Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Mnemonics
Mnemonics
Uploaded by
Angelica Fontanilla Bajo RNOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Mnemonics
Mnemonics
Uploaded by
Angelica Fontanilla Bajo RNCopyright:
Available Formats
PEDIAOKE by Sir Renchie Cainglet Tila INFANT kung maglaro Solitary lagi, Stranger anxiety Weaning 6 months Aspiration
risk precaution On TODDLERHOOD naman Nega at Tantrums ginagawa Separation PRODESDEN May physio-logic anorexia pa Push pull toys like tarak tarak Autonomy vs. Shame and Doubt First dental visit ay 2 and a half Risk for poisoning problema jan PRESCHOOL naman ay PHALLIC Associative Play lagi ang gimik Common fear is mutilation Fear of dark and ghost din yun Behavior ay gender specific At may magi-cal thinking Ang patay is sleeping Initiative vs. guilt Ang SCHOOL AGE latent yan Concrete thinking, Logic reasoning Same sex stage, normal na bading Heroworship and plays competitive Schooler starts to have a bestfriend Takot parati control niya ay mag end Permanent ang concept of death Industry vs inferiority Formal ang adolescent Sa body image may disturbance Ang thelarche ang first sign sa girls At last sign yan ang menarche!
HYPOGLYCEMIA TIRED!!!! T Tired I Irritability (Nightmares) R Restlessness E Excessive Hunger (Polyphagia) D Depression/Diaphoresis
Anticholingergics Side Effects: Can't see Can't pee Can't spit Can't sh*t
Hyperthyroidism (s/s) THYROIDISM HYPERNATREMIA You are FRIED! F - Fever (low grade), flushed skin R - Restless (irritable) I - Increased fluid retention and increased BP E - Edema (peripheral and pitting) D - Decreased urinary output, dry mouth Tremor Heart rate up Yawning (fatigueability) Restlessness Oligomenorrhea & amenorrhea Intolerance to heat Diarrhea Irritability Sweating Muscle wasting & weight loss 5W's of common causes of post-op fever Pressure Ulcer Staging Stage I erythema Stage II breakdown of the dermis Stage III full thickness skin Breakdown Stage IV bones, muscles Wind (think pneumonia, splinting, incentive spirometer exercises not done, DB+ coughing NOT DONE) Water (dehydration...) Wound (infection, dehiscence...) Walking (PE...) Wonder drug (approriate antibiotic...)
HEART MURMURS: SPASM!! S Stenosis P Partial obstruction A Aneurysms S Septal defect M Mitral regurgitation
To apply a telemetry monitor: White over right (top right shoulder) Black beside the white (Over lt shoulder) Checkers (red below the black) Christmas (Green beside the red) Then ofcourse, the brown will be in the middle!
MI Management (MONA) Morphine O2 therapy Nitropglycerine! Aspirin Miotic: Little word= Little pupil (constrict) Mydriatic: Big word= Big pupil (dilated) SALT S Skin flushed A - Agitation L - Low-grade fever T - Thirst
5) All psychiatry drugs have anti cholinergic side effects: Dizziness, drowsiness, dry mouth, constipation, urinary retention M - Medications - ACE inhibitors, NSAIDS A - Acidosis - Metabolic and respiratory "CATS" of "HYPOCALCEMIA" C - Cellular destruction - Burns, traumatic injury H - Hypoaldosteronism, hemolysis C - Convulsions I - Intake - Excesssive A- Arrhythmias N - Nephrons, renal failure T - Tetany E - Excretion - Impaired S - Spasms and stridor The HYPERKALEMIA "Machine" - Causes of Increased Serum K+
R - Reduced breath sounds (& dypsnea) A - Absent fremitus X - X-ray shows collapse PNEUMONIA - risk factors INSPIRATION I - Immunosuppression N - Neoplasia S - Secretion retention P - Pulmonary oedema I - Impaired alveolar macrophages R - RTI (prior) A - Antibiotics & cytotoxics T - Tracheal instrumentation I - IV dug abuse O - Other (general debility, immobility) N - Neurologic impairment of cough reflex, (eg NMJ disorders)
Signs and Symptoms of Increased Serum K+: MURDER !! M - Muscle weakness U - Urine, oliguria, anuria R- Respiratory distress D - Decreased cardiac contractility E - ECG changes R - Reflexes, hyperreflexia, or areflexia (flaccid)
BLEEDING - S/Sx BEEP B - Bleeding gums E - Ecchymoses (bruises) E - Epistaxis (nosebleed) P - Petechiae (tiny purplish spots)
TETRALOGY OF FALLOT DISPLACED AORTA RIGHT VENTRICULAR HYPERTROPHY OPENING INTO THE SEPTUM (VSD) PULMONARY STENOSIS
CROUP - S/Sx SSS S - Stridor S - Subglottic swelling S - Seal-bark cough
HYPOKALEMIA (SUCTION) SKELETAL MUSCLE WEAKNESS U-WAVE ON ECG CONSTIPATION TOXICITY TO DIGOXIN IRREGULAR WEAK PULSE OTOSTASIS NUMBNESS PARESTHESIA
RESPIRATORY DEPRESSION inducing drugs STOP breathing S - Sedatives and hypnotics T - Trimethoprim O - Opiates P - Polymyxins
SHORTNESS OF BREATH - Causes AAAA PPPP A - Airway obstruction A - Angina A - Anxiety A - Asthma P - Pneumonia P - Pneumothorax P - Pulmonary Edema P - Pulmonary Embolus
General rules regarding psychiatry drugs: 1) Cannot be taken with alcohol, stimulants,depressants. 2) Cannot be given to pregnant, lactatingand patients with glaucoma. 3) Cannot be abruptly stooped but mus be tapered slowly 4) All are given after meals except anti anxiety agents( because food interferes with their absorption)
FEMORAL HERNIA FEMoral hernias are more common in FEMales.
PNEUMOTHORAX - S/Sx P-THORAX P - Pleuretic pain T - Trachea deviation H - Hyperresonance O - Onset sudden
"TRY PULLING MY AORTA":
Lactic acidosis Infections Tricuspid Necrosis of renal tubules (ATN) Pulmonary ET TUBE DELIVERABLE DRUGS Mitral O NAVEL: Aorta Oxygen Naloxone Atropine PLACENTA-CROSSING SUBSTANCES Ventolin (albuterol) "Want My Hot Dog": Epinephrine Lidocaine Wastes Antibodies Nutrients ATRIAL FIBRILLATION: CAUSES Teratogens OF NEW ONSET Microorganisms THE ATRIAL FIBS: Hormones/ HIV Drugs Thyroid Hypothermia Embolism (P.E.) EMERGENCY MEDICINE Alcohol ACTIVATED CHARCOAL: Trauma (cardiac contusion) CONTRAINDICATIONS Recent surgery (post CABG) CHEMICAL CamP: Ischemia Atrial enlargement Cyanide Lone or idiopathic Hydrocarbons Fever, anemia, high-output Ethanol states Metals Infarct Iron Bad valves (mitral stenosis) Caustics Stimulants (cocaine, Airway unprotected theo, amphet, caffeine) Lithium CAMphor SHOCK: S/SX Potassium (TV SPARC CUBE) Thirst Vomiting Sweating Pulse weak Anxious Respirations shallow/rapid Cool Cyanotic Unconscious BP low Eyes blank
"Shock, Shock, Shock, Everybody Shock, Little Shock, Big Shock, Momma Shock, Poppa Shock": Shock= Defibrillate Everybody= Epinephine Little= Lidocaine Big= Bretylium Momma= MgSO4 Poppa= Pocainamide
VFIB/VTACH DRUGS USED ACCORDING TO ACLS "Every Little Boy Must Pray": Epinephrine Lidocaine Bretylium Magsulfate Procainamide
DIABETIC KETOACIDOSIS MANAGEMENT (KING UFC) K+ (potassium) Insulin (5u/hour. Note: sliding scale no longer recommended in the UK) Nasogastic tube (if patient comatose) Glucose (once serum levels drop to 12) Urea (check it) Fluids (crytalloids) Creatinine (check it)/ Catheterize
IPECAC: CONTRAINDICATIONS 4 C's: Comatose Convulsing Corrosive hydroCarbon
COMPLICATIONS OF FALCIPARUM MALARIA (CHAPLIN) Cerebral malaria/ Coma Hypoglycemia Anaemia Pulmonary edema
VENTRICULAR FIBRILLATION: TREATMENT
NEUROLOGICAL FOCAL DEFICITS 10 S's: Sugar (hypo, hyper) Stroke Seizure (Todd's paralysis) Subdural hematoma Subarachnoid hemorrhage Space occupying lesion (tumor, avm, aneurysm, abscess) Spinal cord syndromes Somatoform (conversion reaction) Sclerosis (MS) Some migraines
RLQ PAIN: DIFFERENTIAL APPENDICITIS: Appendicitis/ Abscess PID/ Period Pancreatitis Ectopic/ Endometriosis Neoplasia Diverticulitis Intussusception Crohns Disease/ Cyst (ovarian) IBD Torsion (ovary) Irritable Bowel Syndrome Stones Acid-base"ROME" (Respiratory Opposite, Metabolic Equal) Acidosis Respiratory (opposite): pH Pco2 Metabolic(equal): pH HCO3 Alkalosis Respiratory (opposite): pH Pco2 Metabolic(equal): pH HCO3
Anorexia nervosa: clinical features"ANOREXIC" Adolescent women/ Amenorrhea NGT alimentation (most severe cases) Obsession with losing weight/ becoming fat though underweight Refusal to eat (5% die) Electrolyte abnormalities (e.g., K+, cardiac arrhythmia) X - ercise Intelligence often above average/ Induced vomiting Cathartic use (and diuretic abuse)
COMA: CONDITIONS TO EXCLUDE AS CAUSE MIDAS: Meningitis Intoxication Diabetes Air (respiratory failure) Subdural/ Subarachnoid hemorrhage
Appendicitis: assessment "PAINS" Pain (RLQ) Anorexia Increased temperature, WBC (15,00020,000) Nausea Signs (McBurney's, Psoas)
MALIGNANT HYPERTHERMIA TREATMENT "Some Hot Dude Better Give Iced Fluids Fast!" (Hot dude = hypothermia): Stop triggering agents Hyperventilate/ Hundred percent oxygen Dantrolene (2.5mg/kg) Bicarbonate Glucose and insulin IV Fluids and cooling blanket Fluid output monitoring/ Furosemide/ Fast heart [tachycardia]
Neurovascular Occlusion: symptoms "6 P's" Alcohol withdrawal: clinical features"HITS" Hallucinations (visual, tactile) Increased vital signs and insomnia Tremens delirium tremens (potentially lethal) Shakes/ Sweats/ Seizures/ Stomach pains (nausea, vomiting) Pain Pale Pulseless Paresthesia Poikilothermic Paralysis
Blood glucose (rhyme) Angina: precipitating factors "4E's" Eating Emotion Exertion (Exercise) Extreme Temperatures (Hot or Cold weather) Symptom Implication Cold and clammy . . . give hard candy Hot and dry . . . glucose is high
RESUSCITATION: BASIC STEPS ABCDE: Airway Breathing Circulation Drugs Environment
Blood vessels in umbilical cord"AVA" (2 arteries and 1 vein) Artery Vein Artery
Complication of severe preeclampsia"HELLP" syndrome Hemolysis Elevated Liver enzymes Low Platelet count
Coma: causes"A-E-I-O-U TIPS" Alcohol, acidosis (hyperglycemic coma) Epilepsy (also electrolyte abnormality, endocrine problem) Insulin (hypoglycemic shock) Overdose (or poisoning) Uremia and other renal problems Trauma; temperature abnormalities (hypothermia, heat stroke) Infection (e.g., meningitis) Psychogenic ("hysterical coma") Stroke or space-occupying lesions in the cranium
Cholecystitis: risk factors"5F's" Female Fat Forty Fertile Fair
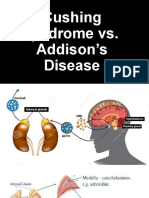
Cushing's syndrome: symptoms"3S's" Sugar (hyperglycemia) Salt (hypernatremia) Sex (excess androgens)
Cleft lip: nursing care plan (postoperative)"CLEFT LIP" Crying, minimize Logan bow Elbow restraints Feed with Brecht feeder Teach feeding techniques; two months of age (average age at repair) Liquid (sterile water), rinse after feeding Impaired feeding (no sucking) Positionnever on abdomen
Diet: low cholesterolavoid the "3C's" Cake Cookies Cream (dairy, e.g., milk, ice cream)
Hypertension: complications "4 C's" CAD (coronary artery disease) CHF (congestive heart failure) CRF (chronic renal failure) CVA (cardiovascular accident; now called brain attack or stroke) Hypertension: nursing care plan "I-TIRED" Intake and output (urine) Take blood pressure Ischemia attack, transient (watch for TIAs) Respiration, pulse Electrolytes Daily weight
Dystocia: etiology"3P's" Powe Passageway Passenger
Cognitive disorders: assessment of difficulties"JOCAM" Judgment Orientation Confabulation Affect Memory Dystocia: general aspects (maternal)"3P's" Psych Placenta Position
Diabetes: signs and symptoms"3P's,"
Episiotomy assessment "REEDA" Redness Edema Ecchymosis Discharge Approximation of skin
Hypoglycemia: signs and symptoms"DIRE" Diaphoresis Increased pulse Restless Extra hungry
Polydipsia (very thirsty) Polyphagia (very hungry) Polyuria (urinary frequency)
Infections during pregnancy "TORCH" Toxoplasmosis Other (hepatitis B, syphilis, group B beta strep) Rubella Cytomegalovirus Herpes simplex virus
Mental retardation: nursing care plan"3R's" Regularity (provide routine and structure) Reward (positive reinforcement) Redundancy (repeat)
Pain: assessment"PQRST" What Provokes the pain? What is the Quality of the pain? Does the pain Radiate? What is the Severity of the pain? What is the Timing of the pain?
Pain: management"ABCs" IUD: potential problems with use "PAINS" Period (menstrual: late, spotting, bleeding) Abdominal pain, dyspareunia Infection (abnormal vaginal discharge) Not feeling well, fever or chills String missing Newborn assessment components"APGAR" Appearance Pulse Grimace Activity Respiratory effort Ask about the pain Believe when clients say they have pain Choiceslet clients know their choices Deliver what you can, when you said you would Empower/Enable clients' control over pain
Obstetric (maternity) history "GTPAL" Manipulation: nursing plan promote the "3C's" Cooperation Compromise Collaboration Gravida Term Preterm Abortions (SAB, TAB) Living children
Postoperative complications: order "4W's" Wind (pulmonary) Wound Water (urinary tract infection) Walk (thrombophlebitis)
Medication administration"six rights" RIGHT medication RIGHT dosage RIGHT route RIGHT time RIGHT client RIGHT technique
Oral contraceptives: signs of potential problems"ACHES" Abdominal pain (possible liver or gallbladder problem) Chest pain or shortness of breath (possible pulmonary embolus) Headache (possible hypertension, brain attack) Eye problems (possible hypertension or vascular accident) Severe leg pain (possible thromboembolic process)
Preterm infant: anticipated problems"TRIES" Temperature regulation (poor) Resistance to infections (poor) Immature liver Elimination problems (necrotizing enterocolitis [NEC]) Sensory-perceptual functions (retinopathy of prematurity [ROP])
Melanoma characteristics"ABCD" Asymmetry Border Color Diameter
Psychotropic medications: common antidepressives (tricyclics)"VENT" Vivactil Elavil Norpramin Tofranil
Traction: nursing care plan "TRACTION" Trapeze bar overhead to raise and lower upper body Requires free-hanging weights; body alignment Analgesia for pain, prn Circulation (check color and pulse) Temperature (check extremity) Infection prevention Output (monitor) Nutrition (alteration related to immobility)
characteristic findings: Retrograde amnesia (recall of some old memories) Anterograde amnesia (ability to form new memories) Confabulation Korsakoff's psychosis SIGNS OF CANCER Change in bowel /bladder habits A sore that doesnt heal Unusual bleeding/ Discharge Thickening of lump breast or elsewhere Indigestion/ Dysphagia Obvious change in wart/ mole Nagging cough/ hoarseness Unexplained anemia Sudden weight loss
Schizophrenia: primary symptoms "4A's" Affect Ambivalence Associative looseness Autism
Sprain: nursing care plan"RICE" Rest Ice Compression Elevation
Trauma care: complications "TRAUMA" Thromboembolism; Tissue perfusion, altered Respiration, altered Anxiety related to pain and prognosis Urinary elimination, altered Mobility impaired Alterations in sensoryperceptual functions and skin integrity (infections)
FOCUS OF PATIENT CARE IN CLIENTS WITH CANCER Chemotherapy Assess body image disturbance (related to alopecia) Nutritional needs when N/V present Comfort from pain Effective response to Tx? (Evaluate) Rest (for patient and family)
Stool assessment"ACCT" Amount Color Consistency Timing
Tracheoesophageal fistula: assessment"3Cs" Coughing Choking Cyanosis
Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome (alcohol-associated neurological disorder)"COAT RACK" Wernicke's encephalopathy (acute phase) clinical features: Confusion Ophthalmoplegia Ataxia Thiamine is an important aspect of Tx
Location of the heart valve from right to left - "A Permanently Temperamental Man" Aortic Pulmonary Tricuspid Mitral
Transient ischemic attacks: assessment"3Ts" Temporary unilateral visual impairment Transient paralysis (one-sided) Tinnitus = vertigo
Korsakoff's psychosis (chronic phase)
"Cut C4, breathe no more" The 3rd, 4th and 5th cervical spinal nerves innervate the diaphragm.
Viruses causing diarrhea "ACNE CAR" Adeno virus Corana virus Norwak virus Entero virus Calci virus Astro virus Rota virus
Order of prevalence of White Blood Cells, most prevalent to least - "Never Let Monkeys Eat Bananas" Neutrophils Lymphocytes Monocytes Eosinophils Basophils
"Point and Shoot!" For remembering that Parasympathetics are involved with erection and Sympathetics with ejaculation.
The Krebs cycle - "Can I Actually See Some Filipina Mothers" Layers of the scalp - "SCALP" Skin Connective tissue Aponeurosis Loose areolar tissue Pericranium Citrate Isocitrate alpha Ketoglutarate Succinyl CoA Succinate Fumarate Malate Oxaloacetate
10 essential amino acids "PVT. TIM HALL" Phenylalanine Valine Tryptophan Threonine Isoleucine Metheonine Histidine(semi-essential) Arginine(semi-essential) Leucine Lysine
Carpal bones of the hand (lateral to medial) - "She Looks Too Proud, Try To Chase Her" Proximal row: Scaphoid Lunate Triquetrum Pisiform Distal row: Trapezium Trapezoid Capitate Hamate Bronchodilators - "TO A SIS" Terbutaline Orciprenaline Adrenaline Salbutamol Isoprenaline Salmeterol
Stages of mitosis/meiosis including interphase as a phase - "In Philippines, Men Are Talented" Interphase Prophase Metaphase Anaphase Telophase
Uses of Chloroquine (other than malaria) - "RED LIP" Rheumatoid arthritis Extra intestinal amoebiasis Discoid lupus erythematosus Lepra reaction Infectious mononucleosis Photogenic reactions
Signs of cor pulmonale "Please Read His Text" Peripheral edema Raised JVP Hepatomegaly Tricuspid incompetence
Portal hypertension features "ABCDE" Ascites Bleeding (hematemesis, piles) Caput medusae Diminished liver Enlarged spleen
Key questions needed in an emergency history taking situation - "AMPLE" Allergies Medication Past medical history Last meal Events and environment related to injury
Cardinal Symptoms of Parkinson's Disease - "TRAP" Tremor Rigidity Akinesia and bradykinesia Postural Instability
LATE SIGNS OF HYPOXIA BRADYCARDIA EXTREME RESTLESSNESS DYSPNEA CYANOSIS
Malignancies that metastisize to bone "Laging Panalo Kung Taga Bulacan" Lung Prostate Kidney Thyroid Breast
Days of appearance of rashesVaricella(chickenpox) "Very Sick Patients Must Take Double Exercise" 1st dayScarlet fever 2nd dayPox(smallpox) 3rd dayMumps 4th dayTyphus
CONGESTIVE HEART FAILURE DIGOXIN MORPHINE AMINOPHYLLINE DOPAMINE DIURETICS O2 GASSES MONITOR (ABG)
Six "S" in Scarlet Fever 5th dayDengue Streptococci causal organism Sorethroat Swollen tonsils Strawberry tongue Sandpaper rash miliarySudamina vesicles over hands, feet, abdomen 6th dayEnteric fever(typhoid)
MG SO4 TOXICITY BP DECREASE URINE OUTPUT DECREASE RESPIRATORY RATE DECREASE PATELLAR REFLEX ABSENT
SHOCK HYPOTACHYTACHY
Signs of anti-cholinergic crisis - "SLUD" Salivation Lacrimation Urination Defecation
HYPOTENSION TACHYPNEA TACHYCARDIA
SICKLE CELL DISEASE HYDRATION OXYGENATION PAIN INFECTION AVOID HIGH PLACES
INCREASE ICP HYPERBRADYBRADY CUSHINGS TRIAD: HYPERTENSION (WIDE PULSE PRESSURE) BRADYCARDIA BRADYPNEA
Causes of huge spleen - "3M's" Myelofibrosis Malaria Myelogenous leukemia
PREGNANCY INDUCED HYPERTENSION HEMOLYSIS ELEVATED LIVER ENZYMES LOW PLATELETS
EARLY SIGNS OF HYPOXIA RESTLESSNESS AGITATION TACHYCARDIA
GI SYMPTOMS AND TOXICITY TO DIGOXIN VOMITTING ANOREXIA NAUSEA DIARRHEA ABDOMINAL PAIN
ANTI TB DRUGS AND SIDE EFFECTS
RIFAMPICIN RED-ORANGE URINE ISONIAZID PERIPHERAL NEURITIS PYRAZINAMIDE INCREASE URIC ACID ETHAMBUTOL EYE PROBLEMS STREPTOMYCIN OTOTOXIC
FRACTURE PRESSURE REST ICE COMPRESSION ELEVATION
USE STRAW BECAUSE THESE DRUGS STAIN THE TEETH NEUROVASCULAR CHECK PAIN PULSELESSNESS PARESTHESIA PARALYSIS PALLOR L - LUGOL'S SOLUTION I - IRON N - NITROFURANTOIN T - TETRACYCLINE
LR6 - LATERAL RECTUS : CN6 SO4 - SUPERIOR OBLIQUE : CN4 VIRCHOWS TRIAD IN DVT VENUS STASIS DAMAGE TO VESSELS HYPERCOAGUABILITY ALL3 - ALL THE REST : CN3
ABDOMINAL AORTIC ANEURISM (4A) ASSYMPTOMATIC ABDOMINAL MASS ABDOMINAL PULSE ACHES LOW BACK
RADIATION TX VIA: MUSTARD ESTROGEN NITROGEN STEROIDS ANTIBIOTICS
DILUTE DECREASE OSMOLALITY
You might also like
- Lumbar Disc Herniation - Franco Postacchini - Springer Verlag Wien (1999)Document628 pagesLumbar Disc Herniation - Franco Postacchini - Springer Verlag Wien (1999)VineethJosephNo ratings yet
- PSY 3206 Health Psychology Final Exam Study GuideDocument14 pagesPSY 3206 Health Psychology Final Exam Study GuideShiv PatelNo ratings yet
- Ob Nursing BulletsDocument22 pagesOb Nursing BulletsDick Morgan FerrerNo ratings yet
- Print Outs PDFDocument7 pagesPrint Outs PDFShanine Alexia CordovezNo ratings yet
- Arellano Pharma HandoutDocument16 pagesArellano Pharma HandoutTimi BCNo ratings yet
- Communicablediseases 110227001506 Phpapp02 PDFDocument30 pagesCommunicablediseases 110227001506 Phpapp02 PDFCrystal Ann Monsale TadiamonNo ratings yet
- Moon Face Buffalo Hump Truncal ObesityDocument6 pagesMoon Face Buffalo Hump Truncal ObesityalvincabatoNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Nursing GastroDocument3 pagesPediatric Nursing GastronieacatleyaNo ratings yet
- PNLE 1 Part 3Document4 pagesPNLE 1 Part 3Ivan LouiseNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Nursing CA Sir Archie Alviz 04-09-2022Document3 pagesPediatric Nursing CA Sir Archie Alviz 04-09-2022Jonah MaasinNo ratings yet
- Nursing Practice V 2010Document16 pagesNursing Practice V 2010rexinne noahNo ratings yet
- Disease and Pathognomonic Signs ADocument7 pagesDisease and Pathognomonic Signs AMary Roan RonatoNo ratings yet
- Communicable Diseases: Chicken Pox (Varicella) Cholera (El Tor) Diptheria Gonorrhea (Drips) Meningitis Measles (Rubeola)Document3 pagesCommunicable Diseases: Chicken Pox (Varicella) Cholera (El Tor) Diptheria Gonorrhea (Drips) Meningitis Measles (Rubeola)ramon santosNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal Disorders: Care of The Patients With Altered MetabolismDocument6 pagesGastrointestinal Disorders: Care of The Patients With Altered MetabolismHazel BandayNo ratings yet
- Nclex EyesDocument9 pagesNclex EyesYoke W Khoo100% (1)
- Grand Coaching: Medical Surgical NursingDocument22 pagesGrand Coaching: Medical Surgical NursingEsarpy (Nana)No ratings yet
- Handouts Psych Prof. AlvizDocument2 pagesHandouts Psych Prof. AlvizKristine QuindozaNo ratings yet
- CDC Immunization 0-6 YrsDocument2 pagesCDC Immunization 0-6 Yrsxoxo318100% (1)
- July 2012 Pnle Pearls of Success Part 6: Medical and Surgical Health NursingDocument7 pagesJuly 2012 Pnle Pearls of Success Part 6: Medical and Surgical Health NursingNicole OrtegaNo ratings yet
- Renal FABS ONLINE RefresherDocument69 pagesRenal FABS ONLINE RefresherAu CassieNo ratings yet
- Oncology - Cancer PreventionDocument1 pageOncology - Cancer PreventionElla MejiaNo ratings yet
- Community Health Nursing - Mr. Jessie Daclis 9/26/19Document3 pagesCommunity Health Nursing - Mr. Jessie Daclis 9/26/19Jasmine JarapNo ratings yet
- Medical Surgical Nursing TionkoDocument40 pagesMedical Surgical Nursing TionkojeshemaNo ratings yet
- GIT DisordersDocument28 pagesGIT Disordersbpt2100% (1)
- Cardio, Respi, GastroDocument11 pagesCardio, Respi, Gastrojeshema100% (1)
- CHN TopicsDocument19 pagesCHN TopicsKristine AnaenNo ratings yet
- Haad QuestionDocument20 pagesHaad QuestionNimraj PatelNo ratings yet
- CHNDocument38 pagesCHNLouie John AbilaNo ratings yet
- Final Prof AdDocument13 pagesFinal Prof AdGaea Angela MACATANGAYNo ratings yet
- Nursing Seminar 1 SAS Session 8Document8 pagesNursing Seminar 1 SAS Session 8ZiaNo ratings yet
- Newborn CareDocument3 pagesNewborn CareBudoy WashupapiNo ratings yet
- Postpartum ExaminationDocument10 pagesPostpartum ExaminationKrystelle Jade LabineNo ratings yet
- Gastro Intestinal Disorders:: Kawasaki DiseaseDocument6 pagesGastro Intestinal Disorders:: Kawasaki DiseaseJoanna TaylanNo ratings yet
- Pedia-Reviewer CompleteDocument36 pagesPedia-Reviewer CompletePotato BroNo ratings yet
- Nursing Practice TestDocument4 pagesNursing Practice TestMarianne BaquilalaNo ratings yet
- Neurologic NursingDocument10 pagesNeurologic NursingAllisson Beckers100% (1)
- MS OncoDocument13 pagesMS Oncokobe.shohei1No ratings yet
- Module 6 - Medical - Surgical NursingDocument4 pagesModule 6 - Medical - Surgical NursingJohiarra TabigneNo ratings yet
- Post Test - Neuro - Dr. Arreglo (SC)Document2 pagesPost Test - Neuro - Dr. Arreglo (SC)Kristen FajilanNo ratings yet
- Ob Ward Rle Drug StudyDocument3 pagesOb Ward Rle Drug StudyArisza Shane B.No ratings yet
- PalmerDocument5 pagesPalmerHershey LerionNo ratings yet
- NCM 116, Cushing Syndrome, Addison's Disease, HypoDocument34 pagesNCM 116, Cushing Syndrome, Addison's Disease, HypoCindy Mamalangkas100% (1)
- IMPAC Alviz 1Document6 pagesIMPAC Alviz 1Yaj CruzadaNo ratings yet
- Cirrhosis NCLEX QuestionsDocument7 pagesCirrhosis NCLEX QuestionsShanice BedecirNo ratings yet
- Handouts Cardio RespiDocument8 pagesHandouts Cardio Respijon elleNo ratings yet
- 3 Post Test PediaDocument4 pages3 Post Test PediaJanine BaticbaticNo ratings yet
- LECTURE BY: Asst. Prof. Margaret M. Natividad, Ed.D., RN ImmunologyDocument21 pagesLECTURE BY: Asst. Prof. Margaret M. Natividad, Ed.D., RN ImmunologyZhantelle A. SantosNo ratings yet
- RENALDocument50 pagesRENALErikaNo ratings yet
- Pruritus PRURITIS Pruritis (Itching) Is One of The Most CommonDocument2 pagesPruritus PRURITIS Pruritis (Itching) Is One of The Most CommonFreeNursingNotesNo ratings yet
- Maternal and Child Nursing 4Document17 pagesMaternal and Child Nursing 4gellie100% (1)
- Nle Tips For OrthopedicDocument2 pagesNle Tips For OrthopedicCharie OcampoNo ratings yet
- TRA Pediatric Nursing 1Document4 pagesTRA Pediatric Nursing 1Gil GanibanNo ratings yet
- Cholera and SalmonellaDocument5 pagesCholera and SalmonellaJonas Marvin Anaque100% (1)
- PointersDocument49 pagesPointersStephanie Villanueva AdvinculaNo ratings yet
- Hospital Diets: Disorder/Condition Recommended DietDocument2 pagesHospital Diets: Disorder/Condition Recommended DietVin BitzNo ratings yet
- Top Up Training Center and Research Consultancy Communicable Disease NursingDocument3 pagesTop Up Training Center and Research Consultancy Communicable Disease NursingSTEFFI GABRIELLE GOLEZNo ratings yet
- PSYCHIATRICDocument8 pagesPSYCHIATRICSusan Loida SorianoNo ratings yet
- HW1 Pathognomonic SignsDocument1 pageHW1 Pathognomonic SignsBonjack ReyesNo ratings yet
- COMPREHENSIVE NURSING ACHIEVEMENT TEST (RN): Passbooks Study GuideFrom EverandCOMPREHENSIVE NURSING ACHIEVEMENT TEST (RN): Passbooks Study GuideNo ratings yet
- Hypernatremia Hyperkalemia: of Increased Serum K+Document3 pagesHypernatremia Hyperkalemia: of Increased Serum K+edited_chenNo ratings yet
- MnemonicsDocument4 pagesMnemonicsKarol Delagana67% (3)
- Article 1186 and 1187Document8 pagesArticle 1186 and 1187Richard Garcia0% (1)
- How To Save River Essay ReportDocument3 pagesHow To Save River Essay ReportRichard Garcia100% (1)
- MarketingDocument10 pagesMarketingRichard GarciaNo ratings yet
- Advertising and Promotion Midterms Ms Leslie PapaDocument1 pageAdvertising and Promotion Midterms Ms Leslie PapaRichard GarciaNo ratings yet
- MnemonicsDocument10 pagesMnemonicsRichard GarciaNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal Malignancies - New Innovative Diagnostics and Treatment PDFDocument712 pagesGastrointestinal Malignancies - New Innovative Diagnostics and Treatment PDFsun sealNo ratings yet
- Pharmacist Based KnowledgeDocument26 pagesPharmacist Based KnowledgePharmacist Ehab HammadNo ratings yet
- Survey Form For ThesisDocument4 pagesSurvey Form For ThesisChristine Joy PerionNo ratings yet
- Recomendacions ERC 2015 Resumo Executivo (Galego)Document100 pagesRecomendacions ERC 2015 Resumo Executivo (Galego)Leonel MeloNo ratings yet
- Clinical GuidlinesDocument200 pagesClinical GuidlinesMujtaba NadeemNo ratings yet
- Quality of Life Impairment in Depression and Anxiety DisordersDocument8 pagesQuality of Life Impairment in Depression and Anxiety DisordersRiham AmmarNo ratings yet
- Swine Diseases in PhilippinesDocument2 pagesSwine Diseases in PhilippinesRowel ManicapNo ratings yet
- Prelim MtlbeDocument6 pagesPrelim MtlbeRachel Ann Eromon100% (1)
- Study Data Reviewer's Guide: LDCP, Inc. Study LDCP-0242-005Document16 pagesStudy Data Reviewer's Guide: LDCP, Inc. Study LDCP-0242-005anon_181306460No ratings yet
- Surgical Patient Care - Improving Safety, Quality and ValueDocument926 pagesSurgical Patient Care - Improving Safety, Quality and ValueYen Ngo100% (2)
- Bholah Et Al-2017-Frontiers in PediatricsDocument14 pagesBholah Et Al-2017-Frontiers in PediatricsLeo MartinNo ratings yet
- Pre-Op Preparation and Assessment of Pediatric PatientsDocument62 pagesPre-Op Preparation and Assessment of Pediatric PatientsBedahanakugmNo ratings yet
- Scales of SedationDocument3 pagesScales of Sedationrajan kumar100% (2)
- Hyperemesis GravidarumDocument17 pagesHyperemesis GravidarumHo PingNo ratings yet
- Doctor X.ep01.480p.x264 (D Addicts)Document54 pagesDoctor X.ep01.480p.x264 (D Addicts)an006No ratings yet
- Methanol & Mushroom Intoxication: Sri SutarniDocument23 pagesMethanol & Mushroom Intoxication: Sri Sutarnik5ng8ntNo ratings yet
- NZ Crisis Handbook - DiagnosingDocument16 pagesNZ Crisis Handbook - DiagnosingSean SmythNo ratings yet
- Thesis LDDocument4 pagesThesis LDashishNo ratings yet
- Denail Codes PDFDocument16 pagesDenail Codes PDFAnonymous u47CziLINo ratings yet
- J PM AspirinDocument7 pagesJ PM AspirinkrisnawatiNo ratings yet
- White Island in The Red SeaDocument1 pageWhite Island in The Red SeaIndach RatnaNo ratings yet
- Health AOE Letter Student COVID Vaccination Age5 AboveDocument1 pageHealth AOE Letter Student COVID Vaccination Age5 AboveRockNo ratings yet
- NCP FormatDocument4 pagesNCP FormatCoreen Kaye TanNo ratings yet
- Cough Management: A Practical ApproachDocument13 pagesCough Management: A Practical ApproachJonathan OverianNo ratings yet
- Presented by Dr. Faisal Muttaqien: 12 February 08Document40 pagesPresented by Dr. Faisal Muttaqien: 12 February 08Faisal M100% (1)
- Platelet DisordersDocument12 pagesPlatelet Disorderstutor tujuhNo ratings yet
- Ex Part 1 Blueprinting Grid NewDocument1 pageEx Part 1 Blueprinting Grid NewKaushika KalaiNo ratings yet
- Transcanal Endoscopic Mastoid Surgery With Tympanoplasty For The Management of CholesteatomaDocument8 pagesTranscanal Endoscopic Mastoid Surgery With Tympanoplasty For The Management of CholesteatomaShawkat Kamal100% (1)