Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cystic Fibrosis
Uploaded by
Rubz JeanCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cystic Fibrosis
Uploaded by
Rubz JeanCopyright:
Available Formats
Case 3 1. Explain the biochemical basis of the patients condition.
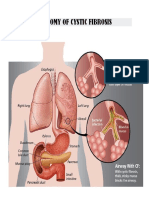
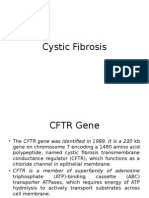
Cystic fibrosis is the most common lethal autosomal recessive disease affecting the Caucasian population. The protein affected is the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR), which is a chloride ion channel. The mutations lead to (1) defective or decreased protein production, (2) defective processing of the protein, (3) protein that is defective in the regulation of the chloride channel, or (4) defect in the transport of chloride ions. The most common mutation, a deletion of a phenylalanine residue at amino acid position 508 (F508), results in misfolding of the protein; it consequently does not traffic to the membrane. Defects in the CFTR decrease the ability of cells to transport Cl- in a number of tissues, particularly the pancreas, airway epithelia, and sweat glands. When Cl- transport is defective in the pancreas, it leads to decreased HCO3- secretion and decreased hydration that leads to thick secretions that block the pancreatic ducts and destruction of the organ. In the lungs, the decreased absorption of Cl- ions is thought to increase the absorption of the airway surface liquid thus increasing the viscosity of mucous, decreasing mucociliary clearance and increasing the incidence of airway infections. In sweat glands, defects in CFTR prevent the reabsorption of Cl- in the sweat gland duct, thusincreasing the concentration of NaCl in sweat.Thus, leading to leading to respiratory infections, gastrointestinal obstruction, pancreatic enzyme dysfunction leading to malabsorption of nutrients, and excessive electrolyte secretion.
2. Explain the role of electrophoresis in the diagnosis of the patients condition. Gel electrophoresis can be applied as a method for detection of genetic diseases such as Cystic fibrosis (CF). Larger deletions in the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) gene will cause it to move differently than the full-length wild type gene. In most cases, the DNA sample of the patient is amplified by a polymerase chain reaction (PCR) using specific primers. After the electrophoresis of the PCR samples the bands are visualized under ultraviolet (UV) light using ethidium bromide staining.
You might also like
- Chapter 259. Cystic FibrosisDocument7 pagesChapter 259. Cystic FibrosisAntónio CarvalhoNo ratings yet
- Fibrosis QuisticaDocument6 pagesFibrosis QuisticaFernanda Del ValleNo ratings yet
- Cystic Fibrosis Impact On Cellular FunctionDocument39 pagesCystic Fibrosis Impact On Cellular FunctionRoszel cardinoNo ratings yet
- Cystic Fibrosis LectureDocument16 pagesCystic Fibrosis Lecturevani reddyNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Cystic FibrosisDocument5 pagesAnatomy of Cystic FibrosislazylawatudentNo ratings yet
- Cystic FibrosisDocument20 pagesCystic FibrosisIndrajit Barua100% (1)
- Test Cystic FiborisisDocument2 pagesTest Cystic Fiborisiscmarino1137No ratings yet
- Cystic Fibrosis: Dr. Pragasam Viswanathan Professor, SBSTDocument16 pagesCystic Fibrosis: Dr. Pragasam Viswanathan Professor, SBSTMaru Mengesha Worku 18BBT0285No ratings yet
- Cystic FibrosisDocument20 pagesCystic FibrosisIndrajit BaruaNo ratings yet
- Cystic Fibrosis PathophysiologyDocument5 pagesCystic Fibrosis PathophysiologyKim Enrico JumarangNo ratings yet
- Cystic FibrosisDocument21 pagesCystic FibrosisGouthamNo ratings yet
- The Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulator: An Intriguing Protein With Pleitropic FunctionsDocument17 pagesThe Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulator: An Intriguing Protein With Pleitropic FunctionsKaren NietoNo ratings yet
- Cystic FibrosisDocument2 pagesCystic Fibrosisthatkid94No ratings yet
- Cystic FibrosisDocument6 pagesCystic Fibrosischurchil owinoNo ratings yet
- CR Project On Cystic FibrosisDocument3 pagesCR Project On Cystic FibrosisMorgan PeggNo ratings yet
- Genetics of Cystic FibrosisDocument3 pagesGenetics of Cystic Fibrosislutfiah_liaNo ratings yet
- Cystic FibrosisDocument31 pagesCystic FibrosisshadabNo ratings yet
- Cystic FibrosisDocument40 pagesCystic FibrosisMoonmoon SinhaNo ratings yet
- Fibroza ChisticaDocument6 pagesFibroza ChisticaFillipp IvanovNo ratings yet
- Cystic FibrosisDocument16 pagesCystic FibrosisAzzahra AzmiNo ratings yet
- Cystic Fibrosis: DescriptionDocument5 pagesCystic Fibrosis: DescriptionJulliza Joy PandiNo ratings yet
- Case 3: Tim Winter: Pathophysiology of Cystic FibrosisDocument4 pagesCase 3: Tim Winter: Pathophysiology of Cystic FibrosisAnonymous vCCQ0qNo ratings yet
- CysticfibrosisDocument6 pagesCysticfibrosisSghir SghirNo ratings yet
- CFTR 2Document8 pagesCFTR 2Linda KurniawanNo ratings yet
- Cystic FibrosisDocument11 pagesCystic FibrosisleinonenxNo ratings yet
- Cystic Fibrosis (Mucoviscidosis)Document18 pagesCystic Fibrosis (Mucoviscidosis)Ananth Sai BadetiNo ratings yet
- Lancet FQ PDFDocument14 pagesLancet FQ PDFYesenia HuertaNo ratings yet
- Cystic FibrosisDocument14 pagesCystic FibrosisDday DonghaeNo ratings yet
- C Ystic Fibrosis (CF) : Learning Issues For Tutorial 2 Cheryl Tompkins, Group 6Document3 pagesC Ystic Fibrosis (CF) : Learning Issues For Tutorial 2 Cheryl Tompkins, Group 6k2m1b6ksNo ratings yet
- Theme1AppliedLecture2 BIO1A03Fall2022Document27 pagesTheme1AppliedLecture2 BIO1A03Fall2022proplayer910No ratings yet
- Leber's Hereditary Optic Neuropathy (LHON) : Clinical FeaturesDocument1 pageLeber's Hereditary Optic Neuropathy (LHON) : Clinical FeaturesDrbee10No ratings yet
- Cystic Fibrosis With Case StudyDocument27 pagesCystic Fibrosis With Case StudyAviva Tuteja100% (1)
- 16.5 Gene Therapy: 10.1 CoordinationDocument18 pages16.5 Gene Therapy: 10.1 Coordinationsohailnoreen5062No ratings yet
- Cystic Fibrosis: Pathophysiology of Lung DiseaseDocument12 pagesCystic Fibrosis: Pathophysiology of Lung DiseaseGaby RojasNo ratings yet
- Bases Da Fisiopatologia Da Diarreia (The Pathophysiology of Diarrhea)Document18 pagesBases Da Fisiopatologia Da Diarreia (The Pathophysiology of Diarrhea)MujiartiNo ratings yet
- Cystic Fibrosis 1Document4 pagesCystic Fibrosis 1Meigi MedikaNo ratings yet
- DR Montaha AL-Iede MD, DCH, FRACP Paediatric Pulmonologist & Sleep PhysicianDocument35 pagesDR Montaha AL-Iede MD, DCH, FRACP Paediatric Pulmonologist & Sleep PhysicianRasha Al MousaNo ratings yet
- Cystic Fibrosis Case StudyDocument8 pagesCystic Fibrosis Case StudyErjen Alexandria Sia100% (2)
- Cysticfibrosisdonebymyfriend 120218095057 Phpapp02Document28 pagesCysticfibrosisdonebymyfriend 120218095057 Phpapp02Elham AlwagaaNo ratings yet
- Cystic FibrosisDocument32 pagesCystic FibrosisSrm Genetics100% (1)
- CFTR Gene: Genetics Home ReferenceDocument6 pagesCFTR Gene: Genetics Home ReferenceserbusabinaNo ratings yet
- Chloride The Queen of ElectrolytesDocument9 pagesChloride The Queen of ElectrolytesYancy Erazo DoradoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Pa Tho Physiology of Aqueous Production and OutflowDocument34 pagesAnatomy and Pa Tho Physiology of Aqueous Production and OutflowChristine TanNo ratings yet
- Fibrosis Quística y Enfermedad PulmonarDocument9 pagesFibrosis Quística y Enfermedad PulmonarMELERYN CRISTY VELASQUEZ MOSTACERONo ratings yet
- The Epithelial Sodium Channel (Enac) As A Therapeutic Target For Cystic Fibrosis Lung DiseaseDocument17 pagesThe Epithelial Sodium Channel (Enac) As A Therapeutic Target For Cystic Fibrosis Lung DiseaseNeysa ArdraNo ratings yet
- European Journal of Internal Medicine: Shankar Kumar, Anand Tana, Anu ShankarDocument5 pagesEuropean Journal of Internal Medicine: Shankar Kumar, Anand Tana, Anu ShankarKeusch ONo ratings yet
- Jove Protocol 52438 Bile Duct Ligation Mice Induction Inflammatory Liver Injury FibrosisDocument11 pagesJove Protocol 52438 Bile Duct Ligation Mice Induction Inflammatory Liver Injury Fibrosis2m96k96vp8No ratings yet
- Cystic FibrosisDocument11 pagesCystic FibrosisSalsabila Putri AmrilNo ratings yet
- Cystic FibrosisDocument29 pagesCystic FibrosisAviva TutejaNo ratings yet
- 2020 Lec2Document7 pages2020 Lec2م.م.زينة عبد الحسينNo ratings yet
- Diseases of the Liver and Biliary TreeFrom EverandDiseases of the Liver and Biliary TreeAnnarosa FloreaniNo ratings yet
- Fibrosis Quística - NEJM02112023Document15 pagesFibrosis Quística - NEJM02112023Jesus A. Pineda GarciaNo ratings yet
- A Review of Trikafta: Triple Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulator (CFTR) Modulator TherapyDocument7 pagesA Review of Trikafta: Triple Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulator (CFTR) Modulator TherapySugi AntoNo ratings yet
- Fibrosis QuisticaDocument23 pagesFibrosis QuisticaGabriel ArayaNo ratings yet
- J of Gastro and Hepatol - 2001 - Strazzabosco - Pathophysiology of The Intrahepatic Biliary EpitheliumDocument10 pagesJ of Gastro and Hepatol - 2001 - Strazzabosco - Pathophysiology of The Intrahepatic Biliary EpitheliumJosé LeãoNo ratings yet
- Cystic Fibrosis - Dr. IonescuDocument60 pagesCystic Fibrosis - Dr. IonescuArleen MatincaNo ratings yet
- Cystic Fibrosis 0Document17 pagesCystic Fibrosis 0Mntdher EadanNo ratings yet
- Cystic FibrosisDocument6 pagesCystic FibrosisabdulNo ratings yet
- Secretin and Cystic FibrosisDocument6 pagesSecretin and Cystic FibrosisantonNo ratings yet
- Nbme 11 ExplainationDocument55 pagesNbme 11 Explainationazankhan9960% (10)
- Lawyer's OathDocument1 pageLawyer's OathRubz JeanNo ratings yet
- Sec 433Document1 pageSec 433Rubz JeanNo ratings yet
- II. The Court of Appeals Erred in Finding That There Can Be No Valid Partition Among The Heirs of The Late Efraim Santibañez Until After The Will Has Been ProbatedDocument1 pageII. The Court of Appeals Erred in Finding That There Can Be No Valid Partition Among The Heirs of The Late Efraim Santibañez Until After The Will Has Been ProbatedRubz JeanNo ratings yet
- The Assailed Court of Appeals Decision Is AFFIRMED. No Costs. So OrderedDocument1 pageThe Assailed Court of Appeals Decision Is AFFIRMED. No Costs. So OrderedRubz JeanNo ratings yet
- II. The Court of Appeals Erred in Finding That There Can Be No Valid Partition Among The Heirs of The Late Efraim Santibañez Until After The Will Has Been ProbatedDocument1 pageII. The Court of Appeals Erred in Finding That There Can Be No Valid Partition Among The Heirs of The Late Efraim Santibañez Until After The Will Has Been ProbatedRubz JeanNo ratings yet
- LawDocument1 pageLawRubz JeanNo ratings yet
- R 138Document1 pageR 138Rubz JeanNo ratings yet
- I. The Honorable Court of Appeals Erred in Finding That The Joint Agreement Should Be Approved by The Probate CourtDocument1 pageI. The Honorable Court of Appeals Erred in Finding That The Joint Agreement Should Be Approved by The Probate CourtRubz JeanNo ratings yet
- Art 1210Document1 pageArt 1210Rubz JeanNo ratings yet
- Penilla Vs AlcidDocument1 pagePenilla Vs AlcidRubz JeanNo ratings yet
- VDocument1 pageVRubz JeanNo ratings yet
- Fare LESS 5.00 Fare LESS 5.00Document2 pagesFare LESS 5.00 Fare LESS 5.00Rubz JeanNo ratings yet
- IVDocument1 pageIVRubz JeanNo ratings yet
- BBBDocument1 pageBBBRubz JeanNo ratings yet
- 1 W 1 SDHDocument6 pages1 W 1 SDHRubz JeanNo ratings yet
- Loss Borne by Proximate Source of NegligenceDocument1 pageLoss Borne by Proximate Source of NegligenceRubz JeanNo ratings yet
- RoleDocument1 pageRoleRubz JeanNo ratings yet
- CasaDocument1 pageCasaRubz JeanNo ratings yet
- Brown Sugar Glazed Pork ChopDocument1 pageBrown Sugar Glazed Pork ChopRubz JeanNo ratings yet
- VVVDocument1 pageVVVRubz JeanNo ratings yet
- FactsDocument2 pagesFactsamber3117No ratings yet
- ShouldersDocument1 pageShouldersRubz JeanNo ratings yet
- UncitralDocument16 pagesUncitralRubz JeanNo ratings yet
- Ramon A. Gonzales For Petitioner.: CRUZ, J.Document1 pageRamon A. Gonzales For Petitioner.: CRUZ, J.Rubz JeanNo ratings yet
- FFFFFDocument1 pageFFFFFRubz JeanNo ratings yet
- IIIDocument1 pageIIIRubz JeanNo ratings yet
- Deed of Sale With Pacto de Retro This Deed of Sale With Pacto de Retro Made and Executed by and BetweenDocument1 pageDeed of Sale With Pacto de Retro This Deed of Sale With Pacto de Retro Made and Executed by and BetweenRubz JeanNo ratings yet
- Title Vii - Commercial Contracts For TransportationDocument4 pagesTitle Vii - Commercial Contracts For TransportationRubz JeanNo ratings yet
- The Undersigned, Upon Sworn Complaint Filed by The Offended Party, Copy of Which Is Attached Hereto, AccusesDocument1 pageThe Undersigned, Upon Sworn Complaint Filed by The Offended Party, Copy of Which Is Attached Hereto, AccusesRubz JeanNo ratings yet
- PPPDocument1 pagePPPRubz JeanNo ratings yet