0% found this document useful (0 votes)
56 views2 pagesZonal Cavity Lighting Design Guide
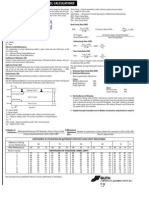
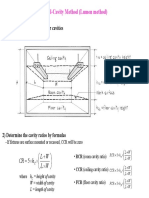
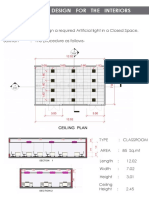
The document provides details for designing lighting in a laboratory space. The lab has dimensions of 30 feet by 20 feet by 10 feet high. It has a working plane of tables 3 feet above the floor. The ceiling and walls are highly reflective at 80% and 50% respectively. The floor is less reflective at 30%. The goal is to provide uniform 100 footcandle illumination using recessed luminaires in 5 continuous rows with a maximum 8 foot spacing. Calculations determine the zonal cavity coefficient of utilization is 0.48 based on the reflectances and room dimensions. This coefficient is used to calculate the number of luminaires needed, which is 25, to provide the desired 100 footcandles of illumination across the 60,000 square foot
Uploaded by
indira_tungCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
0% found this document useful (0 votes)
56 views2 pagesZonal Cavity Lighting Design Guide
The document provides details for designing lighting in a laboratory space. The lab has dimensions of 30 feet by 20 feet by 10 feet high. It has a working plane of tables 3 feet above the floor. The ceiling and walls are highly reflective at 80% and 50% respectively. The floor is less reflective at 30%. The goal is to provide uniform 100 footcandle illumination using recessed luminaires in 5 continuous rows with a maximum 8 foot spacing. Calculations determine the zonal cavity coefficient of utilization is 0.48 based on the reflectances and room dimensions. This coefficient is used to calculate the number of luminaires needed, which is 25, to provide the desired 100 footcandles of illumination across the 60,000 square foot
Uploaded by
indira_tungCopyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd