Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Miniature Flying Air Vechile
Uploaded by
shijo vadakkanOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Miniature Flying Air Vechile
Uploaded by
shijo vadakkanCopyright:
Available Formats
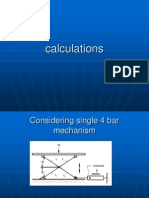
Three small scale flapping mechanisms capable of single plane flapping, flapping with active pitch control, and
flapping/pitch with out-of-plane movement were designed using SolidWorks air bearings Mylar aerodynamics, micro-electronics, sensors, micro-electromechanical systems, and micromanufacturing Air Force Institute of Technology (AFIT) and the Air Force Research Laboratory (AFRL) According to the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA), a MAV is a highly maneuverable aerial robot that has a maximum dimension or 150 mm and a gross weight of 100 grams bio-chemical sensing, targeting, tracking, deployment of small payloads to remote locations, along with many others we cannot even imagine today low cost, low weight, little to no logistical footprint, mission versatility, range, endurance, stealth, and precision remain relatively stationary, or hover, for any length of time. low Reynolds number flowfield characteristics The two primary 1 methods for achieving hovering flight on a small scale are accomplished by either rotary or flapping wings. There is no clear cut frontrunner as to which of the two methods would better lend itself to a MAV, however, it is known for helicopters that efficiency and the ability to tolerate wind gusts diminish as scale decreases On the other hand, one promising factor for a flapping-wing mechanism is that animals rely on the same principle to accomplish hovering flight in nature aerodynamic issues, designers will have to deal with complex wing kinematics, weight and volume constraints for actuators and power supplies, high propulsive power-to-weight ratio requirements, and the ability to operate in a wide range of environments It is clear that no man-made MAV has matched the performance and flying qualities of many small birds and insects found in nature. For this reason, it is no surprise that nature serves as an effective tool to study how a flapping-wing MAV should operate. There are two primary methods for hovering exhibited in nature, one type can be seen with a hummingbird and the other a dragonfly
The issue of what type of airflow a MAV will operate in, whether it be either turbulent or laminar, is dependent on the design and operating conditions photogrammetry
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Jurans TrilogyDocument12 pagesJurans Trilogyshijo vadakkanNo ratings yet
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Presenting The Smartest Cycle EverDocument20 pagesPresenting The Smartest Cycle Evershijo vadakkanNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Text Book of MedicineDocument26 pagesText Book of Medicineshijo vadakkanNo ratings yet
- Jayin CVDocument4 pagesJayin CVshijo vadakkanNo ratings yet
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Requirements of LDC ClerkDocument4 pagesRequirements of LDC Clerkshijo vadakkanNo ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Bio Data ModelDocument2 pagesBio Data Modelshijo vadakkanNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Resume For CompaniesDocument3 pagesResume For Companiesshijo vadakkanNo ratings yet
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Lec3 Robot TechnologyDocument19 pagesLec3 Robot TechnologyPriya SubramanianNo ratings yet
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- PSC Application Form DetailsDocument2 pagesPSC Application Form Detailsshijo vadakkanNo ratings yet
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- RC SUBMARINE: A Wireless Remote Controlled ModelDocument8 pagesRC SUBMARINE: A Wireless Remote Controlled Modelshijo vadakkan100% (1)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- ObccertDocument2 pagesObccertapi-280819942No ratings yet
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Real EssayDocument7 pagesReal Essayshijo vadakkanNo ratings yet
- Industrial TableDocument8 pagesIndustrial Tableshijo vadakkanNo ratings yet
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Designing and Fabrication of Mechanical PorterDocument14 pagesDesigning and Fabrication of Mechanical Portershijo vadakkanNo ratings yet
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (120)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)