Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Intel's Pentium II III Processors
Intel's Pentium II III Processors
Uploaded by
divyeddOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Intel's Pentium II III Processors
Intel's Pentium II III Processors
Uploaded by
divyeddCopyright:
Available Formats
12/11/2008 Er.
Nikhil Marriwala 1
Intels PENTIUM-II / III
PROCESSORS
Presentation By :-
Er. Nikhil Marriwala
Er. Nikhil Marriwala 2
12/11/2008
TODAYS OBJECTIVES
LEARNING ABOUT 6th GENERATION
PROCESSORS
P-6 FAMILY PROCESSORS & THEIR
MAIN FEATURES
MAIN FEATURES OF P-II, P-III .
Er. Nikhil Marriwala 3
12/11/2008
ROAD MAP
6
th
GENERATION PROCESSORS
P-6 MAIN FEATURES
PROCESSORS IN P-6 CATEGORY
P-II, P-III MAIN FEATURES
THREE ENGINES COMMUNICATING
USING INSTRUCTION POOL
Er. Nikhil Marriwala 4
12/11/2008
6
th
Gen. Processor: P6
P6 Processor Variations:
Pentium Pro
Original P6 processor. L2 cache: 256kB, 512kB or 1MB (full-core speed)
Pentium II
P6 with L2-cache: 512kB (half-core speed)
Pentium II Xeon
P6 with L2-cache: 512kB/1MB/2MB (full-core speed)
Celeron
P6 without L2 cache
Celeron-A
P6 with L2-cache: 128kB on-die (full-core speed)
Pentium III
P6 with SSE (MMX2), L2-cache: 256kB on-die (half-core speed)
Pentium III Xeon
P6 with SSE (MMX2), L2-cache: 512kB/1MB/2MB on-die (full-core speed)
Er. Nikhil Marriwala 5
12/11/2008
P6: Main New Features...
Dual Independent Bus (DIB):
Two Separate Data Buses:
One system bus (motherboard)
One cache bus
Also called: back-side bus to the processor
Advantage: Speed of the cache is scalable to the
processor.
In contrast: P5 Cache-speed = motherboard-speed.
(thats why there is no P5 processor > 266MHz)
P6 processors: >1GHz
Er. Nikhil Marriwala 6
12/11/2008
P6: Main New Features...
Dynamic Execution
Multiple Branch Prediction
Predict the flow of the program through several branches.
Goal: Keep the instruction pipelines full.
Dataflow analysis
Detect opportunities for out-of-order instruction execution.
Goal: Optimize the use of the multiple superscalar execution
units.
Speculative execution
Execution of instructions in advance of the actual program
counter. Execute all available instructions in the instruction
pool. Store the results in temporary registers. Retirement
unit searches the instruction pool for completed instructions
that are no longer data dependent on other instructions. If
those instructions are found: Results are committed in the
order they were issued. Instruction are then retired from the
pool.
Er. Nikhil Marriwala 7
12/11/2008
P6: Main New Features...
Three-way superscalar:
P6 has at least six separate instruction units
up to 3 instructions in one cycle
Other new features:
A few new instructions
Enhanced multi-processor support
Only recent Windows Versions (NT/2000/XP) do
take full advantage of the P6s capabilities
Use optimising compilers
to make code as predictable as possible
Er. Nikhil Marriwala 8
12/11/2008
P6: Pentium Pro
Introduced: 11/1995
(before P5 MMX)
Outstanding feature:
Integrated L2 cache
Multi-chip module (MCM)
Dual-cavity PGA
2 silicon dies:
Processor & L2 cache (256kB,
512kB, 1MB)
5.5M + 63M = 68M transistors
Packaging = extremely
expensive !
Er. Nikhil Marriwala 9
12/11/2008
P6: Pentium II
Introduced: 05/1997
Abandoned: chip-in-a-socket
Introduced: 242-pin SEC cartridge
Much less expensive to manufacture
(at the time!)
Er. Nikhil Marriwala 10
12/11/2008
P6: Pentium II
Processor core speeds: 233-450MHz
Bus speeds: 66-100MHz
7.5M transistors. 0.25/0.35 m BiCMOS.
MMX
Power dissipation up to >40W!
Heatsinks and fans required!
A-bus: 36b
Addressable: 64GB
L2 cache
Half core-speed.
Supports up to 512MB
Er. Nikhil Marriwala 11
12/11/2008
P6: Celeron
Cheaper packaging (SEP)
No fancy plastic cartridge
Specifically designed for lower-cost PCs
L2 cache support up to 4GB of RAM
MMX
L1 cache: 2* 16kB
Integral thermal diode for temperature monitoring
0.25/0.18 m technology
Er. Nikhil Marriwala 12
12/11/2008
P6: Pentium III
Introduced: 02/1999
28M transistors
0.18 m coppermine technology
Interconnect: Copper rather than
Aluminum/Tungsten to reduce signal diffusion
Major improvements:
SSE (Streaming SIMD Extensions)
Integrated on-die L2 cache
Available up to 1GHz
Er. Nikhil Marriwala 13
12/11/2008
7
th
Gen. Processor: Pentium 4
Introduced: 11/2000. Also called Net Burst
Main technical details:
Core speed range 1.3GHz..>3GHz?
42M transistors. 0.18 m and 90nm
System (front-side) bus: up to 800MHz
ALU runs at twice the processor core frequency
Hyper-pipelined 20-stage technology
Very deep out-of-order instruction execution
20kB L1 cache. 256kB full-speed L2-cache. 8-way set
associative. L2 supports up to 4GB RAM and ECC.
SSE2 144 new SSE2 instructions
Socket 432. Up to 64W of power dissipation.
Er. Nikhil Marriwala 14
12/11/2008
Pentium 4
Pentium 4 Extreme Edition
Main Features
90nm technology
fclk=3.73GHz
FSB: 1066MHz
L2: 2MB
Socket: LGA775
Chipset: 925XE
Express
Er. Nikhil Marriwala 15
12/11/2008
P6 Family of processors: Pentium Pro,
Pentium II & Pentium III
Major features:
Dynamic program execution
Three 12-stage pipelines
On-chip FPU
Separate L1 code and data caches
with write-back strategy
Out-of-order completion of
instructions
Data forwarding
Dynamic Branch Prediction
Er. Nikhil Marriwala 16
12/11/2008
Speculative Program Execution
Multiprocessing with up to four processors with no
additional logic .
Address bus widened to 36 bits physical address
space of 64Gbytes enabled by new bit in CR4
New functions CMOVcc for conditional MOVs
Integrated L2-cache, within the same package,
connected over a dedicated bus running at the full
(or half ) CPU clock
Major Features ( contd. )
Er. Nikhil Marriwala 17
12/11/2008
Major Features ( contd. )
Pentium II & Pentium III: New MMX
instructions for enhanced floating point
operation when doing graphics
Pentium III: SIMD extensions for
enhanced high speed graphics
Dramatic increases in clock
frequencies supported
A block diagram of the Pentium Pro is
given ahead.
Er. Nikhil Marriwala 18
12/11/2008
Major Features ( contd. )
Three-way superscalar, pipelined micro-architecture.
Decoupled, multi-stage super pipeline,
Pentium II has twelve stages (with a pipe stage time
33 percent less than the Pentium processor)
==> a higher clock rate on any given
manufacturing process.
==> less work per pipe stage for more stages.
The Pentium Pro, Pentium II and III processors use
basically the same dynamic execution (i.e. out-of-order
superscalar) microarchitecture principles.
Er. Nikhil Marriwala 19
12/11/2008
Major Features ( contd. )
A wide instruction window using an
instruction pool.
Execute phase is replaced by decoupled
issue, execute, and retire phases.
instruction execution is started in any
order but always be retired in the
original program order.
Processors in the P6 family may be
thought of as three independent engines
coupled with an instruction pool.
Er. Nikhil Marriwala 20
12/11/2008
P6 family of Processors
The P6 family of processors use a dynamic execution
micro-architecture. This three-way superscalar, pipelined
micro-architecture features a decoupled, multi-stage super-
pipeline, which trades less work per pipe stage for more
stages.
A P6 family processor, for example, has twelve stages with
a pipe stage time 33 percent less than the Pentium
processor, which helps achieve a higher clock rate on any
given manufacturing process.
The approach used in the P6 family micro-architecture
removes the constraint of linear instruction sequencing
between the traditional fetch and execute phases, and
opens up a wide instruction window using an instruction
pool.
Er. Nikhil Marriwala 21
12/11/2008
P6 family of Processors
This approach allows the execute phase of the processor
to have much more visibility into the program instruction
stream so that better scheduling may take place.
It requires the instruction fetch/decode phase of the
processor to be much more efficient in terms of predicting
program flow. Optimized scheduling requires the
fundamental execute phase to be replaced by decoupled
dispatch/execute and retire phases.
This allows instructions to be started in any order but
always be completed in the original program order.
Processors in the P6 family may be thought of as three
independent engines coupled with an instruction pool as
shown in Figure .
Er. Nikhil Marriwala 22
12/11/2008
Three Engines Communicating Using an
Instruction Pool
Er. Nikhil Marriwala 23
12/11/2008
CONCLUSION
Today's objectives have been achieved
which were ,
LEARNING ABOUT 6th GENERATION
PROCESSORS
P-6 FAMILY PROCESSORS & THEIR
MAIN FEATURES
MAIN FEATURES OF P-II, P-III .
Er. Nikhil Marriwala 24
12/11/2008
Queries
Any questions related to the topic
can be mailed to me at
Or can sought out here only in the
class.
Queries
nikhilmarriwala@hotmail.com
You might also like
- Pentium 4 Pipe LiningDocument7 pagesPentium 4 Pipe Liningapi-3801329100% (5)
- 80486Document21 pages80486Khadar Nawas0% (1)
- Comparison of Pentium Processor With 80386 and 80486Document23 pagesComparison of Pentium Processor With 80386 and 80486Tech_MX60% (5)
- Embedded SystemsDocument171 pagesEmbedded SystemsJoseph JohnNo ratings yet
- The Dma Controller 8257 and 8237 .Document78 pagesThe Dma Controller 8257 and 8237 .BETHWEL KIPROTICHNo ratings yet
- Features of 80186, 80286, 80386, 80486 and Pentium Family ProcessorsDocument32 pagesFeatures of 80186, 80286, 80386, 80486 and Pentium Family ProcessorsRahul SinghNo ratings yet
- DMADocument16 pagesDMALavish Garg0% (1)
- Pentium Memory Hierarchy (By Indranil Nandy, IIT KGP)Document6 pagesPentium Memory Hierarchy (By Indranil Nandy, IIT KGP)Indranil Nandy100% (5)
- Upgrading Embedded Design Firmware Via USBDocument5 pagesUpgrading Embedded Design Firmware Via USBreemaroy08100% (1)
- 80286Document28 pages80286Kavitha SubramaniamNo ratings yet
- Microcontrollers and Embedded SystemsDocument35 pagesMicrocontrollers and Embedded SystemsTarek BarhoumNo ratings yet
- Finn RTLDocument22 pagesFinn RTLJayasuryaa G RNo ratings yet
- Module 3 - FullDocument74 pagesModule 3 - Fullsuma_hari6244100% (2)
- Lecture 07 - Performance Measurements - Single and Multiple Cycle Processor DesignsDocument53 pagesLecture 07 - Performance Measurements - Single and Multiple Cycle Processor DesignsOmar AhmedNo ratings yet
- PCMCIA Wireless LAN Card: User's ManualDocument48 pagesPCMCIA Wireless LAN Card: User's Manualrecompacted100% (1)
- Programmable Logic Devices (PLD)Document33 pagesProgrammable Logic Devices (PLD)Rishikesh BhavsarNo ratings yet
- 3.4.2 Block Diagram of 8279: EE2354 Microprocessor and MicrocontrollerDocument4 pages3.4.2 Block Diagram of 8279: EE2354 Microprocessor and Microcontrollersansiy jeyNo ratings yet
- Motherboards LectureDocument88 pagesMotherboards LecturepiusamantaNo ratings yet
- 8051 PPT For MSCDocument138 pages8051 PPT For MSCvikash sharmaNo ratings yet
- MCB2300 CanDocument14 pagesMCB2300 CanMichaelNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1: Introduction To ARM Based Embedded SystemsDocument24 pagesLecture 1: Introduction To ARM Based Embedded SystemsSaurabh HedaNo ratings yet
- Dma ControllerDocument28 pagesDma ControllerVEL TECHNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 8086 System Bus Structures FullunitDocument36 pagesUnit 2 8086 System Bus Structures Fullunitlauro eugin brittoNo ratings yet
- Embedded Systems - An IntroductionDocument281 pagesEmbedded Systems - An IntroductionNiraj KumarNo ratings yet
- Arm Instruction ProgramDocument121 pagesArm Instruction ProgramErmin KatardzicNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: Intel 8086Document135 pagesChapter 3: Intel 8086singhrps8483% (6)
- UNIT-5: 8051 MicrocontrollerDocument25 pagesUNIT-5: 8051 MicrocontrollerSachin KhandelwalNo ratings yet
- 8259a Programmable Interrupt Controller 2Document42 pages8259a Programmable Interrupt Controller 2annushaNo ratings yet
- Microcontroller and Embedded SystemsDocument2 pagesMicrocontroller and Embedded SystemsIndranilNo ratings yet
- 8051Document69 pages8051Raffi SkNo ratings yet
- Input/Output: William Stallings, Computer Organization and Architecture, 9 EditionDocument35 pagesInput/Output: William Stallings, Computer Organization and Architecture, 9 EditionVũ Tâm MinhNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - 2Document47 pagesChapter 2 - 2JeronimoNo ratings yet
- MPMC Unit4Document61 pagesMPMC Unit4Nandhini ShreeNo ratings yet
- 8257 - Microprocessors and Microcontrollers NotesDocument25 pages8257 - Microprocessors and Microcontrollers NotesFathima HeeraNo ratings yet
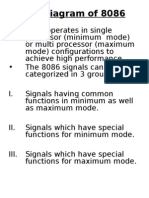
- Minimum and Maximum Modes of 8086Document3 pagesMinimum and Maximum Modes of 8086Riya Chaudhary100% (1)
- COE4DS4 Lab #2 Introduction To Embedded Software For The NIOS II ProcessorDocument7 pagesCOE4DS4 Lab #2 Introduction To Embedded Software For The NIOS II Processormacmaster69No ratings yet
- Mbedded Echnosolutions: We Are India 'S One of The Leading Trainings & Jobs Providing OrganizationDocument23 pagesMbedded Echnosolutions: We Are India 'S One of The Leading Trainings & Jobs Providing OrganizationKalyani ShindeNo ratings yet
- CAN - STM32F107 - John Kneen MicrocontrollersDocument29 pagesCAN - STM32F107 - John Kneen MicrocontrollersSyed OvaisNo ratings yet
- 8085 Microprocessor ArchitectureDocument46 pages8085 Microprocessor ArchitectureNikhl Mahajan100% (1)
- Pin Diagram of 8086Document21 pagesPin Diagram of 8086adithya123456100% (5)
- Multilevel ViewpointDocument2 pagesMultilevel ViewpointVenus KalraNo ratings yet
- ARM CORTEX M4 Memory LayoutDocument11 pagesARM CORTEX M4 Memory LayoutGurram KishoreNo ratings yet
- Interfacing 8255Document13 pagesInterfacing 8255S SIVAKUMAR0% (1)
- Class 2-Introduction To 8085 Microprocessor PDFDocument46 pagesClass 2-Introduction To 8085 Microprocessor PDFDeepika AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Embedded SystemsDocument50 pagesIntroduction To Embedded SystemsAmbika NaikNo ratings yet
- Unit-3 8085 MicroprocessorDocument101 pagesUnit-3 8085 MicroprocessorDonika MarkandeNo ratings yet
- Intel 8051 Micrcontroller: What Is A Microcontroller?Document20 pagesIntel 8051 Micrcontroller: What Is A Microcontroller?satya_vanapalli3422No ratings yet
- A Comprehensive Study of Intel Core I3, I5 and I7 Family: Presentation (2) 'Document29 pagesA Comprehensive Study of Intel Core I3, I5 and I7 Family: Presentation (2) 'Ian John MontalboNo ratings yet
- 80286Document74 pages80286Arannya MonzurNo ratings yet
- MPI Unit 2Document4 pagesMPI Unit 2Dishant RathiNo ratings yet
- Ram RomDocument42 pagesRam Rommohit mishraNo ratings yet
- PDF Cmos Analog and Mixed Signal Circuit Design Practices and Innovations Arjuna Marzuki Ebook Full ChapterDocument53 pagesPDF Cmos Analog and Mixed Signal Circuit Design Practices and Innovations Arjuna Marzuki Ebook Full Chaptersandra.curtis404100% (3)
- CPLDDocument30 pagesCPLDNanda Ganesh Kumar KingNo ratings yet
- 25.ACCESSIBLE DISPLAY DESIGN TO CONTROL HOME AREA NETWORKSDocumentDocument84 pages25.ACCESSIBLE DISPLAY DESIGN TO CONTROL HOME AREA NETWORKSDocumentdileeppatraNo ratings yet
- ARM 4 Part2Document9 pagesARM 4 Part2SUGYAN ANAND MAHARANANo ratings yet
- Unit 5 - A CASE STUDY - Using Pic MicrocontrollerDocument33 pagesUnit 5 - A CASE STUDY - Using Pic MicrocontrollerPoonthalirNo ratings yet
- Flashflex Microcontroller Using The Programmable Counter Array (Pca)Document17 pagesFlashflex Microcontroller Using The Programmable Counter Array (Pca)Darshan ValaNo ratings yet
- Microprocessor Assignment: Priyank Mandal 285/C0/07Document11 pagesMicroprocessor Assignment: Priyank Mandal 285/C0/07Priyank MandalNo ratings yet
- The Pentium Pro Was Introduced in 1995 As The Successor To The PentiumDocument5 pagesThe Pentium Pro Was Introduced in 1995 As The Successor To The PentiumManpreetaaNo ratings yet
- 272CO07Document9 pages272CO07Nishesh AggarwalNo ratings yet
- MS-1012IG ManualDocument28 pagesMS-1012IG ManualLe Chu67% (3)
- 600VPR 170 290Document2 pages600VPR 170 290John GarnetNo ratings yet
- Quotation: PT - Focus Central SecurindoDocument2 pagesQuotation: PT - Focus Central SecurindoPerlu DataNo ratings yet
- Tina v12 ManualDocument443 pagesTina v12 ManualYeferson Mauricio Rodriguez RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Anna University:: Chennai - 600 025 Model Question Paper: V SemesterDocument3 pagesAnna University:: Chennai - 600 025 Model Question Paper: V SemesterChandra SekharNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document30 pagesChapter 5yeshi janexoNo ratings yet
- A Comprehensive Analysis On The State-Of-The-Artdevelopments in Reflectarray, Transmitarray, and Transmit-Reflectarray AntennasDocument22 pagesA Comprehensive Analysis On The State-Of-The-Artdevelopments in Reflectarray, Transmitarray, and Transmit-Reflectarray AntennasZohre NoamadeNo ratings yet
- Mis Apuntes De... Raspberry Pi PDFDocument55 pagesMis Apuntes De... Raspberry Pi PDFleocesar850% (1)
- Elf Basic Series: Digitan Vaf MeterDocument2 pagesElf Basic Series: Digitan Vaf MeterjaikolangaraparambilNo ratings yet
- Ram RomDocument24 pagesRam RomArun AhirwarNo ratings yet
- One Mark QuestionsDocument2 pagesOne Mark QuestionsC V VIJAY KUMASRNo ratings yet
- Autotransformer and Variable Auto Transformer PDFDocument6 pagesAutotransformer and Variable Auto Transformer PDFaesthetepkNo ratings yet
- CAN NetworkDocument18 pagesCAN NetworkAM76No ratings yet
- I Direct Spec Sheet 15 W3 WUni Ku BUC0515Document2 pagesI Direct Spec Sheet 15 W3 WUni Ku BUC0515Promise KumaloNo ratings yet
- UnivLib BookListDocument69 pagesUnivLib BookListVikas PsNo ratings yet
- To Design and Implement An IIR Filter For Given SpecificationsDocument9 pagesTo Design and Implement An IIR Filter For Given Specifications4NM19EC157 SHARANYA R SHETTYNo ratings yet
- BAT54-W BAS40-W & BAS70-W!: Sub-Miniature Schottky Diodes & Arrays inDocument4 pagesBAT54-W BAS40-W & BAS70-W!: Sub-Miniature Schottky Diodes & Arrays inTom TomNo ratings yet
- Lab Setup at SJK (T) Buluh AkarDocument5 pagesLab Setup at SJK (T) Buluh Akarkalai arasanNo ratings yet
- Secondary Testing Report Can Don, Unit 2 Line Protection CubicleDocument28 pagesSecondary Testing Report Can Don, Unit 2 Line Protection Cubiclethiet luongNo ratings yet
- ANSI - SCTE 50 - 2007 Test Procedure For Measuring Regularity of Impedance of Coaxial CableDocument8 pagesANSI - SCTE 50 - 2007 Test Procedure For Measuring Regularity of Impedance of Coaxial CableYung SangNo ratings yet
- Carrier Current Receiver PDFDocument5 pagesCarrier Current Receiver PDFTEDY-RNo ratings yet
- Wheatstone Bridge - WikipediaDocument2 pagesWheatstone Bridge - WikipediadediprayogiNo ratings yet
- Home Theatre BrochureDocument13 pagesHome Theatre BrochurehotaussieguyNo ratings yet
- Experiment 7 Active First Order Filters: 1 BackgroundDocument4 pagesExperiment 7 Active First Order Filters: 1 Backgroundahmed shahNo ratings yet
- Acer Aspire 5920 - 5920G Quanta ZD1 CHAPALA RevB SchematicDocument38 pagesAcer Aspire 5920 - 5920G Quanta ZD1 CHAPALA RevB SchematicPolat IminovNo ratings yet
- SDC Important QuestionsDocument5 pagesSDC Important QuestionsInstagramNo ratings yet
- BTP Report FinalDocument40 pagesBTP Report FinalvikNo ratings yet
- How VDSL Works by Jeff TysonDocument5 pagesHow VDSL Works by Jeff Tysonchaidar_lakare100% (1)
- ERI Equipment SpecificationDocument2 pagesERI Equipment SpecificationAnonymous gq7UQAwNo ratings yet
- Design For Semiconductor ReliabilityDocument10 pagesDesign For Semiconductor Reliabilitygobee5789No ratings yet