Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Drug Study Final
Drug Study Final
Uploaded by
Jazzmin Angel ComalingOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Drug Study Final
Drug Study Final
Uploaded by
Jazzmin Angel ComalingCopyright:
Available Formats
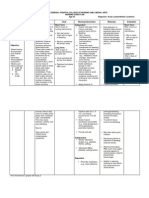
DRUG STUDY Drug Order Pharmacologic Action of Drug Inhibits accumulation of inflammatory cells at inflammatory sites, phagocytosis, lysosomal
enzyme release, synthesis and/or release of mediators of inflammation. Indication/Contraindication Adverse Effects Desired Actions To decrease inflammation. Nursing Responsibilities Assess for any hypersensitivity or any allergic reaction in the patient. Assess weight, BP (take note of hypertension), serum glucose (take note of hyperglycemia) and cholesterol. Monitor electrolytes and note for hypokalemia , nausea and vomiting and irritability. Instruct patient to eat small, frequent meals if prescribed to minimize GI
Hydrocortisone Sodium Succinate (Solu-Cortef) 250 mg IV @ LD and 100 mg IV q 6 Short-acting corticosteroid Anti-inflammatory
Indication: Treatment for people with: Short-term inflammatory disorders Allergic disorders Autoimmune disorders Contraindication: Hypersensitivity to drugs, alcohol, bisulfites, or tartrazine. Concurrent use of other immunosuppressant corticosteroids. Concurrent administration of livevirus vaccines.
CNS: Headache, restlessness, seizure CV: Hypertension, arrhythmias GI: Nausea and vomiting Metabolic: Hypokalemia, hyperglycemia, hypocalcemia, sodium and fluid retention Musculoskeletal: Muscle pain or weakness Respiratory: Cough Skin: Rash, pruritis
upset (nausea and vomiting). Instruct client to avoid stressful activities, physically and mentally, to minimize headache and weakness. Assess for any hypersensitivity or any allergic reaction in the patient. Assess cardiacrespiratory function, breath sounds and heart rate. Monitor patient for any signs of allergic reactions and paradoxical bronchospasm.
Albuterol Salbutamol (Ventolin Expectorant) 5 mg 1 cap TID Symphatomimetic (beta2-adrenergic agonist) Bronchodilator, antiasthmatic
Relaxes smooth muscles by stimulating beta2-receptors, thereby causing bronchodilation and vasodilation.
Indication: Treatment for people with: Respiratory disorders complicated by bronchospasm and excessive secretion of tenacious mucus (bronchial asthma). Contraindication: Hypersensitivity to any ingredients of Ventolin Expectorants.
CNS: Dizziness, headache, insomnia CV: Hypertension, palpitations, tachycardia, chest pain GI: Nausea and vomiting, GI distress Metabolic: Hypokalemia Respiratory: Cough, dyspnea, wheezes Skin: Pallor, rash, flushing, sweating
To activate bronchodilation .
Use cautiously in patients with cardiac disease, hypertension, glaucoma, seizure disorders and hyperthyroidism.
Monitor patients vital signs especially blood pressure and electrolyte levels. Take note of hypertension and hypokalemia. Instruct patient to swallow extendedrelease tablets and not to mix them with food. Advise patient to establish effective bedtime routine and to take drug well before bedtime to minimize insomnia.
Drug Order
Pharmacologic Action of Drug Inhibits cholinergic receptors in
Indication/Contraindication
Adverse Effects
Desired Actions To prevent obstructed airway
Nursing Responsibilities Assess for any hypersensitivity or any allergic
Ipratropium bromideSalbutamol
Indications: Treatment for people with:
CNS: Headache CV: Palpitations, arrhythmias,
(Duavent) 72 mcg q6 Anticholinergic Allergy, cold and cough remedy, bronchodilator
bronchial smooth muscle, decreasing level of cyclic guanosine monophosphate and dilating bronchioles. When used locally, inhibits secretions from glands lining the nasal mucosa.
Management of reversible bronchospasm associated with obstructive airway diseases (e.g., bronchial asthma). For patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
hypotension Respiratory: Chest pain, cough, bronchospasm GI: Nausea and vomiting, GI irritation, throat irritation and dryness Musculoskeletal: Back pain
passages.
reaction in the patient. Assess vital signs especially blood pressure and take note of hypotension. Position patient on high back rest position. Provide back tapping after nebulization. Instruct patient to prevent intake of food right after nebulization. Instruct patient to rinse mouth after each dose to minimize throat irritation and dryness.
Contraindication: Hypersensitivity to components, atrophine or soya lecithin and related food products. Hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy or tachyarrhythmia.
Drug Order
Pharmacologic Action of Drug Ticarcillin impairs the bonds that hold the bacterial cell wall together and Clavulanic Acid prevents these bacteria from inactivating the ticarcillin, and leaves the bacteria susceptible to attack.
Indication/Contraindication
Adverse Effects
Desired Actions To prevent bacterial growth.
Nursing Responsibilities Assess for any hypersensitivity or any allergic reaction in the patient. Assess patients vital signs. Monitor neurologic status and take note of seizures. Monitor serum electrolyte levels for hypernatremia due to drugs high sodium content and for hypokalemia due to increased urinary potassium loss. Monitor patients platelet count, PT and APTT because medicine may cause increase bleeding time and in rare
Ticarcillin Clavulanic Acid (Timentin) 3.2 g IV q8 (-) ANST Penicillin (extended spectrum) Anti-infective
CNS: Headache, dizziness, Treatment for people with: hyperreflexia, fatigue, Systemic and urinary lethargy, seizures GI: Nausea and tract Infections caused by susceptible vomiting, diarrhea, flatulence strains of the Metabolic: designated Hypernatremia, microorganisms. hypokalemia Hematologic: Bleeding, prolonged bleeding time, Contraindication: thrombocytopenia Skin: Rash Hypersensitivity to drug or other penicillins. Use cautiously in cystic fibrosis, renal or hepatic diseases.
Indication:
cases, may induce thrombocytopenia. Assess for signs of bleeding such as easy bruising with induration and frequent or prolonged nose bleeding. Instruct patient to decrease sodium intake to reduce the risk of electrolyte imbalance. Instruct patient to report severe or prolonged diarrhea. Remind patient that watery or bloody stools can occur 2 or more months after antibiotic therapy and can be serious, requiring prompt treatment. Levetiracetam May protect against Indication: CNS: Anxiety, depression, fatigue, To prevent seizure. Assess for any
(Keppra) 500 mg BID Pyrrolidine derivative Anticonvulsant
secondary generalized seizure activity by preventing coordination of epileptiform burst firing. Levetiracetam doesnt seem to involve inhibitory and excitatory neurotransmissio n.
For people with: Partial onset seizure Epilepsy Contraindication: Hypersensitivity to levetiracetam or other pyrrolidone derivatives or any of the excipients of Keppra.
headache, insomnia, somnolence, seizures, irritability GI: Constipation, diarrhea, hepatic failure, nausea and vomiting Respiratory: Asthma, cough Other: Infection, pain
hypersensitivity or any allergic reaction in the patient. Assess vital signs especially temperature and take note of signs and symptoms of infection (such as fever). Instruct patient to take medicine with or without food and to swallow the medicine whole. Instruct patient to take safety measures (such as raise side rails when lying in bed) and avoid dangerous activities to prevent injury. Instruct patient to avoid mental activities that require
mental alertness to prevent mental stress and disorders (such as headache). Instruct patient to take small, frequent meals to minimize GI upset (such as nausea and vomiting). Encourage patient to avoid alcohol during therapy because alcohol can increase incidence of drowsiness and dizziness. Carbamazepine (Tegretol) 200 mg/tab TID Iminostilbene derivative Anticonvulsant Decreases synaptic transmission in the CNS by affecting sodium channels in neurons. Indication: For people with: Partial Seizures Generalized TonicClonic Seizures (Grand Mal) CNS: Drowsiness, fatigue, headache and ataxia CV: Hypertension, hypotension GI: Nausea and vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal pain, anorexia and dry mouth GU: Albuminuria, To prevent seizures. Assess for any hypersensitivity or any allergic reaction in the patient Assess patients vital signs especially BP and intake and output, and take note of hypertension,
Contraindication: Hypersensitivity Bone marrow depression Porphyria
glycosuria, fluid retention
hypotension or Fluid retention. Provide mouth care to help reduce dry mouth. Instruct patient to take medicine with food to prevent gastric irritation. Instruct patient to avoid hazardous activities to prevent mental stress (such as headache, drowsiness and fatigue). Assess for any hypersensitivity or any allergic reaction to the patient. Assess vital signs especially heart rate (take note of tachycardia and arrhythmias) and blood pressure (take note of
Salmeterol xinafoate (Seretide) 250 mcg 1 PUFF BID Beta2-adrenergic receptor agonist (long acting) Bronchodilator
Protects against symptoms, improves lung function and prevents exacerbations of the condition.
Indication: For people with: Asthma Chronic bronchitis Emphysema Prevention of exercise-induced bronchospasm Contraindication:
CNS: Headache, nervousness, dizziness, tremor CV: Palpitations, hypertension, tachycardia, arrhythmias GI: Nausea and vomiting, abdominal pain, dry mouth Metabolic: Hyperglycemia, hypokalemia
To help treat obstructed airway passages.
Hypersensitivity to any ingredient of Seretide. Use cautiously in cardiovascular disease, diabetes mellitus, hyperthyroidism.
Musculoskeletal: Muscle cramps and soreness Respiratory: Paradoxical bronchospasm Skin: Angioedema, rash
hypertension). Assess patients pulmonary status and take note of any signs of rash, urticaria, angioedema, and paradoxical bronchospasm. Instruct patient how to use the inhaler by instructing him to slide the lever only once when preparing dose to avoid wasting doses. Advise him to exhale immediately before using the inhaler and then to place mouthpiece to his lips and inhale through his mouth, not his nose. Then he should remove mouthpiece from his mouth, hold his breath for at least 10 seconds and exhale
slowly. Provide patient with oral care to prevent dry mouth. Potassium chloride (Kalium Durule) Essential for maintenance of intracellular isotonicity, transmission of nerve impulses, contraction of cardiac, skeletal, and smooth muscles, maintenance of normal kidney function, and for enzyme activity. Indication: For people with: Potassium deficit secondary to diuretic or corticosteroid therapy. Contraindication: Severe renal impairment Severe hemolytic reactions Untreated Addisons disease Crush syndrome Early postoperative oliguria (except during GI drainage) Adynamic ileus Acute dehydration Heat cramps Hyperkalemia CNS: Confusion, unusual fatigue, restlessness, paresthesia CV: Hypotension, arrhythmias GI: Nausea and vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal discomfort, flatulence Metabolic: Hyperkalemia Musculoskeletal: Weakness and heaviness of legs Respiratory: Respiratory paralysis To increase patients potassium level. Assess for any hypersensitivity or any allergic reaction in the patient. Assess vital signs of patient especially intake and output pattern and blood pressure. Assess patient for any signs and symptoms of GI ulceration (such as burning pain at ulceration site, nausea and vomiting, vomiting of blood). Monitor patient with cardiac monitor, take note for irregular
20 mEq/1 tab TID Mineral, electrolyte Electrolyte replacement, nutritional supplement
Patients receiving potassium-sparing diuretics
heartbeat and arrhythmias. Instruct patient to take oral medicine with or just after meal (with glass of water or fruit juice) to prevent GI irritation and to swallow extended-release capsules whole without crushing or chewing them. Instruct patient to take small, frequent meals and drink plenty of fluids to prevent GI upset. Instruct patient to minimize intake of foods containing potassium to avoid potassium deficit.
Prednisone (Deltasone) 20 mg 1 tab TID Corticosteroid (immediate acting) Anti-inflammatory, immuno suppressant
Decreases inflammation by suppression of migration of polymorphonucle ar leukocytes and reversal of increased capillary permeability; suppresses the immune system by reducing activity and vol of the lymphatic system; suppresses adrenal function at high doses.
Indication: For people with: Severe allergic reactions Breathing problems Immune system disorders. Contraindication: Hypersensitivity Serious infections (except tuberculous meningitis) Varicella Systemic fungal infections
CNS: Headache, nervousness, depression, seizures, restlessness, paresthesia, insomnia CV: Hypotension, hypertension, heart failure, arrhythmias GI: Nausea and vomiting, abdominal distention, dry mouth Metabolic: Sodium and fluid retention, hypokalemia, hypocalcemia, hyperglycemia, diabetes mellitus, decreased carbohydrate tolerance Musculoskeletal: Muscle weakness or atrophy, myalgia, myopathy Respiratory: Cough, wheezing, bronchospasm
To lessen inflammation
Assess for any hypersensitivity or any allergic reaction to the patient. Assess for patients vital signs especially blood pressure, intake and output pattern and sleep pattern. Assess patients fasting blood glucose and serum glucose levels for hypoglycemia. Monitor patient for changes in mood and behavior, emotional stability or psychomotor activity, especially with longterm therapy. Instruct patient to take medicine with food or milk and to
take once-daily dose in the morning to reduce GI upset (nausea and vomiting). Instruct patient to establish effective bedtime routine and to take drug well before bedtime to minimize insomnia. Instruct patient to avoid alcohol during therapy because of increased risk of GI ulcers and bleeding. Instruct patient to avoid hazardous activities to prevent mental stress. Instruct patient to avoid people with contagious disease because drug has immunosuppressant effect. Advise to report exposure to
contagious disease if any.
Intravenous Fluids Treatment/ Infusion D5NM 1L x 12hours 30 gtts + 40 mEq KCl Classification Indication Contraindication Nursing Responsibilities/ Precautions Check vital signs frequently. Do not administer unless solution is clear and container is undamaged. Caution must be exercised in the administration of parenteral fluids, especially with containing sodium ions receiving corticosteroids. Discard unused portion. Report adverse reactions. Monitor fluid intake and output
Hypertonic, nonpyrogenic, parenteral fluid, electrolyte and nutrient replenisher
Parenteral maintenance of routine daily fluid and electrolyte requirements with minimal carbohydrate calories from dextrose.
Hypersensitivity to any of the components.
Reference: Nurses Drug Handbook by McGraw-Hill 6th edition, Nurses Drug Handbook by Jones and Bartlett Learning 10th edition
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5814)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (844)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- NCP Risk For Bleeding Related To Decreased Platelet CountDocument2 pagesNCP Risk For Bleeding Related To Decreased Platelet CountKC Ignacio83% (24)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- New Era Ladies' Dorm 2Document3 pagesNew Era Ladies' Dorm 2Jazzmin Angel ComalingNo ratings yet
- Osteomyelitis HandoutDocument4 pagesOsteomyelitis HandoutJazzmin Angel ComalingNo ratings yet
- The Volunteers of Dental Mission 2013Document1 pageThe Volunteers of Dental Mission 2013Jazzmin Angel ComalingNo ratings yet
- Name: Patient TL Age: Years Old Diagnosis: Physical AssessmentDocument11 pagesName: Patient TL Age: Years Old Diagnosis: Physical AssessmentJazzmin Angel ComalingNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For Pneumonia With Diagnosis InterventionsDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan For Pneumonia With Diagnosis InterventionsJazzmin Angel ComalingNo ratings yet
- Dipyridamole and FuroDocument11 pagesDipyridamole and FuroJazzmin Angel ComalingNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For Pneumonia With Diagnosis InterventionsDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan For Pneumonia With Diagnosis InterventionsJazzmin Angel ComalingNo ratings yet
- 225 FullDocument17 pages225 FullJazzmin Angel ComalingNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Process: Subjective CuesDocument12 pagesNursing Care Process: Subjective CuesJazzmin Angel ComalingNo ratings yet
- Pleural EffusionDocument1 pagePleural EffusionJazzmin Angel ComalingNo ratings yet
- Coverage: Unit 0-1 and CBTDocument2 pagesCoverage: Unit 0-1 and CBTJazzmin Angel ComalingNo ratings yet
- Ancient Greek LiteratureDocument2 pagesAncient Greek LiteratureJazzmin Angel ComalingNo ratings yet