Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Medications
Uploaded by
api-240039124Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Medications
Uploaded by
api-240039124Copyright:
Available Formats
Ninety percent of patients with diabetes have Type 2 diabetes.
The cause of type 2 diabetes is complex and involves at least one of the four alterations in glucose metabolism. 1. Lack of insulin production from the beta cells in the pancreas 2. Tissues become resistant to the insulin produced 3. Impaired response of the beta cells in the pancreas to the blood glucose levels. 4. Increased production of glucose from the liver. Below is a table of medications used to treat type 2 diabetes and how they work. Drug Class Sulfonylurea Medications Glucotrol (Glipizide), Glyburide, DiaBeta, Amaryl (Glimperide) Metformin (glucophage) Acarbose (Precose), Migitol (Glyset) Pioglitazone (Actose), Rosiglitazone (Avandia) Mateglinide (starlix), Repaglinide (Prandin) Januvia (Sitagliptin), Onglyza (Saxagliptin) Byetta (exenatide), Victoza ( Liragltide) Function Increases the amount of insulin secreted by the pancreas and improves the binding of insulin to insulin receptors. Increases peripheral glucose uptake and utilization, improves the livers response to blood glucose levels so the liver produces appropriate amounts of glucose, and decreases the absorption of glucose by the intestines. Inhibit the absorption of complex carbohydrates from the small bowel. Improves glycemic control by improving insulin sensitivity. Depends on the presence of insulin for their action. Increases utilization of available insulin by the liver, muscle, and fat cells. Also reduce the amount of glucose produced by the liver. Increases the amount of insulin secreted by the pancreas Improves the effectiveness of insulin secreted by the pancreas in response to meals, and reduces the amount of glucose produced by the liver. Improves the effectiveness of insulin secreted by the pancreas in response to meals, and reduces the amount of glucose produced by the liver.
Biguanides Alpha-Glucosidase Inhibitors
Thiazolidinediones
Meglitinides DPP-4 inhibitor Incretins (Non-insulin Injections)
You might also like
- Diabetic Recipes for One and TwoFrom EverandDiabetic Recipes for One and TwoRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- INSULIN Dan Obat Hipoglikemik OralDocument35 pagesINSULIN Dan Obat Hipoglikemik OralSwietenia Rambu SabatiNo ratings yet
- DM DrugsDocument46 pagesDM DrugsQuinonez Anna MarieNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Mellitus.Document42 pagesDiabetes Mellitus.betablockers100% (1)
- Pancreatic Hormones & Antidiabetic DrugsDocument41 pagesPancreatic Hormones & Antidiabetic DrugsSaddamix AL OmariNo ratings yet
- Pharmacotherapy of DMDocument28 pagesPharmacotherapy of DMQueenElsaNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio 2 MojadoDocument10 pagesGen Bio 2 Mojadoraysa sepriaNo ratings yet
- Dr. Solomon Sathishkumar, MD Department of Physiology Christian Medical College Vellore, IndiaDocument48 pagesDr. Solomon Sathishkumar, MD Department of Physiology Christian Medical College Vellore, IndiaKrairat KomdeeNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Antidiabetic Drugs Pharmacy-IIDocument69 pagesUnit 1 Antidiabetic Drugs Pharmacy-IIAsad MirajNo ratings yet
- MBS2-K7-Pharmacology of Endocrine PancreasDocument55 pagesMBS2-K7-Pharmacology of Endocrine PancreasZoga Pratantia TohariNo ratings yet
- AntidiabetesDocument51 pagesAntidiabetesPuri Ratna KartiniNo ratings yet
- Drugs and The Endocrine System: Treatment of Diabetes MellitusDocument108 pagesDrugs and The Endocrine System: Treatment of Diabetes MellitusPnpplorangeNo ratings yet
- Intervention in T2Dm: Klinik Diabetes Terpadu Rs Islam KlatenDocument12 pagesIntervention in T2Dm: Klinik Diabetes Terpadu Rs Islam KlatenAdam HartonoNo ratings yet
- Insulin and Anti Diabetic DrugsDocument38 pagesInsulin and Anti Diabetic DrugsDharun Ranganathan100% (1)
- Obat Hipoglikemik Oral: Oleh: DhaneswaraDocument11 pagesObat Hipoglikemik Oral: Oleh: DhaneswaraDwiyanti SwandayaniNo ratings yet
- Insulin Dan Oral DiabetesDocument30 pagesInsulin Dan Oral DiabetesIrsan Fahmi ANo ratings yet
- Physiology of Diabetes: Dr. Solomon Sathishkumar. MDDocument36 pagesPhysiology of Diabetes: Dr. Solomon Sathishkumar. MDKhaled LajmiNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument4 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyBeRnAlieNo ratings yet
- Diabetes - Oral KnowledgeDocument19 pagesDiabetes - Oral KnowledgeKSeegurNo ratings yet
- Insulin PharmacologyDocument4 pagesInsulin PharmacologySunilNo ratings yet
- DM 1Document8 pagesDM 1Rose RigorNo ratings yet
- 08&09 Oral Hypoglycemics-Level 11Document48 pages08&09 Oral Hypoglycemics-Level 11Usman Ali AkbarNo ratings yet
- T2DM AgentsDocument57 pagesT2DM AgentsDUEÑAS, MARIELNo ratings yet
- Pancreatic Hormones & Antidiabetic Agents: A. InsulinDocument4 pagesPancreatic Hormones & Antidiabetic Agents: A. InsulinUsman Ali AkbarNo ratings yet
- IJAMSCR-17-223 - 426-433 Review On Adverse Drug Reaction of Antidiabetic Drugs PDFDocument8 pagesIJAMSCR-17-223 - 426-433 Review On Adverse Drug Reaction of Antidiabetic Drugs PDFtrupetiNo ratings yet
- Preop PBLD 2 Preoperative and Perioperative Glucose Management - PDF Instructor VersionDocument13 pagesPreop PBLD 2 Preoperative and Perioperative Glucose Management - PDF Instructor VersionhvNo ratings yet
- PHARMACARDS GonzagaDocument38 pagesPHARMACARDS GonzagaJay Marie GonzagaNo ratings yet
- Anti-Diabetic Drugs Part A-2Document35 pagesAnti-Diabetic Drugs Part A-2rimsha waseemNo ratings yet
- Oha in Diabetes ManagementDocument11 pagesOha in Diabetes ManagementAdam HartonoNo ratings yet
- Pharmacologic TheraphyDocument32 pagesPharmacologic TheraphyquinnNo ratings yet
- Insulin and The Oral HypoglycemicsDocument9 pagesInsulin and The Oral HypoglycemicsHasibNo ratings yet
- Drugs in Type 2 DMDocument18 pagesDrugs in Type 2 DMhussain AltaherNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Mellitus Type 11Document44 pagesDiabetes Mellitus Type 11MARICRIS NEBIARNo ratings yet
- ADO1 Agst 2013Document48 pagesADO1 Agst 2013blackjackNo ratings yet
- NRSE 3010 Chapter 47Document52 pagesNRSE 3010 Chapter 47Karina IvanchenkoNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Mellitus Type 2Document42 pagesDiabetes Mellitus Type 2alexandrajane2007No ratings yet
- Update On Diabetes Treatment - 2018Document33 pagesUpdate On Diabetes Treatment - 2018Nanda SalmasNo ratings yet
- ANTIDIABETICSDocument25 pagesANTIDIABETICSkookiescream100% (2)
- Pancreatic HormonesDocument41 pagesPancreatic HormonesBodea Doru100% (1)
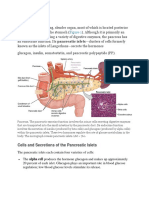
- Pancreas: Cells and Secretions of The Pancreatic IsletsDocument8 pagesPancreas: Cells and Secretions of The Pancreatic IsletsansahNo ratings yet
- Diabetic DrugsDocument38 pagesDiabetic Drugsbrianmuthomi851No ratings yet
- Insulin, Glucagon, and Diabetes Mellitus: Fatima Abdulwahid Ghadeer AlarayedhDocument22 pagesInsulin, Glucagon, and Diabetes Mellitus: Fatima Abdulwahid Ghadeer Alarayedhghadeer1No ratings yet
- For Nursing1604-212: Department of Physiology College of Medicine Imam Abdulrahman Bin Faisal UniversityDocument18 pagesFor Nursing1604-212: Department of Physiology College of Medicine Imam Abdulrahman Bin Faisal UniversityARAK AldarwishNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Mellitus (DM) : ContentDocument30 pagesDiabetes Mellitus (DM) : ContentMompati LetsweletseNo ratings yet
- CC 11 GlucoseDocument9 pagesCC 11 GlucoseJohn OgunsolaNo ratings yet
- InsulinDocument6 pagesInsulinAmbroseNo ratings yet
- Oral Hypoglycemic AgentsDocument31 pagesOral Hypoglycemic AgentsBivek Singh RathoreNo ratings yet
- Type I Diabetes MellitesDocument71 pagesType I Diabetes MellitesMuthu LakshmiNo ratings yet
- Diabetes MellitusDocument13 pagesDiabetes MellitusGeoffreyNo ratings yet
- Physiologic Response To Hypoglycemia in Healthy Individuals and Patients With Diabetes MellitusDocument14 pagesPhysiologic Response To Hypoglycemia in Healthy Individuals and Patients With Diabetes Mellitus11. Nguyễn Võ Như HuỳnhNo ratings yet
- Group 3 Concepcion Contacto Cordero Cornejo Cornell Cortez CruzDocument62 pagesGroup 3 Concepcion Contacto Cordero Cornejo Cornell Cortez CruzConcepcion Kevin ChuckNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Melitus Dan KomplikasinyaDocument60 pagesDiabetes Melitus Dan Komplikasinyahandiwijaya_85No ratings yet
- Diabetes MellitusDocument27 pagesDiabetes Mellitusuzzal ahmedNo ratings yet
- Insulin and Oral AntidiabeticsDocument24 pagesInsulin and Oral AntidiabeticsMirza Shaharyar Baig100% (1)
- Insulin, Glucagon, and Diabetes MellitusDocument22 pagesInsulin, Glucagon, and Diabetes Mellitusghadeer1No ratings yet
- Management of Diabetes MellitusDocument42 pagesManagement of Diabetes Mellitusayu ersa lestari100% (1)
- GI and Reproductive HormoneDocument74 pagesGI and Reproductive Hormonepranutan739No ratings yet
- Current Modalities in The Treatment of Non-Insulin Dependent DMDocument6 pagesCurrent Modalities in The Treatment of Non-Insulin Dependent DMSemir1989No ratings yet
- Diabetes Mellitus Final SibiDocument62 pagesDiabetes Mellitus Final SibiSibi JohnNo ratings yet
- Oral Antidiabetic AgentsDocument4 pagesOral Antidiabetic AgentsFendi Ali100% (1)