Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Write Up On Better Mixes
Uploaded by
Jack SullivanOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Write Up On Better Mixes
Uploaded by
Jack SullivanCopyright:
Available Formats
Static Mix
A static mix is the mix you get when you use only the volume faders and maybe the pan knobs. No EQ, no compression, no effects. Just volume faders and pan knobs. The goal is to give each instrument its place, both volume-wise and panning-wise
Signal to Noise Ratio (SNR)
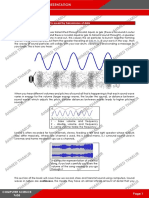
Signal to noise ratio is the ratio of level of the desired signal that a microphone records compared to the level of noise that it picks up from the background. The desired signal, which can be speech, music, etc. is the sound that a user wants recorded by the microphone. The noise in the background we want the microphone to record as little of this signal as possible. Signal to noise ratio is calculated by taking the level of the desired signal and subtracting from it the level of the noise signal. Decibels relative to full scale (dbfs) Is the measurement to how loud music is anything above 0db means that its clipping. You can keep on top of it by constantly checking your peak indication box which tells you the highest point the channel has hit in dbfs. Digital sound levels are measured in terms of how far they are below 0 dbs
Dynamic Range
is the ratio between the largest and smallest possible values of an audio file
Headroom is the difference between the peak level indication box in your stereo output under 0.db. When adding a new channel you are increasing the overall level of your output. So even if all your channels are under 0.db your overall output still could be clipping EQ / Frequency Spectrum Digital Distortion (as opposed to analogue)
You might also like
- Static Mix: Decibels Relative To Full Scale (DBFS)Document2 pagesStatic Mix: Decibels Relative To Full Scale (DBFS)Jack SullivanNo ratings yet
- Analog & Digital Sound.: Dy - Director (Engg) Nabm-BbsrDocument26 pagesAnalog & Digital Sound.: Dy - Director (Engg) Nabm-BbsrKamal Singh RajputNo ratings yet
- T4.2 Defined TermsDocument3 pagesT4.2 Defined TermsJonFromingsNo ratings yet
- Signal To Noise Ratio or SNRDocument5 pagesSignal To Noise Ratio or SNRTopherJosephNo ratings yet
- Digital Audio PrimerDocument90 pagesDigital Audio PrimerJumper KingNo ratings yet
- Music Technology: Digitalization of SoundDocument4 pagesMusic Technology: Digitalization of SoundfaheemNo ratings yet
- Unit 25 Sound RecordingDocument21 pagesUnit 25 Sound Recordingapi-480389176No ratings yet
- Sound #1Document28 pagesSound #1amalsharaf598No ratings yet
- How To Gain Stage Properly in Apple MainStageDocument5 pagesHow To Gain Stage Properly in Apple MainStageDavid KaeserNo ratings yet
- Adobe Audition Help - Digitizing AudioDocument3 pagesAdobe Audition Help - Digitizing AudioHansNo ratings yet
- The Essential Checklist: Preparing For MasteringDocument10 pagesThe Essential Checklist: Preparing For MasteringAlberto ChagasNo ratings yet
- 1.1.3 SoundDocument10 pages1.1.3 SoundGamer ManNo ratings yet
- Description Sound Level Example Sound Intensity: How Loud Is That?Document2 pagesDescription Sound Level Example Sound Intensity: How Loud Is That?NakkolopNo ratings yet
- 5-Audio Level & MeteringDocument18 pages5-Audio Level & MeteringMDDANISH KHANNo ratings yet
- 08 CompressorsDocument7 pages08 CompressorsAlex SantosNo ratings yet
- SoundDocument35 pagesSoundSandeep ThoniparambilNo ratings yet
- Denoiser: User ManualDocument8 pagesDenoiser: User ManualAlejandro OleaNo ratings yet
- FCP Audio PeakDocument6 pagesFCP Audio PeakmyfacebookloginNo ratings yet
- Digital AudioDocument4 pagesDigital Audiobudscamora8261No ratings yet
- PREamp & Level MetersDocument21 pagesPREamp & Level MetersGautham KarthikNo ratings yet
- Multimedia Digital AudioDocument7 pagesMultimedia Digital AudioMohammed Abdel Khaleq DwikatNo ratings yet
- SoundDocument21 pagesSoundRushilNo ratings yet
- Multimedia 4Document24 pagesMultimedia 4MohammedNo ratings yet
- Unit 25 - Sound Recording 1Document72 pagesUnit 25 - Sound Recording 1api-477227067No ratings yet
- Stu!o Terminology: Audio Interface: An Audio Interface Is Also Known As A Sound Card. Most Sound Cards Are InternalDocument6 pagesStu!o Terminology: Audio Interface: An Audio Interface Is Also Known As A Sound Card. Most Sound Cards Are InternalCharlotte BakerNo ratings yet
- RBassDocument10 pagesRBassDavid SantinhoNo ratings yet
- Sound ReinforcementDocument43 pagesSound Reinforcementshreya puthranNo ratings yet
- Understanding Microphone SensitivityDocument3 pagesUnderstanding Microphone SensitivityEric SkinnerNo ratings yet
- Unit 25 Sound Recording1 2Document15 pagesUnit 25 Sound Recording1 2api-500436700No ratings yet
- Basic Audio MeasurementDocument11 pagesBasic Audio MeasurementhadifarilaNo ratings yet
- A Level 1.1.3 SoundDocument15 pagesA Level 1.1.3 SoundGiorno GiovannaNo ratings yet
- What Is A DecibelDocument18 pagesWhat Is A DecibeledbaroNo ratings yet
- Digital Audio: Summary: SourcesDocument14 pagesDigital Audio: Summary: SourcesameliaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 11 Sound NotesDocument14 pagesLecture 11 Sound NotesmauraNo ratings yet
- 10B 11A Pyle PMXU128BT 12Ch Bluetooth Studio Mixer PDFDocument9 pages10B 11A Pyle PMXU128BT 12Ch Bluetooth Studio Mixer PDFwaleed.murad@gmail.comNo ratings yet
- Lecture5 SOUNDDocument26 pagesLecture5 SOUNDAdrean ChongNo ratings yet
- Mastering With LevelsDocument14 pagesMastering With LevelsSteveNo ratings yet
- 09 SoundDocument14 pages09 SoundCSE AP1No ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document68 pagesChapter 5ghimirekabin060No ratings yet
- 6-Audio Basics FileType MP3ComprDocument145 pages6-Audio Basics FileType MP3Comprعلی احمدNo ratings yet
- 01 MetersDocument6 pages01 MetersDom RaphaellNo ratings yet
- Multimedia System: Chapter Five: Basics of Digital AudioDocument42 pagesMultimedia System: Chapter Five: Basics of Digital Audiosolo IvorNo ratings yet
- Dynaudio Air Series Placement and Calibration Whitepaper2Document8 pagesDynaudio Air Series Placement and Calibration Whitepaper2Isone SoriesNo ratings yet
- Waves - Doubler Software Audio Processor User's GuideDocument6 pagesWaves - Doubler Software Audio Processor User's GuideTalkingStringsNo ratings yet
- SOUND Is Vibration in An Elastic Medium Word FileDocument7 pagesSOUND Is Vibration in An Elastic Medium Word Filesandeep BhanotNo ratings yet
- Audio Production.p101-149Document49 pagesAudio Production.p101-149James PlianoNo ratings yet
- EST Ignals: For Setting Up Subwoofer-Based SystemsDocument7 pagesEST Ignals: For Setting Up Subwoofer-Based SystemsDanny BlaisNo ratings yet
- Understanding Noise Figure: PDF VersionDocument12 pagesUnderstanding Noise Figure: PDF VersionFahim Ahmed AbbasiNo ratings yet
- Chapter4 SoundDocument35 pagesChapter4 SoundNik Muhammad Afiq AzlanNo ratings yet
- Technical JargonsDocument6 pagesTechnical JargonsDeepakNo ratings yet
- Digital Audio Coding - Dr. T. Collins: Standard MIDI Files Perceptual Audio Coding MPEG-1 Layers 1, 2 & 3 MPEG-4Document23 pagesDigital Audio Coding - Dr. T. Collins: Standard MIDI Files Perceptual Audio Coding MPEG-1 Layers 1, 2 & 3 MPEG-4Antony RajNo ratings yet
- Better MixesDocument2 pagesBetter MixestherealmmtNo ratings yet
- Audio Theory Basics PDFDocument10 pagesAudio Theory Basics PDFGolnaz AfsharNo ratings yet
- Acoustic TerminologyDocument4 pagesAcoustic Terminologyhagh_mostafa2787No ratings yet
- Tuning Your System: Tools For Sound Vol IDocument2 pagesTuning Your System: Tools For Sound Vol Imatheme2000No ratings yet
- Visdes FinalDocument379 pagesVisdes Finalmj fullenteNo ratings yet
- By The End of This Lecture Students Will Have Learned The FollowingDocument26 pagesBy The End of This Lecture Students Will Have Learned The FollowingRana WahabNo ratings yet
- Gain Staging Like A ProDocument1 pageGain Staging Like A ProcaavaradossiNo ratings yet
- What Is Loudness? - Sonarworks BlogDocument8 pagesWhat Is Loudness? - Sonarworks BlogCHakornNo ratings yet