Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Two-Dimensional Harmonic Motion
Uploaded by
Tol Ralph Sab0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views5 pagesCFADA
Original Title
3. Two-Dimensional Harmonic Motion
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCFADA
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views5 pagesTwo-Dimensional Harmonic Motion
Uploaded by
Tol Ralph SabCFADA
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 5
TWO-DIMENSIONAL HARMONIC MOTION Session VII
CHEM 211 Quantum Chemistry 2nd Semester 2013-2014 Chemistry Department, College of Science & Technology, Adventist University of the Philippines Prof Laverne De Guzman Ladion
x, y
force constant along x axis kx force constant along y axis ky
r = r=
xi + yi
dr = dxi + dyi dt dt assume kx = ky dt xi + yi
Find: 1) L = ? 2) H = ?
r=
= dr = dxi i + dyi j dt dt dt
r = r(
,r)
j
= dr = dxi i + dyi j dt dt dt
2
l r ll r l cos =
2
+
+
2
2
T = mv2 = m ( 2 + 2) 2 2
U = kx2 2 + ky2 2
L = T - U L = m ( 2 + 2) - ( kx2 + ky2) 2 2 2
answer to # 1
for the 2-D Hamiltonian Equation of Motion:
the purpose is to eliminate and to show Px and Py let q1 = x coordinate q2 = y coordinate P1 = Px
(momentum along x axis) P2 = Py (momentum along y axis)
Px = L/ Px = m Px = m Py = L/ Py = m Py = m
H = + Pi - L = Px + Py - m(2+2) (kx2 +ky2)
2 2 2
= P2x + P2y - [._1_.P2x ._1_.P2y] = kx2 + ky2 m m 2m 2m 2 2
H = H(x,y,Px,Py,t)
You might also like
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Sample Land Use AgreementDocument1 pageSample Land Use AgreementTol Ralph SabNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
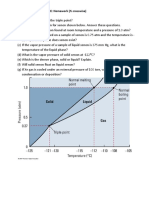
- Phychem 1 Lec-HW-phase DiagramDocument1 pagePhychem 1 Lec-HW-phase DiagramTol Ralph SabNo ratings yet
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- BIR EFPS JobAid For EnrollmentDocument12 pagesBIR EFPS JobAid For EnrollmentMark Lord Morales BumagatNo ratings yet
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- BDO Credit Card Online Application FormDocument2 pagesBDO Credit Card Online Application FormTol Ralph SabNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Catalytic Efficiency of Enzymes in Accelerating Metabolic ReactionsDocument27 pagesCatalytic Efficiency of Enzymes in Accelerating Metabolic ReactionsTol Ralph SabNo ratings yet
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Gimp TutDocument421 pagesGimp Tutpallavi_chopra_2No ratings yet
- One-Dimensional Harmonic MotionDocument4 pagesOne-Dimensional Harmonic MotionTol Ralph SabNo ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Gimp TutDocument421 pagesGimp Tutpallavi_chopra_2No ratings yet
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Mixxx ManualDocument101 pagesMixxx ManualJosephSetiawanNo ratings yet
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Hamiltonian Canonical Equation of MotionDocument5 pagesHamiltonian Canonical Equation of MotionTol Ralph SabNo ratings yet
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- In Uence of Organic Films On The Evaporation and Condensation of Water in AerosolDocument6 pagesIn Uence of Organic Films On The Evaporation and Condensation of Water in AerosolTol Ralph SabNo ratings yet
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- FileDocument2 pagesFileTol Ralph SabNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1aDocument8 pagesChapter 1aJan Angela Almiranes0% (1)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Science 2010 Ospelkaus 853 7Document6 pagesScience 2010 Ospelkaus 853 7Tol Ralph SabNo ratings yet
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Group 4 ReportDocument55 pagesGroup 4 ReportTol Ralph SabNo ratings yet
- Loven Ralph T. Sabellano: P1L7B7 Sta. Rosa Heights, Tagaytay Road, Putting Kahoy, Silang, 4118, CaviteDocument2 pagesLoven Ralph T. Sabellano: P1L7B7 Sta. Rosa Heights, Tagaytay Road, Putting Kahoy, Silang, 4118, CaviteTol Ralph SabNo ratings yet
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Loven Ralph T. Sabellano: P1L7B7 Sta. Rosa Heights, Tagaytay Road, Putting Kahoy, Silang, 4118, CaviteDocument2 pagesLoven Ralph T. Sabellano: P1L7B7 Sta. Rosa Heights, Tagaytay Road, Putting Kahoy, Silang, 4118, CaviteTol Ralph SabNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1aDocument8 pagesChapter 1aJan Angela Almiranes0% (1)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Nots Wla Dak DFDDFDocument1 pageNots Wla Dak DFDDFTol Ralph SabNo ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Boron FamilyDocument52 pagesBoron FamilyTol Ralph SabNo ratings yet
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Advanced InorganicDocument19 pagesAdvanced InorganicTol Ralph SabNo ratings yet
- Acquaintance Party DraftDocument3 pagesAcquaintance Party Draftluke014100% (3)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (120)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)