Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Normal Summary
Uploaded by
JiongHow Sosad0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views2 pages~
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document~
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
3 views2 pagesNormal Summary
Uploaded by
JiongHow Sosad~
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
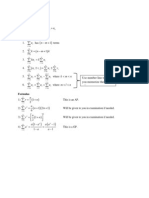
Normal Summary
X ~ N ( , 2 )
P ( a < X < b ) = normalcdf ( a, b, , )
P ( X < a) = p a = invNorm ( p, , ) This function can obtained by pressing
This function can obtained by pressing
Note: a) The TI-84 requires you to key in the standard deviation! b) To find P( X < a ) = P( < X < a ) . In the GC use -1E99 or 1099 to represent . c) Similarly, to find P( X > a ) = P(a < X < ) . Use 1E99 or 1099 to represent + . Standard Normal Distribution
Z ~ N 0,12
Given any normal distribution X ~ N ( ,
2
( )
x x <Z< 2 P ( x1 < X < x2 ) = P 1 2 We standardise when the or are unknown
Linear Combination Given X ~ N ( , 2 )
aX b ~ N ( a b, a 2 2 )
Addition and Subtraction of normal distributions 2 Given X ~ N ( x , x ) and Y ~ N ( y , y2 )
2 2 X Y ~ N ( x y , x + y )
Note the difference between 2 X and X1 + X 2 for variances Generally, 1. E ( aX b ) = a E ( X ) b 2. E ( X Y ) = E ( X ) E (Y ) 3. Var ( aX b ) = a 2 Var ( X ) 4. Var ( X Y ) = Var ( X ) + Var (Y )
Sample mean distribution
Given X =
X1 + X 2 + X 3 + n + Xn
. i.e the mean of n observations of X .
2 X ~ N , n
You might also like
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Recurrence SummaryDocument4 pagesRecurrence SummaryJiongHow SosadNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Graph Transformations: Translations, Reflections, Stretching and ShrinkingDocument8 pagesGraph Transformations: Translations, Reflections, Stretching and ShrinkingJiongHow SosadNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Vectors Summary PDFDocument10 pagesVectors Summary PDFJiongHow SosadNo ratings yet
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Summation SummaryDocument2 pagesSummation SummaryJiongHow SosadNo ratings yet
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Sampling Summary Sampling Methods Population Sample: Methods Process Advantages Disadvantages RandomDocument3 pagesSampling Summary Sampling Methods Population Sample: Methods Process Advantages Disadvantages RandomJiongHow SosadNo ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Maclaurin Series SummaryDocument1 pageMaclaurin Series SummaryJiongHow SosadNo ratings yet
- Graphs SummaryDocument2 pagesGraphs SummaryJiongHow SosadNo ratings yet
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Hypothesis Extra NotesDocument12 pagesHypothesis Extra NotesJiongHow SosadNo ratings yet
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Mathematical Induction Steps Summation Recurrence Relation ProofDocument2 pagesMathematical Induction Steps Summation Recurrence Relation ProofJiongHow SosadNo ratings yet
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Inequalities SummaryDocument6 pagesInequalities SummaryJiongHow SosadNo ratings yet
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Definite Integral SummaryDocument4 pagesDefinite Integral SummaryJiongHow SosadNo ratings yet
- Differentiation and Integration RelationDocument4 pagesDifferentiation and Integration RelationJiongHow SosadNo ratings yet
- Y X y X X X y y y X X y X X X: Differential EquationsDocument2 pagesY X y X X X y y y X X y X X X: Differential EquationsJiongHow SosadNo ratings yet
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Functions Summary: Domain RuleDocument2 pagesFunctions Summary: Domain RuleJiongHow SosadNo ratings yet
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Complex SummaryDocument8 pagesComplex SummaryJiongHow SosadNo ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- AP GP SummaryDocument2 pagesAP GP SummaryJiongHow Sosad100% (1)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Call DiagramsDocument1 pageCall DiagramsJiongHow SosadNo ratings yet
- Binomial and Poisson SummaryDocument1 pageBinomial and Poisson SummaryJiongHow SosadNo ratings yet
- Apps of Differentiation SummaryDocument4 pagesApps of Differentiation SummaryJiongHow SosadNo ratings yet
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- X N N NP X NP: Approximation SummaryDocument1 pageX N N NP X NP: Approximation SummaryJiongHow SosadNo ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Call DiagramsDocument2 pagesCall DiagramsJiongHow SosadNo ratings yet
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)