Professional Documents
Culture Documents
01 Transportation
Uploaded by
mohdhafizmdaliCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
01 Transportation
Uploaded by
mohdhafizmdaliCopyright:
Available Formats
CHAPTER 1: TRANSPORTATION
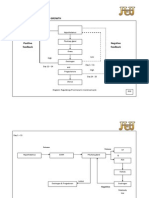
- initiated and coordinated by pacemaker
P1 P4 P5
Sinoatrial nodes (SA Nodes)
Atria Cause Wall
Atrial wall contract
Effect
blood pumped into ventricles
P3
SA nodes Spread
Generate electrical impulse
P2 P7 P8 P9 P10
Spread AV impulse Impulse reach
P6
Bundle branches Bundle of His fibres Throughout Purkinje fibres
Ventricles Cause Wall
Venrical Effect Contract
Blood pump out of ventricles to lungs and body
- controlled by: i. parasympathetic nerve slow down the pacemaker ii. sympathetic nerve speed up the pacemaker iii. hormone e.g: adrenaline
D1
Diagram: The pumping of the Heart
Change of BP
Baroreceptor } location: arch of aorta and carotid arteries
BP increases
Baroreceptor
BP decreases
Cardiovascular centre
Weaker cardiac muscles contraction Relax and widening (vasodilation) To lower the resistance of blood flow
Heart Smooth muscles of the arteries
Stronger cardiac muscles contraction Contract and narrowing (vasoconstriction) To higher the resistance of blood flow
Normal BP Diagram: How blood pressure is regulated
D2
Clumped platelets Damage cells Clotting factors in the plasma
Form activator: Thromboplastin vit K & Ca Prothrombin
+
Fibrinogen (soluble protein)
Thrombin
(inactive plasma protein)
(active plasma proptein)
Fibrin (insoluble protein)
Mesh (trapping RBC)
Scab D3
Diagram: Mechanisme of Blood Clotting
1. blood that enter the arterial end of a capillary is under high hydrostatic pressure 2. cause some of plasma diffuse blood capillaries to space between cells. 3. form Interstitial fluid 4. Content: all blood components except RBC, plasma protein, albumin, globulin, fibrinogen, platelets
5. Function: exchange materials between blood capillaries and cells occurs 6. 85% of the interstitial fluid re-enter blood circulation at the end of the venule 7. 15% diffused into lymphatic vessels 8. to form lymph 9. transported lymphatic system subclavian vein D4 12. blood circulatory system Diagram: Formation of Lymphatic system ileum 11. lacteal 10. diffuses fatty acids
glyserol
1. Surface of mesophyll covered with a thin layer of water 2. heat from the sun cause water on the external surface evaporate 3. saturating the air spaces 4. concentration water vapour compare in surrounding
5. water vapour evaporate and diffuse out through stomata 6. movement of air carry away water vapour
Root pressure Adjacent cell Root hair 4. diffuse 2. water osmosis 1. surrounding soil is hypotonic 3. hypotonic Cortex 5. moves inward through: i. cytoplasm ii. vacuole iii. cell walls 8. Create a pushing force that result the inflow of water into the xylem root pressure Capillary action 9. Cohesive force between water molecules draw up water in the xylem vessels 10. Adhesive force between water molecule and wall of xylem vessel Endodermis 6. has Cosparian strip block the water through cell wall Xylem vessel
7. moves inward through: i. cytoplasm ii. vacuole
Transpiration pull 11. water evaporates from the surface of the mesophyll cells into air spaces 12. the water evaporates into surrounding through stomata 13. the water is lost from mesophyll cell is replaced by water in the xylem Diagram: Transportation of water from soil to leaves D6
You might also like
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- pdf20201108 210815Document1 pagepdf20201108 210815mohdhafizmdaliNo ratings yet
- The Oxidation of D-Glucose To Glucaric Acid Using Au-C CatalystsDocument11 pagesThe Oxidation of D-Glucose To Glucaric Acid Using Au-C CatalystsmohdhafizmdaliNo ratings yet
- Strengthening Conceptual Connections in Introductory ChemistryDocument9 pagesStrengthening Conceptual Connections in Introductory ChemistrymohdhafizmdaliNo ratings yet
- Synergistic Effects of Bimetallic PtPd-TiO2 Nanocatalysts in Oxidation ofDocument54 pagesSynergistic Effects of Bimetallic PtPd-TiO2 Nanocatalysts in Oxidation ofmohdhafizmdaliNo ratings yet
- Establishing An Organic Chemistry Intuition For ElectrochemistryDocument11 pagesEstablishing An Organic Chemistry Intuition For ElectrochemistrymohdhafizmdaliNo ratings yet
- SainsDocument32 pagesSainsmohdhafizmdaliNo ratings yet
- Standard Practice Sampling ASTM D 5451-93Document2 pagesStandard Practice Sampling ASTM D 5451-93mohdhafizmdaliNo ratings yet
- Spiking Into Aqueous Samples: Standard Guide ForDocument6 pagesSpiking Into Aqueous Samples: Standard Guide Formohdhafizmdali100% (1)
- SainsDocument23 pagesSainsmohdhafizmdaliNo ratings yet
- Bubble Laplace LawDocument9 pagesBubble Laplace LawYu Shu HearnNo ratings yet
- Trial Kedah 2016 k2 PDFDocument20 pagesTrial Kedah 2016 k2 PDFmohdhafizmdaliNo ratings yet
- Mate PassyearDocument7 pagesMate PassyearmohdhafizmdaliNo ratings yet
- Probability 1Document7 pagesProbability 1azirawani100% (2)
- Introduction to the Basics of ScienceDocument8 pagesIntroduction to the Basics of ScienceAnonymous 7pbegA100% (2)
- 04 Production and GrowthDocument7 pages04 Production and GrowthFarah ZamriNo ratings yet
- Test Graphs of Functions 2Document2 pagesTest Graphs of Functions 2mohdhafizmdaliNo ratings yet
- Freeze Drying Guide in LAB PDFDocument10 pagesFreeze Drying Guide in LAB PDFjcamacho95No ratings yet
- Pre-Contract Study Guide for Insurance ExamDocument36 pagesPre-Contract Study Guide for Insurance Exammohdhafizmdali0% (2)
- Proofreading TipsDocument2 pagesProofreading TipsmohdhafizmdaliNo ratings yet
- Latihan Lines and AngelsDocument2 pagesLatihan Lines and AngelsAlnalyn A JamilNo ratings yet
- Microorganism Form 5 Chapter 1Document11 pagesMicroorganism Form 5 Chapter 1mohdhafizmdaliNo ratings yet
- Guidelines - Science FundDocument27 pagesGuidelines - Science FundzeyrieNo ratings yet
- SEO-Optimized Title for SPM 2013 Science Paper 1 Exam DocumentDocument52 pagesSEO-Optimized Title for SPM 2013 Science Paper 1 Exam DocumentHaspreet GillNo ratings yet
- Formula Matematik Dan Nota RingkasDocument9 pagesFormula Matematik Dan Nota RingkasPurawin Subramaniam100% (11)
- Pceia - Bi Full NotesDocument407 pagesPceia - Bi Full Notesmohdhafizmdali100% (3)
- 10 Tips For Responding To Reviewer - S and Editor - S CommentsDocument4 pages10 Tips For Responding To Reviewer - S and Editor - S CommentsmohdhafizmdaliNo ratings yet
- SN k2 Trial WP 2012 SkemaDocument8 pagesSN k2 Trial WP 2012 SkemamohdhafizmdaliNo ratings yet
- Form 5 Biology - Coordination&ResponseDocument16 pagesForm 5 Biology - Coordination&ResponseAcapSuiNo ratings yet
- Form 5 Biology - Coordination&ResponseDocument16 pagesForm 5 Biology - Coordination&ResponseAcapSuiNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Presented By: Ayu Aqilah Binti Khazani Nurul Dhiya Binti Hassannuddin Narisa Samaradhantia Supervisor: DR .Dr. Khalid Saleh SPPD-KKV, FinasimDocument34 pagesPresented By: Ayu Aqilah Binti Khazani Nurul Dhiya Binti Hassannuddin Narisa Samaradhantia Supervisor: DR .Dr. Khalid Saleh SPPD-KKV, Finasimekhysyifka0% (1)
- Interventional Cardiology 1133 Questions An Interventional Cardiology Board Review 3rd Edition 2019Document901 pagesInterventional Cardiology 1133 Questions An Interventional Cardiology Board Review 3rd Edition 2019Waleed Shabanh100% (1)
- OCC Nursing Case LetterDocument2 pagesOCC Nursing Case LetterJigesh JosephNo ratings yet
- CARDIODocument11 pagesCARDIOJenica SorianoNo ratings yet
- The Most CommonsDocument80 pagesThe Most CommonsJmee8No ratings yet
- Congestive Heart Failure LectureDocument102 pagesCongestive Heart Failure Lectureluke100% (1)
- Hipertensi JNC 8Document7 pagesHipertensi JNC 8Elisse StephanieNo ratings yet
- (HeartSim 200 DfU) - 982Document86 pages(HeartSim 200 DfU) - 982edgargadoNo ratings yet
- Inferior Myocardial InfarctionDocument25 pagesInferior Myocardial InfarctionAkbar IskandarNo ratings yet
- Heart Health GuideDocument7 pagesHeart Health GuideYAO CESAR KOFFINo ratings yet
- Clinical Experience With Affinity Pixie™ Oxygenation System in Paediatric and Infant PatientsDocument5 pagesClinical Experience With Affinity Pixie™ Oxygenation System in Paediatric and Infant Patientsفرید رضاییNo ratings yet
- Left Ventricle To Left Atrial Fistula Caused by Perforated Perivalvular AbscessDocument2 pagesLeft Ventricle To Left Atrial Fistula Caused by Perforated Perivalvular AbscessAlznoskillNo ratings yet
- Econdary ABCD (Airway, Breathing, Circulation, Differential Diagnosis)Document20 pagesEcondary ABCD (Airway, Breathing, Circulation, Differential Diagnosis)Nikol NataliaNo ratings yet
- Understanding CAD Risks and ProceduresDocument5 pagesUnderstanding CAD Risks and ProceduresNise Mon KuriakoseNo ratings yet
- BT Discourse Cohesion SVDocument3 pagesBT Discourse Cohesion SVToàn Lê ĐứcNo ratings yet
- Vital SignDocument40 pagesVital SignYoelBagusGiarto0% (1)
- Lesson 5 ECG BiopacDocument6 pagesLesson 5 ECG BiopacJavier VeintimillaNo ratings yet
- 2023 ESH Hypertension Guideline Update - Bringing Us Closer Together Across The Pond - American College of CardiologyDocument7 pages2023 ESH Hypertension Guideline Update - Bringing Us Closer Together Across The Pond - American College of Cardiologyhalticabral2022No ratings yet
- 3 - Vascualr DisordersDocument7 pages3 - Vascualr DisordersKatelinne DabucolNo ratings yet
- Mitral Valve SurgeryDocument2 pagesMitral Valve SurgeryLena MarieNo ratings yet
- Pdii Bipedal EdemaDocument5 pagesPdii Bipedal EdemacarlosNo ratings yet
- Non Rheumatic CarditisDocument13 pagesNon Rheumatic CarditisJavier SaadNo ratings yet
- Aortic StenosisDocument19 pagesAortic StenosisPraveen RamasamyNo ratings yet
- Critical Care Intravenous Infusion Drug Handbook 3rd EditionDocument61 pagesCritical Care Intravenous Infusion Drug Handbook 3rd Editionsharon.correia689100% (38)
- Clinical Features and Diagnosis of Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm - UpToDateDocument53 pagesClinical Features and Diagnosis of Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm - UpToDateALVARO ARIASNo ratings yet
- PPT Cardiovascular Disease in Pregnancy REVISEDDocument43 pagesPPT Cardiovascular Disease in Pregnancy REVISEDAdhe SetiawanNo ratings yet
- 2008 Tale of The Seven MaresDocument9 pages2008 Tale of The Seven MaresEduardo Alfredo Gutierrez PardoNo ratings yet
- Experience With A Chest Pain CenterDocument8 pagesExperience With A Chest Pain CenterGabriel Cadavid GilNo ratings yet
- Advanced Life Support Algorithm: Version: July 2016Document45 pagesAdvanced Life Support Algorithm: Version: July 2016Dwi RinaNo ratings yet
- Department of Clinical Biochemistry: Fasting Plasma GlucoseDocument2 pagesDepartment of Clinical Biochemistry: Fasting Plasma Glucosearavind sNo ratings yet