Professional Documents
Culture Documents
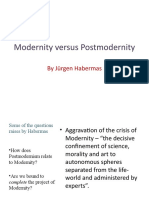
Key Questions:: Enquiry Into The Origins of Cultural Change, Oxford, Blackwell
Key Questions:: Enquiry Into The Origins of Cultural Change, Oxford, Blackwell
Uploaded by
Georgina RoyOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Key Questions:: Enquiry Into The Origins of Cultural Change, Oxford, Blackwell
Key Questions:: Enquiry Into The Origins of Cultural Change, Oxford, Blackwell
Uploaded by
Georgina RoyCopyright:
Available Formats
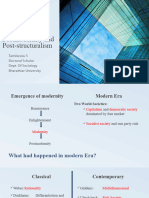
Postmodernity: Lecture Outline Key Questions: What does it mean to refer to Postmodernity and how has it been conceptualised?
ed? What are the theorised differences between Modernity and Postmodernity Can we see postmodernity in the world around us and how might it impact our everyday lives
Conceptualising Postmodernity Theoretically Historically and Politically Stylistically
Key Theorists: Lyotard - Abandoning Metanarratives Baudrillard - Simulation, Simulacra and Hyper-reality Harvey - Shift from Fordism to a "more flexible mode of accumulation" Butler - Identities Jameson - Late Capitalism Bauman - Liquid Modernity Giddens - High Modernity
Differences between Modernity and Post-Modernity, in terms of: Rationality and order Enlightenment and reason Progress, Production and Consumption Key Historical and Political Events
Postmodernity around us: Art, Architecture, Media, Identities, Culture.... etc...
Discussion Activities In small groups discuss each image in terms of what it might say about postmodernity in society. Images: Architecture, Shopping Malls, Human Rights, Style, Family life, Internet Networks, Sports, Non-western cultures Questions based on a reading from: Harvey, D. (1990) The Condition of Postmodernity: An Enquiry into the Origins of Cultural Change, Oxford, Blackwell. Watch a film Clip of The Matrix and discuss the ways in which the film reflects some of the ideas of postmodernism and postmodernity
Conclusions and Critiques Do you think we live in a Postmodern world? Critiques of Postmodernity
You might also like
- PostmodernismDocument36 pagesPostmodernismMuhammed Kaldırım100% (1)
- Cova - 1996 - The Postmodern Explained To Managers Implications For Marketing PDFDocument9 pagesCova - 1996 - The Postmodern Explained To Managers Implications For Marketing PDFrcmuellerNo ratings yet
- Introducing Baudrillard: A Graphic GuideFrom EverandIntroducing Baudrillard: A Graphic GuideRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (30)
- A Fad, A Cult of Jargon, or A Significant Intellectual Trend?Document12 pagesA Fad, A Cult of Jargon, or A Significant Intellectual Trend?JMannathNo ratings yet
- PostmodernismDocument31 pagesPostmodernismManal SaidNo ratings yet
- Modernity and ModernizationDocument34 pagesModernity and ModernizationAlvin Cabalquinto100% (1)
- Assignment: 05Document6 pagesAssignment: 05Lasantha AbeykoonNo ratings yet
- Postmodernism Theories, Theorists and TextsDocument65 pagesPostmodernism Theories, Theorists and Textsraybloggs75% (4)
- Chapter On PostmodernismDocument11 pagesChapter On PostmodernismAti SharmaNo ratings yet
- PostmodernismDocument36 pagesPostmodernismReid Nichols100% (2)
- Habermas and Giddens on Praxis and Modernity: A Constructive ComparisonFrom EverandHabermas and Giddens on Praxis and Modernity: A Constructive ComparisonNo ratings yet
- PostmodernismDocument36 pagesPostmodernismprabhajeswin100% (2)
- Giddens 1991 Chapter-1 ArvanitakisDocument13 pagesGiddens 1991 Chapter-1 ArvanitakisVaishali Venkatesh PrasadNo ratings yet
- PostmodernismDocument21 pagesPostmodernismveterensd100% (1)
- POSTMODERNISMDocument31 pagesPOSTMODERNISMmuhammad haris100% (3)
- What Is Post-Modern Conservatism: Essays On Our Hugely Tremendous TimesFrom EverandWhat Is Post-Modern Conservatism: Essays On Our Hugely Tremendous TimesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Introduction To PostmodernismDocument57 pagesIntroduction To Postmodernismmilkovicius100% (4)
- Marxist-Humanism in the Present Moment: Reflections on Theory and Practice in Light of the Covid-19 Pandemic and the Black Lives Matter UprisingsFrom EverandMarxist-Humanism in the Present Moment: Reflections on Theory and Practice in Light of the Covid-19 Pandemic and the Black Lives Matter UprisingsNo ratings yet
- Postmodernity Features: 12 Major Features of PostmodernityDocument8 pagesPostmodernity Features: 12 Major Features of PostmodernityAahmadNo ratings yet
- Modernisation and GlobalisationDocument27 pagesModernisation and GlobalisationDigvijay SahniNo ratings yet
- Media TheoristsDocument4 pagesMedia TheoristsMrsMellish100% (1)
- L.O: To Understand The Origins and Key Features of PostmodernismDocument11 pagesL.O: To Understand The Origins and Key Features of PostmodernismJane KnightNo ratings yet
- Douglas Kerner - in Search of The PostmodernDocument86 pagesDouglas Kerner - in Search of The PostmodernROWLAND PASARIBUNo ratings yet
- Postmdernism Theory: Abdulazim Ali N.Elaati 25-5-2016Document7 pagesPostmdernism Theory: Abdulazim Ali N.Elaati 25-5-2016NUSANo ratings yet
- Modernity Versus Postmodernity: by Jürgen HabermasDocument10 pagesModernity Versus Postmodernity: by Jürgen HabermasJasmin MedjedovicNo ratings yet
- Navigating The Complexities of PostmodernismDocument4 pagesNavigating The Complexities of PostmodernismMark Russel Sean LealNo ratings yet
- Postmodernism Theory: June 2016Document8 pagesPostmodernism Theory: June 2016khadijaNo ratings yet
- Abubakaer PDFDocument9 pagesAbubakaer PDFmuheabuki0No ratings yet
- Theorists - Important Media NotesDocument17 pagesTheorists - Important Media NotesShahana Zozo MegninNo ratings yet
- L.O: To Understand The Origins of Postmodernism To Identify The Key Features of PostmodernismDocument11 pagesL.O: To Understand The Origins of Postmodernism To Identify The Key Features of PostmodernismJane KnightNo ratings yet
- Cross Cultural 4Document50 pagesCross Cultural 4eecekaratasNo ratings yet
- SOC 505 Week 8Document6 pagesSOC 505 Week 8Eojin LeeNo ratings yet
- Postmodernity and PoststructuralismDocument16 pagesPostmodernity and PoststructuralismTamilarasuNo ratings yet
- RTA101 Week 7 Lecture NoteDocument3 pagesRTA101 Week 7 Lecture Notemingyuan.gaoNo ratings yet
- Postmodernism RevisedDocument4 pagesPostmodernism Revisedapi-510458728No ratings yet
- Post ModernismDocument13 pagesPost ModernismGAGAN ANANDNo ratings yet
- Classes - Sociological Diagnoses of Our Times (2) .Docx660f8c3f47e5018628Document4 pagesClasses - Sociological Diagnoses of Our Times (2) .Docx660f8c3f47e5018628kihumbamartin5No ratings yet
- Activity 3. Modernity and PostmodernityDocument11 pagesActivity 3. Modernity and PostmodernityRoberto DomínguezNo ratings yet
- Technology, Capital, and Virtuality: The Postmodern Condition of The MatrixDocument18 pagesTechnology, Capital, and Virtuality: The Postmodern Condition of The MatrixRoo_88No ratings yet
- Presentation1 PDFDocument7 pagesPresentation1 PDFShan RkhNo ratings yet
- Sociology KeyDocument38 pagesSociology KeyMuhammed EK NellikuthNo ratings yet
- Philosophies of Administrative Sciences: Postmodernism and System TheoryDocument11 pagesPhilosophies of Administrative Sciences: Postmodernism and System TheoryBabarSirajNo ratings yet
- Post ModernismDocument3 pagesPost ModernismMaham MaqsoodNo ratings yet
- Postmodern MarketingDocument16 pagesPostmodern MarketingAkeem AremNo ratings yet
- HASAN Hoca Midterm DERYADocument3 pagesHASAN Hoca Midterm DERYAMuzaffer Derya NazlıpınarNo ratings yet
- Postmodern Marketing and Its Impact On Traditional Marketing Approaches: Is Kotler Dead?Document5 pagesPostmodern Marketing and Its Impact On Traditional Marketing Approaches: Is Kotler Dead?AJHSSR JournalNo ratings yet
- ModernityDocument5 pagesModernityMuhammad usmanNo ratings yet
- Duke University PressDocument18 pagesDuke University PressHakan TopateşNo ratings yet
- The Politics of Bitcoin Software As Right Wing ExtremismDocument55 pagesThe Politics of Bitcoin Software As Right Wing ExtremismjustingoldbergNo ratings yet
- Modernism and Post ModernismDocument11 pagesModernism and Post ModernismBirce OzcanNo ratings yet
- Postmodernism PDFDocument1 pagePostmodernism PDFadin_obsangaNo ratings yet
- Allan - Classical Sociological Theory-Seeing The Social World 3rd Ed (2016)Document385 pagesAllan - Classical Sociological Theory-Seeing The Social World 3rd Ed (2016)dianaNo ratings yet
- Modernism Vs PostmodernismDocument2 pagesModernism Vs PostmodernismShan Fàn100% (1)
- On Postmodernism by Aijaz AhmadDocument36 pagesOn Postmodernism by Aijaz Ahmad5705robinNo ratings yet
- Definitions and Expressions of "Postmodernism": by Maria I. MartinezDocument3 pagesDefinitions and Expressions of "Postmodernism": by Maria I. MartinezNoel J HaNo ratings yet
- Postmodern Theory: Bryan C. TaylorDocument28 pagesPostmodern Theory: Bryan C. TaylorRamona Rizescu100% (1)
- Pasquinelli Radical MachinesDocument5 pagesPasquinelli Radical MachinesΑλέξανδρος ΓεωργίουNo ratings yet
- Post Modernity/modernismDocument7 pagesPost Modernity/modernismVarsha 왈사 RayNo ratings yet