fed to the load. Thus SCR combines the features of a rectifier and a transistor.
3. Distinguish pinch off and cut off in FET? Pinch off voltage It is the minimum drain-source voltage at which the drain current essentially becomes constant.
Cut-off voltage It is the gate source voltage where the channel completely cut off and the drain current becomes zero.
4. Distinguish CB, CE, CC configurations in Transistors? Common base configuration - If the base terminal is connected common to the input and output , it is called common base. The input is fed between the emitter and base and the out put between the collector and base. CE configuration If the emitter is common to both input and output , it is called CE configuration. Here input is applied between base and emitter and output is taken from collector and emitter. CC configuration If the collector is common to both input and output , it is called CC configuration. Here input is applied between base and collector and output is taken from emitter and collector.
5. Discuss the applications of SCR? In many applications SCR is used as a power control device. The common applications includes 1. Relay control 2. Regulated power supplies 3. Static switches 4. Motor control 5. Inverters 6. Battery chargers 7. Heater control
8. Phase control
6. What is a Thermistor? Thermistor is a combination of thermal and resistance. A thermistor is a resistance with definite thermal characterisics. Thermistors are widely used for temperature compensation. ie cancelling the effect of temperature, liquid level, gas flow etc. Thermistors are made in the shape of beads, probes, discs, washers etc.
7. Explain Tunneling principle? The tunnel diode is PN junction device, which operates in certain regions of its IV characteristics by the quantum mechanical tunneling of electrons through the potential barrier of the junction.The tunneling process for reverse current is essentially the zener effect, although negligible reverse bias is needed to initiate the process in tunnel diodes.It is also called Esaki diode.
8. What the applications of Tunnel diode? 1. High speed switching circuits 2. Logic circuits 9. Define and in a transistor? - current amplification factor It is the ratio of output current to input current. In a common base connection, The ratio of change in collector current to the change in emitter current at constant collector-base voltage VCB is known as current amplification factor.ie, = Ic/IE at constant VCB - Base current amplification factor In a common emitter connection, The ratio of change in collector current to the change in base current is known as base current amplification factor. ie, = Ic/IB
10. Name the different types of Negative feedback. What are their characteristics? 1. Negative current series feedback 2. Negative current shunt feedback 3. Negative voltage series feedback 5. Negative voltage shunt feedback
Characteristics 1. Higher fidelity 2. Higher stabilized gain 3. Increased bandwidth 4. Less amplitude distortion 4. Less harmonic distortion 5. Less frequency distortion 6. Less phase distortion 10. Reduced noise.
11. What are the different types of interrupts? a. Hardware b. Software Hardware interrupts- The interrupts where the CPU pins are used to receive interrupt requests , are called hardware interrupts. Software interrupts This interrupt is caused by the execution of the instruction. These are special instructions supported by the microprocessor.
12. What are the types of hardware interrupts? TRAP RST 7.5 RST 6.5 RST 5.5 INTR
13. Define PIV? It is the maximum reverse voltage that a diode can withstand without destroying the junction.
14. What is a Ripple factor? What is its value for a half wave and Full wave rectifier? The ratio of r.m.s value of a.c component to the d.c component in the rectifier output is known as ripple factor.It decides the effectiveness of the rectifier. Ripple factor = r.m.s value of a.c component r.m.s value of d.c component For half wave rectifier, Irms = Im/2 ; Idc = Im/
2 ) 1 = 1.21
Ripple factor = ( Im/2 / Im/ For full wave rectifier, Irms = Im/ 2
; Idc = 2Im/
2 ) 1 = 0.48
Ripple factor = ( Im/ 2 / 2 Im/ 14. How transistor amplifies?
When a weak a.c signal is given to the base of the transistor, a small base current starts flowing. Due to transistor action, a larger ( times the base current) a.c current flows through collector load Rc. As the value of Rc is quite high, a large voltage appears across Rc. Thus a weak signal applied in the base circuit appears in amplified form in the collector. In this way it amplifies the signal.
15. Classification of Transistor Amplifiers? The transistor amplifiers are classified as a. According to use: These includes voltage amplifiers and power amplifiers.
b. According to frequency capabilities: These includes audio amplifiers, radio frequency amplifiers etc. c. According to coupling methods: These includes RC coupled amplifiers, Transformer Coupled amplifiers etc. d. According to mode of operation:These includes class A, class B, Class C amplifiers. Class A amplifier one in which collector current flows for the entire a.c signal. Class B amplifier is one in which collector current flows for half cycle of input a.c signal.Class C amplifier is one in which collector current flows for less than half cycle of a.c signal.
16. What is a multi-stage amplifier? A transistor circuit containing more than one stage of amplification is known as multi-stage amplifier. Here output of one stage is connected to the input of second stage through coupling device. 17. What is the relation between and ? = Ic / IB = Ic / IE IE = IB +Ic IE = IB +Ic IB = IE - Ic Substituting the value of IB in exp(1), we get, = Ic / IE - Ic Dividing the numerator and denominator of R.H.S by IE, we get, =/1-
18. What is microprocessor? It is a program controlled semi conductor device (IC), which fetches, decodes and execute instructions.
19. What are the basic units of microprocessor?
The basic units or blocks of microprocessor are ALU, an array of registers and control unit.
20. What is a bus? Bus is a group of conducting lines that carries data, address and control signals.
21. Why data bus is bi-directional? The microprocessor is to fetch (read) the data from memory or input device for processing and after processing it has to store (write) the data to memory or output devices. Hence the data bus is bi-directional.
22. Why address bus is uni-directional? The address is an identification number used by the microprocessor to identify or access a memory location or input/output device. It is an output signal from the processor. Hence the address bus is unidirectional.
23. Define machine cycle? Machine cycle is defined as the time required to complete one operation of accessing memory input/output, or acknowledging an external request. This cycle may consists of three to six T-states.
24. Define T-state? T-state is defined as one subdivision of operation performed in one clock period. These subdivisions are internal states synchronized with the system clock, and each T-state is precisely equal to one clock period.
25. What is an instruction cycle?
The sequence of operations that a processor has to carry out while executing the instruction is called instruction cycle. Each instruction cycle of processor contains a number of machine cycles.
26. What is fetch and execute cycle? The instruction cycle is divided in to fetch and execute cycles. The fetch cycle is executed to fetch the opcode from memory. The execute cycle is executed to decode the instruction and to perform the work instructed by the instruction.
27. List the flags of 8085? There are five flags in 8085.They are sign flag, zero flag, auxiliary carry flag, parity flag and carry flag.
28. What does memory-mapping mean? The memory mapping is the process of interfacing memories to microprocessor and allocating addresses to each memory locations.
29. Difference between memory mapped I/o and I/O mapped I/o? Memory mapped I/O I/O mapped I/O
1. In this device address is 16- bit. Thus 1. In this device address is 8-bit. Thus Ao to A15 lines are used to generate the device address 2. MEMR and MEMW control signals are used to control read and write I/O operations. 3. Instructions available are LDA,STA,MOV R,M , ADD M etc 4. Data transfer is between any register and I/O device. 5. Decoding 16-bit address may Ao to A7 or A8 to A15 lines are used to generate device address. 2. IOR and IOW control signals are used to control read and write I/O operations. 3. Instructions available are IN and OUT. 4. Data transfer is between accumulator and I/O device. 5. Decoding 8-bit address will require
require more hardware.
less hardware.
30. Describe the function of the following pins in 8085? a) READY b) ALE c) IO/M d) HOLD e)SID and SOD READY It is used by the microprocessor to sense whether a peripheral is ready or not for data transfer. If not, the processor waits. It is thus used to synchronize slower peripherals to the microprocessor. ALE In 8085 , ADo to AD7 lines are multiplexed and lower half of address (Ao to A7) is available only during T1 of the machine cycle. The latching of lower half address from the multiplexed address lines by using ALE signal. IO/M - indicates whether I/O operation or memory operation is being carried out. HOLD This signal indicates that another master is requesting for the use of address bus, data bus and control bus. SID(Serial Input Data) This input signal is used to accept serial data bit by bit from the external device. SOD(Serial Output Data) This is an output signal which enables the transmission of serial data bit by bit to the external device.
31. Comparison between full address decoding and partial address decoding? Full Address Decoding 1. All higher address lines are decoded to select the memory or I/O device. Partial Address decoding 1. Few higher address lines are decoded to select the memory or I/O device. 2. More hardware is required to design 2. Hardware required to design decoding logic. decoding logic is less and sometimes it can be eliminated. 3. Higher cost for decoding circuit. 4. No Multiple addresses. 3. Less cost for decoding circuit. 4. It has a advantage of multiple addresses. 5. Used in large systems 5. Used in small systems
32. What is ALE? The ALE (Address latch enable) is a signal used to demultiplex the address and data lines using an external latch. It is used to enable the external latch.
33. Where is the READY signal used? READY is an input signal to the processor, used by the memory or input/output devices to get extra time for data transfer or to introduce wait states in the bus cycles.
34. What is program counter? How it is useful in program execution? The program counter keeps track of program execution. To execute a program the starting address of the program is loaded in program counter. The PC sends out an address to fetch a byte of instruction from memory and increments its content automatically.
35. Define opcode and operand? Opcode(operation code) is the part of an instruction that identifies a specific operation. Operand is a part of instruction that represents a value on which the instruction acts.
36. How the 8085 processor differentiates a memory access and I/O access? The memory access and I/O access is differentiated using IO/M signal. The 8085 processor asserts IO/M low for memory operation and high for I/O operations.
37. Why interfacing is needed for I/O devices?
Generally I/O devices are slow devices. Therefore the speed of I/O devices does not match with the speed of microprocessor. And so an interface is provided between system bus and I/O devices.
38. What is interrupt I/O? If the I/O device initiate the data transfer through interrupt then the I/O is called interrupt driven I/O.
39. What is a port? The port is a buffered I/O, which is used to hold the data transmitted from the microprocessor to I/O devices and vice versa.
40. What is synchronous data transfer scheme? For synchronous data transfer scheme, the processor does not check the readiness of the device after a command have been issued for read/write operation. For this scheme the processor will request the device to get ready and then read/write to the device immediately after the request.
41. What is asynchronous data transfer scheme? In asynchronous data transfer scheme, first the processor sends a request to the device for read/write operation. Then the processor keeps on polling the status of the device. Once the device is ready, the processor executes a data transfer instruction to complete the process.
42. What is scanning in keyboard and what is scan time? The process of sending a zero to each row of a keyboard matrix and reading the columns for key actuation is called scanning. The scan time is the time taken by the processor to scan all the rows one by one starting from first row and coming back to the first row again.
43. What are the tasks involved in keyboard interface?
The tasks involved in keyboard interfacing are sensing a key actuation, Debouncing the key and generating key codes( Decoding the key). These tasks are performed software if the keyboard is interfaced through ports and they are performed by hardware if the keyboard is interfaces through 8279.
44. How a keyboard matrix is formed in keyboard interface using 8279? The return lines, RL0 toRL7 of 8279 are used to form the columns of keyboard matrix. In decoded scan lines SL0 t0SL3 of 8279 are used to form the rows of keyboard matrix. In encoded scan mode, the output lines of external decoder are used as rows of keyboard matrix.
45. What is GPIB? GPIB is the General Purpose interface Bus. It is used to interface the test instruments to the system controller. 46. Comparison between full address decoding and Partial address decoding? Full address decoding 1. All higher address lines are decoded to select the memory or I/O device. Partial address decoding 1. Few higher address lines are decoded to select the memory or I/O device. 2. More hardware is required to design 2. Hardware required to design decoding logic. decoding logic is less and sometimes it can be eliminated. 3. Higher cost for decoding circuit. 4. No multiple addresses. 3. Less cost for decoding circuit. 4. It has a disadvantage of multiple addresses. (Shadow addresses) 5. Used in large systems. 5. Used in small systems.
47. What is the difference between SHLD and LHLD? SHLD- Store HL register pair in memory.
This instruction is used to store the contents of H and L register directly in to memory. LHLD- Load HL register pair from memory. This instruction copies the contents of memory location given with in the instruction in to the L register and the contents of next memory location in to the H register.
48. What is the difference between STAX and LDAX? STAX rp Store the contents of Accumulator register (A) in memory location whose address is specified by BC or DE register pair. LDAX rp Load Accumulator register (A) with the contents of memory location whose address is specified by BC or DE register pair.
49. Write an assembly language program to transfer data from memory block B1 to memory block B2? MVI C,0AH; Initialize counter LXI H, 2200H; Initialize source memory pointer LXI D, 2300H; Initialize destination memory pointer Loop: MOV A,M; Get byte from source memory block STAX D; Store byte in the destination memory block INX H; Increment source memory pointer INX D; Increment destination memory pointer DCR C; Decrement counter JNZ Loop ; If counter 0 repeat HLT
50. What are the types of branching instructions? 1. Jump instructions 2. Call and Return instructions 3. Restart instructions
51. Write an assembly language program to add 2 BCD numbers? LXI H,2200H; Initialize pointer MOV A,M ; Get the first number INX H; Increment the pointer ADD M ; Add two numbers DAA ; Convert HEX to valid BCD STA 2300; store the result HLT
52. Explain the instruction LXI rp,data (16)? LXI rp, data(16) Load 16 bit immediate data to specified register pair or stack pointer. The rp is 16 bit register pairs such as BC, DE, HL or stack pointer.
53. Write the difference between LDA and STA instruction? LDA Load data in to Accumulator register(A) directly from the address specified with in the instruction. STA Store the contents of Accumulator register(A) to the address specified with in the instruction.
54. What are the types of rotate instructions? RLC Rotate Accumulator Left RRC- Rotate Accumulator Right RAL Rotate Accumulator Left through Carry RAR - Rotate Accumulator Right through Carry 15. What is meant by stabilization of operating point? The process of making operating point independent of temperature variations or changes in a transistor parameter is known as stabilization.
55. What is Thermal runaway? The self destruction of an unstabilised transistor is known as thermal runaway.
58. What is Accumulator Register? It is an 8 bit register. It holds a source operand and receives the result of the arithmetic instructions (Addition, Subtraction, Multiplication and Division) 59. What is the difference between SISO and SIPO? The serial in serial out shift register accepts data serially -ie one bit at a time on a single line. It produces the stored information on its output also in serial form. In Sserial in parallel out, the data bits are entered serially (right most bit first) and once the data bits are stored, each bits apperas on its respective output line, and all bits are available simultaneously, rather than one bit at a time basis as with serial output.
60. What are the applications of shift registers? a) Time derlay - SISO register can be used to provide a time delay from input to output ie a function of both number of stages in the register and the clock frequency. b) USRT ( Universal synchronous Receiver Transmitter) c)Keyboard encoder - used as a ring counter
61. What is the function of shift register? Shift register consists of an arrangement of flip-flops used for storage and transfer of data in a digital system.
62. What are the characteristics of digital Ic's? 1. Speed of operation 2. Power dissipation 3. Fan-out 4. current and voltage parameter 5. Noise immunity 6. Operating temperature
7. Power supply requirements 8. Flexibility available
63. Convert the binary number 101101.10101 to decimal? Multiply each digit by its weight Ans:45.65625
64. Convert decimal number 247 to octal? Divide the number by 8. Take remainder as output. Ans:367
65. Convert decimal fraction .5100098 to octal? Multiply the fraction by 8. Take the integer part as output. Ans:(.4651)
66. Convert ocatal number 736 to binary? By replacing each octal digit by its equivalent binary. Ans:111 011 010
67. Convert the hexa decimal number to decimal? Multiply each digit by its weight. Ans: 58.1836
68. Convert the the binary number 101101110.11001010011 to hexa decimal? Split the numbers to 4 bit groups, then write the corresponding hex digit. Ans:0010 1101 1110 . 1100 1010 0110 2 D E C A 6
69. Comparison between analog and digital systems? Analog systems It has continous set of values. Digital systems 1.Discrete set of values
2. It involve frequency and time domain concepts 3. Complicates circuit analysis 4. Effect of fluctuations in the electrical characteristics of the component, temperature and noise are high 5. Speed is low
2. It involves Boolean algebra 3. Very simple 4. Here these components are very small. 5. Highly reliable and high speed used in computers,calculators etc.
70. What are the types of multivibrators? a)Monostable multivibrator b)Astable multivibrator c)Bi-stable multivibrator
71. What is a counter? What are the types of counter? A circuit used foe counting the pulses are called counters. Two types. 1. Synchronous counter 2. Asynchronous counter
72. What is the differnce between synchronous and asynchronous counters? In the case of asynchronous counters, all the flipflops are not clocked simultanously. eg: Ripple counter In synchronous counters, all the flip-flops are clocked simultaneously. eg: Ring counter
73. What is the function of adders? It is used not only in computers but also in many types of digital systems in which numerial data are processed. Two types 1. Half adder 2. Full adder
74. What is the difference between multiplexer and demultiplexer? Multiplexer (MUX) is a device that allows digital information from several sources to be routed on to a single line for transmission over that line to a common destination. The basic multiplexer has several data input lines and a single output line.It also has a data-select inputs,which permit digital data on any one of the input to be switched to the output line. Multiplexers are also called data selectors. Demultiplexer (DEMUX) basically reverses the multiplexing action. It takes digital information from one line and distributes it to a given number of output lines. It is also called data distributor.
75. Differentiate encoder and decoder? The basic function of decoder is to detect the presence of a specified combination of bits on its inputs and to indicate the presence of that code by a specified output level. Ie decoders are used to decode binary states of inputs. Encoder is a combinational logic circuit that performs reverse order decoder function. It accepts active level on one of its inputs representing a digit, such as a decimal or octal digit , and converts it to a coded output, such as a BCD or Binary. Encoders can also be devised to encode various symbols and alphabetic characters. The process of converting from familiar symbols or numbers to a coded format is called encoding.
76. Define Flip-flops? Flip-flops are synchronous bi-stable devices , synchronous means that the output changes state only at a specified point on a triggering input called clock(CLK) , which is defined as a control input, C; ie changes in the output occur in synchronization with the clock. The edge-Triggered flip-flop changes state either at the positive edge (rising edge) or at the negative edge (falling edge) of the clock pulse and is sensitive to the inputonly at this transition of the clock.
77. Draw the Truth table of SR flip-flop?
Inputs S R CLK Q
Outputs Q
Comments
0 0 1 1
0 1 0 1
Qo 0 1 ?
Qo 1 0 ?
No change RESET SET Invalid
- Clock transition LOW or HIGH Qo - Output level prior to clock transition X irrelevant (dont care)
78. Draw the Truth table of JK flip-flop? Inputs J K CLK Q Outputs Q Comments
0 0 1
0 1 0
Qo 0 1 Qo
Qo 1 0 Qo
No change RESET SET Toggle
- Clock transition LOW or HIGH Qo - Output level prior to clock transition 79. What are the steps involved in the fabrication of monolithic ICs? a)Wafer preparation b)Epitaxial growth c)Oxidization
d)Photolithiography process e)Isolation diffusion f)Pre ohmic etch g)Metallization h)Circuit probing i)Scribing and separation into chips j)Mounting and packing j)Encapsulation
80. Describe briefly about floppy disks? -These are commonly used as secondary storage and back up memories. They are also called diskettes. -These disks are very thin and flexible., hence it is called floppy. They are very small,inexpensive and convenient. They are removable diska. The popular sizes of floppy disks are 5.25 and 3.5. It is a surface device.
81. Describe briefly about Hard disks? These are made up of aluminium or other metals or metal alloys instead of plastic. It has high speed ie 3600rpm. It is more stable as it is rigid and contained in the dust-free environment. Its track and bit densities are much higher compared to floppy disks. Its data transfer rate is 10MB/sec. The average access time is from 25-50ms. The reliability of data is 1 in 1011.
82. What are the advantages of magnetic memory? It is a non-volatile memory without any moving part. It has semi random access and nondestructive read out property.
It has high reliability High data density Small size Light weight Limited power dissipation Used as a mass storage device.
83. Compare RAM and ROM? RAM 1.Volatile memory.The information written in to it is retained as long as the power supply is on. 2. The information stored is not permanent. 3. not cheaper compared to RAM. 4. It is Read and Write memory ROM 1.Non-volatile memory.ie the information stored in it is not lost even if the power supply goes off. 2. Used for permanent storage of information. 3. cheaper. 4. It is a Read only memory.
84. What are the steps in memory interfacing? 1. be able to select the chip. 2. identift the register 3. enable the appropriate buffer
85. What are the interrupts in 8085? TRAP RST 7.5 RST 6.5 RST 5.5 INTR
86. What are the segment registers in 8086? 1. Code segment register
2. Data segment register 3. Stack segment register 4. Extra segment register
87. What is vectored and non-vectored interrupt? When an interrupt is accepted, if the processor control branches to a specific address defined by the manufacturer then the interrupt is called vectored interrupt. In Non-vectored interrupt there is no specific address for storing the interrupt service routine. Hence the interrupted device should give the address of the interrupt service routine.
88. List the software and hardware interrupts of 8085? Software interrupts : RST 0,RST 1,RST 2,RST 3,RST 4,RST 5,RST 6,RST 7 Hardware interrupts : TRAP,RST 7.5,RST 6.5,RST 5.5, INTR.
89. What is TRAP? The TRAP is a non-maskable interrupt of 8085. It is not disabled by processor reset or after recognition of interrupt.
90. How clock signals are generated in 8085 and what is the frequency of the internal clock? The 8085 has the clock generation circuit on the chip but an external quartz crystal or LC circuit or RC circuit should be connected at the pins X1 andX2. The maximum internal clock frequency of 8085 is 3.03MHz.
91. Define stack? Stack is a sequence of RAM memory locations defined by the programmer.
92. What is USART?
The device which can be programmed to perform Synchronous or Asynchronous serial communication is called USART (Universal Synchronous Asynchronous Receiver Transmitter). Eg: INTEL 8251
93. What is scanning in keyboard and what is scan time? The process of sending a zero to each row of a keyboard matrix and reading the columns for key actuation is called scanning. The scan time is the time taken by the processor to scan all the rows one by one starting from first row and coming back to the first row again.
94. What are the different types of Address decoding Techniques? Absolute decoding/Full decoding Linear decoding/Partial decoding
95. Define Addressing modes? What are the types of Addressing modes? It specify the ways in which data are processed. 1. Immediate Addressing modes 2. Register Addressing modes 3. Direct Addressing modes 4. Register Indirect Addressing modes 5. Implied Addressing modes.
96. What are the types of instruction formats? 1-bte instruction 2-bte instruction 3-bte instruction
97. Explain the different stages of a power amplifier? It is used to amplify a weak signal until sufficient power is available to operate a loud speaker or other output device. It has 3 stages. 1)voltage amplification stage
2)Driver stage 3)Output stage. Eg: Push-pull amplifier
98. Why we use printers? What are the types of printers? Printers are commonly used output device. They provide information in a permanent readable form. They produce printed output of results, programs, and data. Depend up on the technology used in their manufacture, printers are classified in to 1. Impact printers 2. Non-impact printers
99. What is the use of Memory refresh register in Z-80? Used to refresh dynamic memories.
100.
What is VMA? virtual memory address
101.
Define Transistor Biasing?
The proper flow of zero signal collector current and the maintenance of proper collector-emitter voltage during the passage of signal is known as transistor biasing.
Essay Questions 1. Explain the different stages of a power amplifier? What are the classifications of power amplifier? It is used to amplify a weak signal until sufficient power is available to operate a loud speaker or other output device. It has 3 stages. 1)voltage amplification stage 2)Driver stage
3)Output stage. Eg: Push-pull amplifier Classifications Class A power amplifier Class B power amplifier Class C power amplifier
2. What are the steps involved in the fabrication of monolithic ICs? a)Wafer preparation b)Epitaxial growth c)Oxidization d)Photolithiography process e)Isolation diffusion f)Pre ohmic etch g)Metallization h)Circuit probing i)Scribing and separation into chips j)Mounting and packing j)Encapsulation
3. Give the construction details and explain the working of FET showing its characteristics? Circuit diagram Theory of operation
Two types 1.JFET 2.MOSFET Characteristics 1. Drain characteristics 2. Transfer characteristics
4.Compare CB,CE,CC with respect to i/p resistance,gain,o/p resistance? Distinguish CB, CE, CC configurations in Transistors? Circuit dgms Input characteristics Output characteristics.
5.Define feed back amplifier? What are the types of feed back amplifier? 1. Positive feed back Negative feedback a) . Negative current series feedback b). Negative current shunt feedback c). Negative voltage series feedback d). Negative voltage shunt feedback
6. Why we use printers? What are the types of printers? Printers are commonly used output device. They provide information in a permanent readable form. They produce printed output of results, programs, and data. Depend up on the technology used in their manufacture, printers are classified in to 1. Impact printers 2. Non-impact printers
7.Explain DMA data transfer scheme with example? a. Diagram b. Eg: Intel 8237 (DMA controller) Pin diagram - Explanation 8.With a neat block diagram, explain the working of Transformer coupled amplifier? Derive its gain expression? Diagram Operation Gain expression
9.Draw the diagram of half wave and Full wave rectifiers and explain their operation. Also compare them? Circuit diagrams Theory of operation Calculate efficiency
10.Draw the circuit diagram of RC coupled amplifier with neat diagram of self bias circuit and explain the operation. Comment on its low frequency and high frequency performance? Diagram Operation Frequency curve at low, high and mid frequencies.
11.Why we use multi-vibrators in digital systems? In digital systems rectangular wave form is most desirable. The generators of rectangular wave forms are referred to as multi-vibrators. Three types 1. Astable multi-vibator 2. mono stable multi-vibator 3. bi-stable multi-vibator
7. Draw the circuit diagrams of a 4-bit shift register using flip-flops and explain? They are 1. SISO 2. SIPO 3. PISO 4. PIPO
12.What are the drawbacks of Ripple counter? How they can be overcome by synchronous counters? Ripple counters are asynchronous counters. The problems are avoided by a common clock pulse used in synchronous counters.
13.Define filters? What are the types of filters used? It is a device which removes the a.c component of a rectifier output but allows the d.c component to reach the load. Types 1. capacitor filter 2. inductor filter 3. choke input filter 4. capacitor input filter or filter. 8. Explain the types of counters? Sunchronous counters Asynchronous counters.
14.Explain the applications of microprocessors in aerospace? 15.Explain the operations of hard disk drive? Diagrams Explanation
16.Explain serial and Parallel data transfer? Serial data transfer Duplex Half duplex Full duplex Eg:USART (Universal synchronous/Asynchronous Receiver Transmitter) Parallel data transfer eg: PPI (Programmable peripheral interface) 17.Explain about A/D and D/A converters? A/D converters 1. Weighted resistor DAC 2. R-2R ladder 3. Inverted R-2R ladder
D/A converters a)Direct Types 1. Flash type converter 2. Counter type converter 3. Tracking or servo converter 4. Successive approximation type converter b)Integrating types 1. Charge balancing ADC 2. Dual slope ADC
18.With Neat diagram, explain the Architecture of 8085? Block diagram Explaination
19. Explain the instruction sets of 8085? Data transfer instructions Arithmetic instructions Logical instructions Branching instructions Machine control instructions
20. Explain about memory interfacing? 1. EPROM memory 2. RAM memory 21. .With Neat diagram, explain the Architecture of Z-80? Block diagram Explanation 22. With Neat diagram, explain the Architecture of M 6800? Block diagram Explanation
23. Write an Assembly language program to find largest number from a given set of numbers? Algorithm
Program Output
24. Write an Assembly language program to sort a set of numbers? Algorithm Program Output
25. Define Addressing modes? What are the types of Addressing modes? Addressing modes specify the ways in which data are processed. 1. Immediate Addressing modes 2. Register Addressing modes 3. Direct Addressing modes 4. Register Indirect Addressing modes 5. Implied Addressing modes
NOORUL ISLAM COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING
DEPARTMENT OF COMPUTER SCIENCE & ENGINEERING
FIFTH SEMESTER
EC1269 Microprocessors & Applications
2 MARKS AND 16 MARKS Q & A
Prepared by, Sinciya. P.O L/CSE NICE
You might also like
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (589)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (842)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5806)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1091)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Delem: Installation Manual V3Document73 pagesDelem: Installation Manual V3Marcus ChuaNo ratings yet
- 5.24!07!2016 J (A) Minor Test Paper 1Document80 pages5.24!07!2016 J (A) Minor Test Paper 1Namrata SinghNo ratings yet
- Matrices ProblemsDocument2 pagesMatrices ProblemsNamrata SinghNo ratings yet
- Classification - K Nearest Neighbor Classifier Example Matlab Code Found at Mathworks Cannot Understand - Stack OverflowDocument1 pageClassification - K Nearest Neighbor Classifier Example Matlab Code Found at Mathworks Cannot Understand - Stack OverflowNamrata SinghNo ratings yet
- Computational Statistics - Getting Started With Classification Using MATLAB - MathWorks Webinar - MathWorks IndiaDocument2 pagesComputational Statistics - Getting Started With Classification Using MATLAB - MathWorks Webinar - MathWorks IndiaNamrata SinghNo ratings yet
- Multi Class SVM - File Exchange - MATLAB CentralDocument2 pagesMulti Class SVM - File Exchange - MATLAB CentralNamrata SinghNo ratings yet
- Hidden Markov Model in MATLAB - Stack OverflowDocument2 pagesHidden Markov Model in MATLAB - Stack OverflowNamrata SinghNo ratings yet
- Journal of Inequalities in Pure and Applied Mathematics: New Inequalities About Convex FunctionsDocument3 pagesJournal of Inequalities in Pure and Applied Mathematics: New Inequalities About Convex FunctionsNamrata SinghNo ratings yet
- Electronic Measurements & Instrumentation 8Document15 pagesElectronic Measurements & Instrumentation 8Namrata SinghNo ratings yet
- Driver, Servo Motores ... DX02 - WAR1Document44 pagesDriver, Servo Motores ... DX02 - WAR1Mario ArayaNo ratings yet
- Bzx84-Y2 3PINES PDFDocument12 pagesBzx84-Y2 3PINES PDFenriquevazquez27No ratings yet
- Assignment 12Document4 pagesAssignment 12VenkatGollaNo ratings yet
- Application Note AN05 - Bench Testing OBD Interfaces: Doubly Terminated!Document3 pagesApplication Note AN05 - Bench Testing OBD Interfaces: Doubly Terminated!2791957No ratings yet
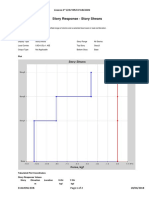
- Story Response - Story Shears: ETABS 2016 16.2.0 License # 1Z8VYN5FWWBEHHNDocument2 pagesStory Response - Story Shears: ETABS 2016 16.2.0 License # 1Z8VYN5FWWBEHHNjosNo ratings yet
- Activity 4 6Document3 pagesActivity 4 6Jules Nikko Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Tugas 2 PDFDocument3 pagesTugas 2 PDFRahmatNo ratings yet
- Example4 PDFDocument5 pagesExample4 PDFsarim rizviNo ratings yet
- A Filter For A Noise Generator PDFDocument5 pagesA Filter For A Noise Generator PDFjgalindesNo ratings yet
- Elite 21es63Document29 pagesElite 21es63dann222No ratings yet
- Course of Digital Techniques Lectures2 017 - PDF - 1Document51 pagesCourse of Digital Techniques Lectures2 017 - PDF - 1juber mullaNo ratings yet
- Laplace MatlabDocument21 pagesLaplace MatlabIrwan WahyudiNo ratings yet
- Switch Less Bidirectional RF Amplifier For 2.4 GHZ Wireless Sensor NetworksDocument7 pagesSwitch Less Bidirectional RF Amplifier For 2.4 GHZ Wireless Sensor NetworksHam Radio HSMMNo ratings yet
- SIC9552A SISemiconductorsDocument9 pagesSIC9552A SISemiconductorsDiego OliveiraNo ratings yet
- 15A99301 Basic Electrical and Electronics Engineering - 3 PDFDocument2 pages15A99301 Basic Electrical and Electronics Engineering - 3 PDFMadhuSudanNo ratings yet
- Digital Object Counter Using MicrocontrollerDocument60 pagesDigital Object Counter Using MicrocontrollerKishan Amara82% (22)
- Ansi C57.12&iec 76 PDFDocument8 pagesAnsi C57.12&iec 76 PDFfreddy vargas100% (1)
- Features General Description: Dual-Phase Synchronous-Rectifier Buck ControllerDocument26 pagesFeatures General Description: Dual-Phase Synchronous-Rectifier Buck ControllerVịnh DemoNo ratings yet
- Department of Information Technology: Code Name of Paper Class Name of FacultyDocument13 pagesDepartment of Information Technology: Code Name of Paper Class Name of FacultyAparna kunduNo ratings yet
- Mother BoardDocument29 pagesMother BoardSwayamprakash PatelNo ratings yet
- EC2208 Lab ManualDocument2 pagesEC2208 Lab ManualImmanuel JsrNo ratings yet
- Signal CatalogueDocument246 pagesSignal CatalogueWen-Sheng JangNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12Document107 pagesChapter 12shivani1401No ratings yet
- Digital Input Module SM 321 DI 16 X DC 24 V High Speed (6ES7321-1BH10-0AA0)Document3 pagesDigital Input Module SM 321 DI 16 X DC 24 V High Speed (6ES7321-1BH10-0AA0)Fabio CavalheiroNo ratings yet
- Nanotechnology Nram Nano Random Access Memory IJERTCONV2IS01029Document5 pagesNanotechnology Nram Nano Random Access Memory IJERTCONV2IS01029ShrishtiNo ratings yet
- Frs Gmrs PMR Murs Bus Marine WX Ham 2013f (1) .CSVDocument7 pagesFrs Gmrs PMR Murs Bus Marine WX Ham 2013f (1) .CSVChuck HestonNo ratings yet
- Cse-1100 1Document25 pagesCse-1100 1Showmik AhmedNo ratings yet
- Marshall Bass State B30 / B65 / B150 Bass Combo'sDocument6 pagesMarshall Bass State B30 / B65 / B150 Bass Combo'sd.timmerNo ratings yet
- Zwickau University of Applied Sciences EMC Lab Testing For Automotive Ethernet Physical Layer QualificationDocument22 pagesZwickau University of Applied Sciences EMC Lab Testing For Automotive Ethernet Physical Layer Qualificationamritpati14No ratings yet