Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ccnarouting 2
Ccnarouting 2
Uploaded by
israelsisisisiOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ccnarouting 2
Ccnarouting 2
Uploaded by
israelsisisisiCopyright:
Available Formats
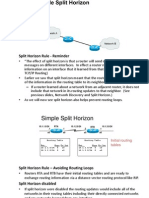
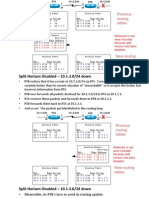
These metrics will be discussed later or in CCNP Advanced Routing, with their appropriate Routing Protocols: RIP hop
op count IGRP bandwidth, delay, reliability, load EIGRP bandwidth, delay, reliability, load OSPF bandwidth BGP attribute values and shortest path
Most routing algorithms can be classified as one of two basic algorithms: distance vector link state. The distance-vector routing approach determines the direction (vector) and the cost or metric (distance) to any link in the internetwork. RIP, IPX RIP and IGRP (CCNA) AppleTalk, RTMP and others (non-CCNA)
The link-state (also called shortest path first) approach re-creates the exact topology of the entire internetwork (or at least the portion in which the router is situated). OSPF IS-IS
The balanced hybrid approach combines aspects of the linkstate and distance-vector algorithms. These are really distance-vector routing protocols which apply some of the advantages of a link-state routing protocols, and also known as advanced-distance-vector routing protocols. EIGRP
When all routers in an internetwork are operating with the same knowledge, the internetwork is said to have converged. Fast convergence is a desirable network feature because it reduces the period of time in which routers would continue to make incorrect/wasteful routing decisions.
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5814)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (845)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- CCN A Routing 11Document5 pagesCCN A Routing 11israelsisisisiNo ratings yet
- CCN A Routing 12Document5 pagesCCN A Routing 12israelsisisisiNo ratings yet
- CCN A Routing 10Document4 pagesCCN A Routing 10israelsisisisiNo ratings yet
- Ccnarouting 8Document5 pagesCcnarouting 8israelsisisisiNo ratings yet
- Routing Loop ExampleDocument5 pagesRouting Loop ExampleisraelsisisisiNo ratings yet
- How Do Routers Learn About Other Networks and Determine The Best Routes To These Networks?Document5 pagesHow Do Routers Learn About Other Networks and Determine The Best Routes To These Networks?israelsisisisiNo ratings yet
- Next Round of Routing Updates: Then It Is Two Hops For You."Document5 pagesNext Round of Routing Updates: Then It Is Two Hops For You."israelsisisisiNo ratings yet
- Split Horizon RuleDocument5 pagesSplit Horizon RuleisraelsisisisiNo ratings yet
- Cellular Automata in MIDI Based Computer Music: Figure 1a: Wiring of Periodic Boundary Cells (Left and Right)Document8 pagesCellular Automata in MIDI Based Computer Music: Figure 1a: Wiring of Periodic Boundary Cells (Left and Right)israelsisisisiNo ratings yet
- Disaster Recovery&Business Continuity Related But NOT The Same Teri Stokes PHDDocument34 pagesDisaster Recovery&Business Continuity Related But NOT The Same Teri Stokes PHDisraelsisisisiNo ratings yet
- Ch. 6 - Routing Theory - Part 2 CCNA Semester 2: Originally by Rick Graziani, Instructor Modified by Prof. YousifDocument5 pagesCh. 6 - Routing Theory - Part 2 CCNA Semester 2: Originally by Rick Graziani, Instructor Modified by Prof. YousifisraelsisisisiNo ratings yet
- Adding Multiple Interface Support in NS-2Document72 pagesAdding Multiple Interface Support in NS-2israelsisisisiNo ratings yet