Professional Documents
Culture Documents
H 3.5 Notes Food Chain
Uploaded by
Madeleine AgiusCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
H 3.5 Notes Food Chain
Uploaded by
Madeleine AgiusCopyright:
Available Formats
Handout 3.
Our Environment
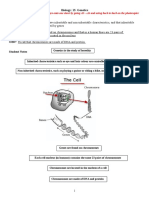
Different animals eat different things. Some animals eat plants. These are called herbivores. Some animals eat other animals. These are called carnivores. Some examples of herbivores include: deer, cows, horses, and some insects (grasshoppers, locusts). Some examples of carnivores include: lions, cheetahs, hyenas, and leopards. Some animals or insects eat both plant and other animals. These are called omnivores. Some examples of omnivores include: humans, chickens, rats, and cats. Producers in the environment are usually plants which use the suns rays in order to produce food for themselves. Consumers in the environment are usually animals which consume other plants and animals. Herbivores, carnivores and omnivores are consumers. Usually, herbivores are primary consumers, carnivores are secondary consumers, and omnivores are tertiary consumers. A food chain represents a linear sequence of links, which starts from a species which eats no other species in the web, with species that are not eaten by other species in the web. When linking two or more different food chains together, we get a food web. Below we can see an example of a food chain (left) and a food web (right). Note that the arrow points to the species which eats the species. For example: mouse ----------> snake, means that the snake eats the mouse.
You might also like
- Food Chains and Webs WorksheetsDocument10 pagesFood Chains and Webs Worksheetsitz tyreezyNo ratings yet
- Food Chains & Food Webs: DecomposersDocument14 pagesFood Chains & Food Webs: DecomposersGladys Claire BaguilatNo ratings yet
- Assign 2 - Food Chains and WebsDocument11 pagesAssign 2 - Food Chains and WebsRard Tangangco LozanoNo ratings yet
- Animal Hunting and FeedingDocument111 pagesAnimal Hunting and FeedingMyNo ratings yet
- The Food Chain vs. The Food Web - From Simple to Complex Systems | Children's Nature BooksFrom EverandThe Food Chain vs. The Food Web - From Simple to Complex Systems | Children's Nature BooksNo ratings yet
- Food WebDocument28 pagesFood WebLouie Jane EleccionNo ratings yet
- Food ChainDocument19 pagesFood ChainSonia Sánchez Barranco100% (1)
- Story StartersDocument7 pagesStory StartersMadeleine AgiusNo ratings yet
- Food Chain and Food WebDocument12 pagesFood Chain and Food Websriyoga100% (2)
- Food ChainsDocument5 pagesFood ChainsAishath NashwaNo ratings yet
- Chapter Zero BookDocument11 pagesChapter Zero BookShawna FisherNo ratings yet
- Food Chain PPT Final Report NewDocument28 pagesFood Chain PPT Final Report NewSreeja JsNo ratings yet
- Ecology Reading and ReviewDocument8 pagesEcology Reading and Reviewjohan preciadoNo ratings yet
- 6th Chapter 1 SolvedDocument2 pages6th Chapter 1 SolvedpardeeplusNo ratings yet
- Za NST 1683701260 Food Chains Cloze Procedure Activity - Ver - 1Document3 pagesZa NST 1683701260 Food Chains Cloze Procedure Activity - Ver - 1Harini NatashaNo ratings yet
- Food Chain and Food WebDocument8 pagesFood Chain and Food WebMarielle QuirayNo ratings yet
- Circle of Life ProjectDocument4 pagesCircle of Life Projectapi-238444838No ratings yet
- Food Chain and Food WebDocument3 pagesFood Chain and Food WebRenard Vince MalunesNo ratings yet
- What Animals EatDocument2 pagesWhat Animals EatlindileeNo ratings yet
- FoodDocument6 pagesFoodamrit123qsNo ratings yet
- gr4 wk27 What S For DinnerDocument26 pagesgr4 wk27 What S For Dinnerapi-250423071No ratings yet
- Producers and Consumers Are The Living Components of EcosystemsDocument6 pagesProducers and Consumers Are The Living Components of EcosystemsPaul Jeremy MendozaNo ratings yet
- Animals OdtDocument2 pagesAnimals OdtManishi PatelNo ratings yet
- Animals Are Living Things. They Can't Make Their Own FoodDocument11 pagesAnimals Are Living Things. They Can't Make Their Own Foodnisya pramitha sariNo ratings yet
- Matter and Energy PresentationDocument92 pagesMatter and Energy Presentationapi-25442847475% (4)
- The Food Chain Consists of Four Main PartsDocument3 pagesThe Food Chain Consists of Four Main PartskoiaitraazNo ratings yet
- InsectsDocument3 pagesInsectsSumaiya FaizalNo ratings yet
- Food Chains: Adapted by Yair Herrera FDocument11 pagesFood Chains: Adapted by Yair Herrera FyairherreraNo ratings yet
- Relationships of Organisms With One Another Biology 5090 NotesDocument18 pagesRelationships of Organisms With One Another Biology 5090 NotesBalakrishnan MarappanNo ratings yet
- Food Chains and Food WebsDocument5 pagesFood Chains and Food WebsJohn John AppleseedNo ratings yet
- Compassion Adaptation For FoodDocument27 pagesCompassion Adaptation For FoodPrachi UppalNo ratings yet
- Food ChainDocument8 pagesFood ChainMJ CorpuzNo ratings yet
- Interdependence of OrganismsDocument3 pagesInterdependence of OrganismsSabita SinghNo ratings yet
- Animals and Plants Are Linked by Food Chains .Document21 pagesAnimals and Plants Are Linked by Food Chains .saikripa121No ratings yet
- Ecology of LifeDocument10 pagesEcology of LifePaul Jeremy MendozaNo ratings yet
- What Is A Food Chain?Document1 pageWhat Is A Food Chain?Marlon Palattao CaragNo ratings yet
- Web and Chain FoodDocument3 pagesWeb and Chain FoodLorena Ruiz BenaventeNo ratings yet
- Animals Around Us DeleteDocument11 pagesAnimals Around Us DeletejugnoosamarNo ratings yet
- Food ChainDocument1 pageFood ChainSounak MukhopadhyayNo ratings yet
- What Is A Food ChainDocument2 pagesWhat Is A Food ChainLuzANgelaBAenaNo ratings yet
- Food Chain & WebDocument14 pagesFood Chain & WebJun Bryan AcobNo ratings yet
- Ficha 1. Whats For DinnerDocument2 pagesFicha 1. Whats For Dinneryolanda álvarez del viejoNo ratings yet
- Ecological MGTDocument42 pagesEcological MGTShakeerah SadeeqNo ratings yet
- Food ChainDocument1 pageFood ChainSpring GateNo ratings yet
- Food Chains PowerpointDocument11 pagesFood Chains PowerpointSantiaNo ratings yet
- Food ChainsDocument15 pagesFood ChainsFerdinand Abalos NamquiNo ratings yet
- What Is Food WebDocument1 pageWhat Is Food WebDashtan SalvosaNo ratings yet
- Ecology Part 2 Competition Predation Symbiosis Mutualism Commensalism or ParasitismDocument36 pagesEcology Part 2 Competition Predation Symbiosis Mutualism Commensalism or Parasitismapi-326376804No ratings yet
- These Notes Are For Learning and Not To Be Written in NotebookDocument4 pagesThese Notes Are For Learning and Not To Be Written in NotebookStepping PebblesNo ratings yet
- Principles and Concept of EcosystemDocument16 pagesPrinciples and Concept of EcosystemJay Bianca Abera Alistado100% (1)
- Ecosystems - Class 8 SyllabusDocument12 pagesEcosystems - Class 8 SyllabusMuhammad HaqNo ratings yet
- Nutrition and Mode of NutritionDocument2 pagesNutrition and Mode of NutritionRica NorcioNo ratings yet
- Energy PyramidDocument10 pagesEnergy PyramidganeshmamidiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Wildlife ConservationDocument7 pagesChapter 10 Wildlife ConservationMae SabuelvaNo ratings yet
- Concept of Food ChainDocument31 pagesConcept of Food ChainSachin ShrivastavNo ratings yet
- Essay On AnimalsDocument11 pagesEssay On AnimalsSwee Kwang TanNo ratings yet
- T SC 2549595 Ks1 Carnivores Herbivores and Omnivores Powerpoint Ver 5Document12 pagesT SC 2549595 Ks1 Carnivores Herbivores and Omnivores Powerpoint Ver 5Lauren ForresterNo ratings yet
- 4.12 WS - Food Chains and WebsDocument10 pages4.12 WS - Food Chains and WebsXue Li ChinNo ratings yet
- Trophic LevelsDocument4 pagesTrophic LevelsBaileyNo ratings yet
- ICT ProjectDocument2 pagesICT ProjectVineeta DattNo ratings yet
- B7 Food Webs ReadingDocument4 pagesB7 Food Webs ReadingMatt StromNo ratings yet
- Identification & Classificatiion of Organisms Identification & Classificatiion of OrganismsDocument1 pageIdentification & Classificatiion of Organisms Identification & Classificatiion of OrganismsMadeleine AgiusNo ratings yet
- Science Academic Celebration Activity Lab 1 Teachers ActivitiesDocument2 pagesScience Academic Celebration Activity Lab 1 Teachers ActivitiesMadeleine AgiusNo ratings yet
- Action Plan - DETENTIONDocument16 pagesAction Plan - DETENTIONMadeleine AgiusNo ratings yet
- ICTaDocument2 pagesICTaMadeleine AgiusNo ratings yet
- AQUARKDocument28 pagesAQUARKMadeleine AgiusNo ratings yet
- Wind or Insect Pollination? Teaching Notes and AnswersDocument2 pagesWind or Insect Pollination? Teaching Notes and AnswersMadeleine AgiusNo ratings yet
- Wind or Insect Pollination?: © WWW - Teachitscience.co - Uk 2014 22853 Page 1 of 3Document3 pagesWind or Insect Pollination?: © WWW - Teachitscience.co - Uk 2014 22853 Page 1 of 3Madeleine AgiusNo ratings yet
- End of Term 2 Study ListDocument4 pagesEnd of Term 2 Study ListMadeleine AgiusNo ratings yet
- Characteristics Are Controlled by GenesDocument4 pagesCharacteristics Are Controlled by GenesMadeleine AgiusNo ratings yet
- ChemistrySec4ExpressPreliminaryExam2011 P2Document213 pagesChemistrySec4ExpressPreliminaryExam2011 P2Madeleine AgiusNo ratings yet
- Exam Questions Ireland - GoodDocument25 pagesExam Questions Ireland - GoodMadeleine AgiusNo ratings yet
- Biology Higher Level: Namibia Senior Secondary CertificateDocument4 pagesBiology Higher Level: Namibia Senior Secondary CertificateMadeleine AgiusNo ratings yet