Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lecture Single Phase Induction Motor
Lecture Single Phase Induction Motor
Uploaded by
ankit_elect27Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lecture Single Phase Induction Motor
Lecture Single Phase Induction Motor
Uploaded by
ankit_elect27Copyright:
Available Formats
19 May 2012 Study of Single Phase Induction Motor 1
Study of Single Phase Induction Motors
Teacher Ali A. Razzaq Al - Tahir
MSc. Electrical Power and Machines
ali.altahir@uokerbala.edu.iq
University of Kerbala
Collage of Engineering
Electrical and Electronic Engineering Department
ali.altahir@uokerbala.edu.iq /elearning/main
19 May 2012 Study of Single Phase Induction Motor 2
The Main Objectives for This Lecture are:
1- Construction of Single Phase I.M.
2- Practical Motor Applications.
3- The Principle of Operation for Single
Phase I.M.
4- Torque / Speed Characteristics.
5- Starting of Single Phase I.M.
19 May 2012 Study of Single Phase Induction Motor 3
References:
1- Electrical Machines Theory and Practice
by M.N. Bandyopadhyay, First
Edition,2007.
2- Electrical Machines and Drive Systems
by J.Hindmarsh, Third Edition, 1998.
19 May 2012 Study of Single Phase Induction Motor 4
Fig.(1)
1. The Principle of Operation for
Single Phase I.M.
19 May 2012 Study of Single Phase Induction Motor 5
1- Construction of Single Phase I. M
One is called main
winding .
The other is called
auxiliary winding or
starting winding.
The motor uses a squirrel
cage rotor, which has a
laminated iron core with
slots.
The single-phase I.M
motor stator has a
laminated iron core with
two windings arranged
perpendicularly.
Stator with laminated
iron core Slots with winding
Bars
Ring to short
circuit the bars Starting winding
+
_
Main winding
Rotor with
laminated
iron core
+
_
Fig.( 2): Single-Phase Induction
Motor.
19 May 2012 Study of Single Phase Induction Motor 6
1- Construction of rotor part Single
Phase Induction Motor
Fig.(3): Construction of Squirrel Cage Rotor for I.M
19 May 2012 Study of Single Phase Induction Motor 7
2- Practical Motor Applications
The single-phase induction machine is
the most frequently used for:
1. Refrigerators
2. Washing machines
3. Clocks
4. Drills
5. Pumps.
19 May 2012 Study of Single Phase Induction Motor 8
A single-phase A.C current supplies the
main winding that produces a pulsating
magnetic field.
Mathematically, the pulsating field could be
divided into two fields, which are rotating in
opposite directions.
The interaction between the fields and the
current induced in the rotor bars generates
opposing torque .
3- The Principle of Operation for
Single Phase I.M.
19 May 2012 Study of Single Phase Induction Motor 9
The interaction between
the fields and the current
induced in the rotor bars
generates opposing
torque.
Under these conditions,
with only the main field
energized the motor will
not start
However, if an external
torque moves the motor
in any direction, the
motor will begin to
rotate.
Starting winding
Main winding
+et -et
Main winding flux
Fig.(4) : Single-phase motor main winding
generates two rotating fields.
3- The Principle of Operation for
Single Phase I.M.
19 May 2012 Study of Single Phase Induction Motor 10
The pulsating filed is divided a forward
and reverse rotating field
Motor is started in the direction of
forward rotating field this generates
small (5%) positive slip
Reverse rotating field generates a
larger (1.95%) negative slip
sy m sy pos
n n n s ) ( =
sy m sy neg
n n n s ) ( + =
3- The Principle of Operation for Single Phase
I.M.
19 May 2012 Study of Single Phase Induction Motor 11
Starting Torque for Single Phase I.M
The single-phase I.M motor starting torque is zero
because of the pulsating single-phase magnetic flux.
The starting of the motor requires the generation of a
rotating magnetic flux similar to the rotating flux in
a three-phase motor.
Two perpendicular coils that have currents 90 out-
of-phase can generate the necessary rotating
magnetic fields which start the motor.
Therefore, single-phase I.M motors are built with
two perpendicular windings.
19 May 2012 Study of Single Phase Induction Motor 12
Electrical Equivalent Circuit
Each of the rotating fields induces a voltage in the rotor, which drives
current and produces torque.
An equivalent circuit, similar to the equivalent circuit of a three
phase motor, can represent each field
The parameters of the two circuits are the same with the
exception of the slip.
The two equivalent circuits are connected in series.
The current, power and torque can be calculated from the
combined equivalent circuit using the Ohm Law.
Fig.(5) shows the equivalent circuit of a single-phase motor in
running condition.
Input power: P in = I sta. * Vsta
Developed Power:
neg
neg
rot
pos
pos
rot
dev
s
s
R
s
s
R
P
+
=
1
2
1
2
2 2
neg pos
I I
19 May 2012 Study of Single Phase Induction Motor 13
Single Phase Induction Motor
Forward
rotating field
X
sta
/2
V
sta
I
sta
R
rot
(1-s
pos
)/(2s
pos
)
R
sta
/2
R
c
/2 X
m
/2
X
rot
/2 R
rot
/2
Reverse
rotating field
X
sta
/2
R
rot
(1-s
neg
)/(2s
neg
)
R
sta
/2
R
c
/2 X
m
/2
X
rot
/2 R
rot
/2
I
pos
I
neg
Fig(5): Equivalent circuit of a single-phase
motor in running condition.
I
C
Main
winding
Rotor
Centrifugal switch
V
Starting
winding
Fig.(6): Connection of Single-
Phase I.M motor.
19 May 2012 Study of Single Phase Induction Motor 14
Mathematical Calculations for
Single Phase Induction Motor
The results of the calculations are:
Input power:
Developed or output power:
*
sta sta in
I V S =
neg
neg
rot
pos
pos
rot
dev
s
s
R
s
s
R
P
+
=
1
2
1
2
2 2
neg pos
I I
19 May 2012 Study of Single Phase Induction Motor 15
5- Torque Speed Characteristic.
Operating Point
n
m
0.1rpm 1rpm , n
sy
.. :=
0 500 1000 1500
0
2
4
6
8
10
12
T
sm
n
m
( )
N m
T
m
n
m
( )
N m
T n
m
( )
N m
T
nom
N m
n
m
rpm
Starting winding
is disconnected
Main winding
generated torque
Combined main and
starting windings
generated torque
Fig.(6): Torquespeed
characteristic of a small
single-phase induction
motor.
19 May 2012 Study of Single Phase Induction Motor 16
6. Starting Torque for Single
Phase I.M
The single-phase I.M motor starting torque is zero
because of the pulsating single-phase magnetic flux.
The starting of the motor requires the generation of a
rotating magnetic flux similar to the rotating flux in
a three-phase motor.
Two perpendicular coils that have currents 90 out-
of-phase can generate the necessary rotating
magnetic fields which start the motor.
Therefore, single-phase I.M motors are built with
two perpendicular windings.
19 May 2012 Study of Single Phase Induction Motor 17
6: Single Phase Induction Motor
The phase shift is achieved by
connecting
a resistance,
an inductance, or
a capacitance
in series with the starting winding.
Most frequently used is a capacitor to
generate the starting torque.
19 May 2012 Study of Single Phase Induction Motor 18
6. connection diagram for Single
Phase Induction Motor
Figure 6. shows the
connection diagram of a
motor using a capacitor
to generate the starting
torque.
When the motor reaches
the operating speed, a
centrifugal switch turns
off the starting winding.
I
C
Main
winding
Rotor
Centrifugal switch
V
Starting
winding
Figure 6: Single-phase motor
connection.
19 May 2012 Study of Single Phase Induction Motor 19
6. Single Phase Induction Motor
The centrifugal switch is
necessary because most
motors use a cheap
electrolytic capacitor that
can only carry a.c current
for a short period of time.
A properly selected
capacitor produces
around 90 phase shift
and large starting torque.
I
C
Main
winding
Rotor
Centrifugal switch
V
Starting
winding
Figure 7: Single-phase motor
connection.
19 May 2012 Study of Single Phase Induction Motor 20
7. Torquespeed characteristic of a
small single-phase induction motor.
Operating Point
n
m
0.1rpm 1rpm , n
sy
.. :=
0 500 1000 1500
0
2
4
6
8
10
12
T
sm
n
m
( )
N m
T
m
n
m
( )
N m
T n
m
( )
N m
T
nom
N m
n
m
rpm
Starting winding
is disconnected
Main winding
generated torque
Combined main and
starting windings
generated torque
Figure 8:
Torquespeed
characteristic of
a small single-
phase induction
motor.
19 May 2012 Study of Single Phase Induction Motor 21
7. Shaded Pole Single Phase I.M
A less effective, but more economical method using
shaded pole I.M motors
The motor has two salient poles excited by a.c
current.
Each pole includes a small portion that has a short-
circuited winding. This part of the pole is called the
shaded pole.
The main winding produces a pulsating flux that
links with the squirrel cage rotor.
This flux induces a voltage in the shorted winding.
19 May 2012 Study of Single Phase Induction Motor 22
7. Single Phase Induction Motor
The induced voltage produces a current in the
shorted winding.
This current generates a flux that opposes the main
flux in the shaded pole (the part of the pole that
carries the shorted winding).
The result is that the flux in the unshaded and
shaded parts of the pole will be unequal.
Both the amplitude and the phase angle will be
different.
19 May 2012 Study of Single Phase Induction Motor 23
7. Single Phase Induction Motor
These two fluxes generate an unbalanced rotating
field. The field amplitude changes as it rotates.
Nevertheless this rotating field produces a torque,
which starts the motor in the direction of the shaded
pole.
The starting torque is small but sufficient for fans
and other household equipment requiring small
starting torque.
The motor efficiency is poor, but it is cheap
19 May 2012 Study of Single Phase Induction Motor 24
7. Concept of single-phase shaded
pole motor
The motor has two
salient poles excited
by a.c current.
Each pole includes a
small portion that has
a short-circuited
winding.
This part of the pole
is called the shaded
pole
Main winding
Shorted
coil
Unshaded
pole
Unshaded
pole
Shaded
pole
Shaded
pole
Shorted
coil
Squirrel cage
rotor
Figure 9: Concept of single-phase
shaded pole motor.
19 May 2012 Study of Single Phase Induction Motor 25
7. Shaded Pole Motor For
Household Fan.
Figure 10:
Shaded pole
motor for
household fan.
19 May 2012 Study of Single Phase Induction Motor 26 19 May 2012 Study of Single Phase Induction Motor 26
Key Points:
1- The most Widely used form of A.C motors is the single
phase induction motors.
2- The induced torque is zero if the motor rotates at the
synchronous speed.
3- Single phase induction motor is no - self starting torque
due to the pulsating magnetic field.
4- The main and auxiliary coils physically are
perpendicular in plane.
5- Capacitor start induction motor is used to increase the
starting torque to be greater than full load torque.
6- The principle of operation can be analyzed according
to double revolving field theory.
19 May 2012 Study of Single Phase Induction Motor 27
Q// Choose the Correct Answer for the Following :
1. The least expensive fractional horse power motor is . Motor
a) Shaded pole.
b) Capacitor start.
c) Split phase.
d) A.C series.
2. A (50) Hz, 4 pole single phase induction motor will have a synchronous
speed of
a) 1500 r.p.m.
b) 750 r.p.m.
c) 1200 r.p.m.
d) None of the above.
3. for the same rating, the efficiency of a single phase induction motor is
.. that of 3 phase induction motor.
a) Less than.
b) The same as.
c) More than.
d) None of the above.
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5814)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (845)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Netgear Dgn1000 UmDocument108 pagesNetgear Dgn1000 Umsatyakar_vvkNo ratings yet
- Chapter4 Synchronous MachinesDocument34 pagesChapter4 Synchronous Machinessatyakar_vvk100% (2)
- Lecture Notes ELE-B7: Ramadan El Shatshat Synchronous MachineDocument25 pagesLecture Notes ELE-B7: Ramadan El Shatshat Synchronous Machinesatyakar_vvkNo ratings yet
- Modeling of Synchronous Generators: 99% of The Electric Power Allover The World Is Generated by Synchronous GeneratorsDocument22 pagesModeling of Synchronous Generators: 99% of The Electric Power Allover The World Is Generated by Synchronous Generatorssatyakar_vvkNo ratings yet
- PDC Question PapersDocument56 pagesPDC Question Paperssatyakar_vvkNo ratings yet
- Control Systems Question PapersDocument76 pagesControl Systems Question Paperssatyakar_vvkNo ratings yet
- PS-1 Question PapersDocument98 pagesPS-1 Question Paperssatyakar_vvkNo ratings yet
- ECA-II Question PapersDocument86 pagesECA-II Question Paperssatyakar_vvkNo ratings yet
- Unit5 LMDocument13 pagesUnit5 LMsatyakar_vvkNo ratings yet
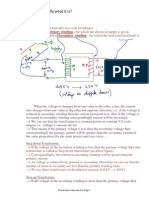
- Transformer-Basically What It IsDocument2 pagesTransformer-Basically What It Issatyakar_vvkNo ratings yet
- Induction Motor ModellingDocument4 pagesInduction Motor Modellingsatyakar_vvkNo ratings yet
- HVDC Unit-1Document88 pagesHVDC Unit-1satyakar_vvk100% (3)
- DC MotorsDocument64 pagesDC Motorssatyakar_vvk0% (1)