Professional Documents
Culture Documents
TE Assignment Design Principles
Uploaded by
Felix Nana Sarpong0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views4 pagesWIRELESS NETWORK ESSENTIALS
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentWIRELESS NETWORK ESSENTIALS
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views4 pagesTE Assignment Design Principles
Uploaded by
Felix Nana SarpongWIRELESS NETWORK ESSENTIALS
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 4
ACCRA INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
ADVANCED SCHOOL OF SYSTEM AND DATA STUDIES (ASSDAS)
DEPARTMENT OF INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY
COURSE: TE303 WIRELESS AND MOBILE COMMUNICATION.
Assignment 5.
BY:
SANDRA OWENS AYAME ADS11B00136Y
24th MAY, 2014
(1) What are the design principals, radio aspects and applications of LMDS and
MMDS?.
(2) What is routing?
Routing: Is the process of determining the route or path through the network that
a message will travel from the sending computer to the receiving computer.
(3) What is your understanding of routing protocols?
A routing protocol is a protocol that is used to exchange information among
computers to enable them to build and maintain their routing tables.
(4) Describe the three fundamental approaches to routing.
Centralized routing: - all routing decisions are made by one central
computer or router. Centralized is commonly used in host-based networks
and in this case, routing decisions are rather simple. All computers are
connected to the central computer, so any message that needs to be
routed is simply sent to the central computer, which in turn retransmits the
message on the appropriate circuit to the destination.
Static Routing is decentralized:- which means that all computers or routers
in the network make their own routing decisions following a formal routing
protocol. In MANs and WANs, the routing table for each computer is
developed by its individual network manager.
Dynamic routing (or adaptive routing):- routing decisions are made in a
decentralized manner by individual computers. This approach is used when
there are multiple routes through a network, and it is important to select
the best route. Dynamic routing attempts to improve network performance
by routing messages over the fastest possible route, away from busy
circuits and busy computers. There are two drawbacks to dynamic routing.
First, it requires more processing by each computer or router in the
network than does centralized routing or static routing. Second, the
transmission of routing information wastes network capacity.
(5) Describe the following protocols: BGP, ICMP, RIP, IS-IS, OSPF and EIGRP.
Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) is a dynamic distance vector exterior routing
used on the Internet to exchange routing information between autonomous
systems that is, large sections of the Internet.
Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) is the simplest interior routing
protocol on the Internet. ICMP is simply an error-reporting protocol that enables
computers to report routing errors to message senders.
Routing Information Protocol (RIP) is a dynamic distance vector interior routing
protocol that is commonly used in smaller networks, such as those operated by
one organization. The network manager uses RIP to develop the routing table.
When new computers are added, RIP simply counts the number of computers in
the possible routes to the destination and selects the route with the least
number. Computers using RIP send broadcast messages every minute or so (the
timing is set by the network manager) announcing their routing status to all other
computers.
Intermediate System to Intermediate System (IS-IS)is a link static interior routing
protocol that is commonly used in large networks. IS-IS is an ISO protocol that has
been added to many TCP/IP networks.
Open Shortest Path First (OSPF): is a dynamic link state interior routing protocol
that is commonly used on the Internet. It uses the number of computers in a
route as well as network traffic and error rates to select the best route. OSPF is
more efficient than RIP because it normally doesnt use broadcast messages.
Instead, it selectively sends status update messages directly to selected
computers or routers.
Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP): is a dynamic link state
interior routing protocol developed by Cisco and is commonly used inside
organizations. EIGRP is an improved version of IGRP. EIGRP records information
about a routes transmission capacity, delay, reliability, and load. EIGRP is unique
in that computer or routers store their own routing table as well as the routing
tables for all of their neighbors so they have a more accurate understanding of
the network.
(6) Explain the six types of security applied to WLANs
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5795)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- AJSPR V19A LG - Vol.2Document310 pagesAJSPR V19A LG - Vol.2TuPro FessionalNo ratings yet
- Routing Protocols RIP, OSPF, BGPDocument22 pagesRouting Protocols RIP, OSPF, BGPTaha KhanNo ratings yet
- Link State Routing ProtocolsDocument49 pagesLink State Routing ProtocolsDimitrije PaunovicNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Ip RoutingDocument67 pagesChapter 5 Ip RoutingWilfredo AparicioNo ratings yet
- OSPF LabsDocument83 pagesOSPF LabsGulsah BulanNo ratings yet
- 18 Connectivity Troubleshooting Answer KeyDocument2 pages18 Connectivity Troubleshooting Answer KeyTent DorinNo ratings yet
- 01 OSPF LAB SolutionDocument53 pages01 OSPF LAB SolutionMahmudul HaqueNo ratings yet
- DCN - 1 - Diagram - ML OM Solution (MSC HUB Sites) - RevADocument29 pagesDCN - 1 - Diagram - ML OM Solution (MSC HUB Sites) - RevAtembakaujawaNo ratings yet
- Comandos Más Usuales para JuniperDocument36 pagesComandos Más Usuales para JuniperSucioPolicia100% (3)
- Ospf - Summary Cheatsheet (Atech) - Part: Ospf Neighbor Process & LSDB ExchangeDocument1 pageOspf - Summary Cheatsheet (Atech) - Part: Ospf Neighbor Process & LSDB ExchangeMonojit KarNo ratings yet
- Comandos Configuracion OSPFDocument6 pagesComandos Configuracion OSPFVicente LunaNo ratings yet
- Routing in Data Networks and Internet RoutingDocument12 pagesRouting in Data Networks and Internet RoutingEstelle MandengNo ratings yet
- 01-07 IP Routing CommandsDocument428 pages01-07 IP Routing CommandsMwai JannaNo ratings yet
- Analysis of RIP, OSPF, and EIGRP Routing": Synopsis ON "Document9 pagesAnalysis of RIP, OSPF, and EIGRP Routing": Synopsis ON "Đěěpâķ ŠîňğhNo ratings yet
- Packet Tracer 10.3.1.2Document1 pagePacket Tracer 10.3.1.2Ryan JohnsonNo ratings yet
- Routing: Eng - Ahmed NabilDocument16 pagesRouting: Eng - Ahmed Nabilhooda3No ratings yet
- Packet Tracer Multiarea Ospf Exploration Physical Mode Part 2 SabordoDocument11 pagesPacket Tracer Multiarea Ospf Exploration Physical Mode Part 2 Sabordounlocky dayNo ratings yet
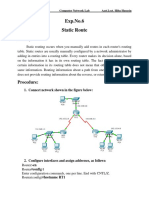
- Exp - No. 6 Static RouteDocument4 pagesExp - No. 6 Static RouteMohammed Al-RahmaweeNo ratings yet
- CCNA Training Border Gateway Protocol BGP TutorialDocument4 pagesCCNA Training Border Gateway Protocol BGP Tutorialokotete evidenceNo ratings yet
- Narbik - OSPFv3 Lab 2Document23 pagesNarbik - OSPFv3 Lab 2p4pajiNo ratings yet
- Lista de Comandos - ClsDocument11 pagesLista de Comandos - ClsTaumar MoraisNo ratings yet
- 09-1-IP RoutingDocument30 pages09-1-IP RoutingChristine ArthurNo ratings yet
- IEWB-RS Advanced Technologies Labs RIPDocument45 pagesIEWB-RS Advanced Technologies Labs RIPJoffre Ramiro Pesantez VerdezotoNo ratings yet
- Acn-6 2Document30 pagesAcn-6 2Maysam AlkeramNo ratings yet
- EscenarioDocument26 pagesEscenarioSebas MayorgaNo ratings yet
- Basic Notes On OSPF (Open Shortest Path First) - Sysnet NotesDocument6 pagesBasic Notes On OSPF (Open Shortest Path First) - Sysnet NotesvelramsenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Correct AnswersDocument3 pagesChapter 4 Correct Answersdeerhntr22100% (1)
- EIGRP Vs OSPF: What's The Difference?: Posted On August 1, 2018 53 9082Document6 pagesEIGRP Vs OSPF: What's The Difference?: Posted On August 1, 2018 53 9082pippoNo ratings yet
- Troubleshooting OSPFv2Document15 pagesTroubleshooting OSPFv2free dumpsNo ratings yet
- Yasser-Auda CCIEv5 Quick Guide For Redistribution & Path ControlDocument12 pagesYasser-Auda CCIEv5 Quick Guide For Redistribution & Path ControlphamvanhaNo ratings yet