0% found this document useful (0 votes)
45 views2 pagesEssential Physics Equations Guide
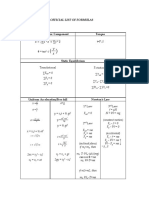
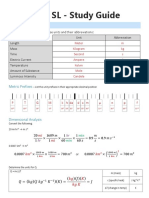
This document contains physics equations for motion, acceleration, force, work and energy, momentum, circular and rotary motion, waves, and other topics. It includes equations such as v = Δd/Δt for velocity, Fnet = ma for net force, W = Fd for work, p = mv for momentum, ac = v^2/r for centripetal acceleration, T = 1/f for period, and v = fλ for wave speed. Over 20 fundamental physics equations are listed without explanations.
Uploaded by
Syed Mairaj Ul HaqCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
45 views2 pagesEssential Physics Equations Guide
This document contains physics equations for motion, acceleration, force, work and energy, momentum, circular and rotary motion, waves, and other topics. It includes equations such as v = Δd/Δt for velocity, Fnet = ma for net force, W = Fd for work, p = mv for momentum, ac = v^2/r for centripetal acceleration, T = 1/f for period, and v = fλ for wave speed. Over 20 fundamental physics equations are listed without explanations.
Uploaded by
Syed Mairaj Ul HaqCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd