Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Imunoglobulinas
Imunoglobulinas
Uploaded by
Saah Batista0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views16 pagesIgG, IgE and monomeric IgA are small and can diffuse from blood easily. Secretory component masks protease cleavage sites in the IgA hinge region, allowing secretory IgA to survive longer in the mucosal environment. IgM and IgE lack hinge regions, but contain an extra heavy chain domain. IgA and IgM can form multimers: Both contain an 18 amino acid C-region tailpiece with a cysteine residue
Original Description:
Original Title
imunoglobulinas
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentIgG, IgE and monomeric IgA are small and can diffuse from blood easily. Secretory component masks protease cleavage sites in the IgA hinge region, allowing secretory IgA to survive longer in the mucosal environment. IgM and IgE lack hinge regions, but contain an extra heavy chain domain. IgA and IgM can form multimers: Both contain an 18 amino acid C-region tailpiece with a cysteine residue
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views16 pagesImunoglobulinas
Imunoglobulinas
Uploaded by
Saah BatistaIgG, IgE and monomeric IgA are small and can diffuse from blood easily. Secretory component masks protease cleavage sites in the IgA hinge region, allowing secretory IgA to survive longer in the mucosal environment. IgM and IgE lack hinge regions, but contain an extra heavy chain domain. IgA and IgM can form multimers: Both contain an 18 amino acid C-region tailpiece with a cysteine residue
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 16
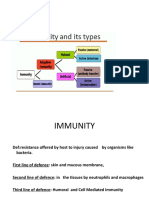
Imunoglobulinas
Fig 3.21 J aneway 4th ed.
Structural organisation of the main human
immunoglobulin isotype monomers
IgM & IgE lack hinge regions, but contain an extra
heavy chain domain
IgA and IgM can form multimers:
Both contain an 18 amino acid C-region tailpiece with a cysteine residue
esential for polymerisation
A single 15 kDa J chain initiates polymerisation
IgA is a dimer in mucous secretions (but not plasma)
IgM is a pentamer (or hexamer) in plasma
Fig 4.13
Kuby
4th ed.
Immunoglobulin isotypes are selectively
distributed in the body
Plasma: IgG + IgM
Extracellular fluids: IgG + monomeric
IgA
Secretions (including breast milk):
polymeric IgA
Beneath epithelia: IgE (associated with
mast cells)
Transplacental transport: IgG
Fig 9.19 J aneway 4th ed.
Size: IgG, IgE and monomeric IgA are
small and can diffuse from blood easily
Transcytosis: dimeric IgA
Fig 4.15
Kuby 4th ed.
Structure and formation of secretory IgA
basolateral membrane
Secretory component masks protease cleavage sites in the IgA hinge region,
allowing secretory IgA to survive longer in the mucosal environment
Activation of complement: Flexibility (even without a hinge) allows access
for complement binding (IgG3, IgM)
Figs. 9.35 &
9.36,
J aneway
4th ed
Summary: Properties of the human
immunoglobulin isotypes:
Fig 4-2 Kuby 4th ed. Or Fig 3.20 J aneway 4th ed.
Table 4-2 Kuby 4th ed.
The B-cell receptor (BCR)
Fig. 5.7 J aneway 4th ed
Gerao de Diversidade Imunolgica - LB 2 parte
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5813)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (844)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (348)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- AAO McqsDocument199 pagesAAO Mcqssafasayed50% (2)
- COVID-19 Vaccination & Testing ETSDocument14 pagesCOVID-19 Vaccination & Testing ETSCato InstituteNo ratings yet
- Defnese Mechanism of Oral CavityDocument87 pagesDefnese Mechanism of Oral CavityLavanya KalapalaNo ratings yet
- Types of ImmunoglobulinDocument14 pagesTypes of ImmunoglobulinZubair AlamNo ratings yet
- Rheum MCQDocument11 pagesRheum MCQMudassar Iqbal100% (2)
- Unit 14Document4 pagesUnit 14Martha LeivaNo ratings yet
- Care of Clients With Hypersensitivity: Check For UnderstandingDocument5 pagesCare of Clients With Hypersensitivity: Check For UnderstandingK.A.ANo ratings yet
- Antibodies - Immuno AssignmentDocument30 pagesAntibodies - Immuno AssignmentShubham PandeyNo ratings yet
- Antibody Structure & Function 11Document30 pagesAntibody Structure & Function 11Alison HinesNo ratings yet
- Catalogo AlergiaDocument60 pagesCatalogo AlergiaMoreira SuNo ratings yet
- PIEPIEDocument23 pagesPIEPIEJaycee NodadoNo ratings yet
- ERS MONOGRAPH - PULMONARY MANIFESTATIONS OF SYSTEMIC DISEASES/ Artritis ReumatoideaDocument24 pagesERS MONOGRAPH - PULMONARY MANIFESTATIONS OF SYSTEMIC DISEASES/ Artritis ReumatoidearocioanderssonNo ratings yet
- Hematology & Immune SystemDocument81 pagesHematology & Immune SystemAmanuel Maru100% (1)
- IMMUNITYDocument58 pagesIMMUNITYkamala 123No ratings yet
- Haemophilus InfluenzaeDocument20 pagesHaemophilus Influenzaevignesh9489No ratings yet
- MCQsDocument15 pagesMCQsmanin1804No ratings yet
- Plasma ChonDocument41 pagesPlasma ChonTwinkle SalongaNo ratings yet
- Basic ImmunologyDocument29 pagesBasic ImmunologyHema Duddukuri0% (1)
- Chitosan Nanoparticles A Promising System For Drug Delivery, 51-66Document16 pagesChitosan Nanoparticles A Promising System For Drug Delivery, 51-66Tira MaharaniNo ratings yet
- 2020 Biochem Activity 13Document5 pages2020 Biochem Activity 13Gabrielle John HernaezNo ratings yet
- 2018 Calf Immunology and The Role of Vaccinations in Dairy CalvesmvzDocument11 pages2018 Calf Immunology and The Role of Vaccinations in Dairy CalvesmvzDavid Julian ClavijoNo ratings yet
- Current Understanding of The Gut Microbiota Shaping MechanismsDocument11 pagesCurrent Understanding of The Gut Microbiota Shaping MechanismsRuzgardan AzizgizNo ratings yet
- Milk Geocities SiteDocument28 pagesMilk Geocities SiteAmit KasaudhanNo ratings yet
- Dermatitis Herpetiformis: Timo L. Reunala, MDDocument9 pagesDermatitis Herpetiformis: Timo L. Reunala, MDListya NormalitaNo ratings yet
- A. Natural Passive Immunity: Igg & Iga Are ConsideredDocument9 pagesA. Natural Passive Immunity: Igg & Iga Are ConsideredIme.No ratings yet
- Immunodeficiency DisordersDocument67 pagesImmunodeficiency DisordersAkbar SaleemNo ratings yet
- Basic and Clinical Immunology PDFDocument86 pagesBasic and Clinical Immunology PDFAbbass El-Outa100% (1)
- ImmunologyDocument80 pagesImmunologyMaged HusseinNo ratings yet
- Raw Milk Balance Between Hazards and Benefits Carvalho Full Download ChapterDocument51 pagesRaw Milk Balance Between Hazards and Benefits Carvalho Full Download Chapterclyde.alsberry705100% (17)
- Antigen & Antibody: Dr. Hasina Banu Assistant Professor Dept - of Microbiology Ipgme&RDocument48 pagesAntigen & Antibody: Dr. Hasina Banu Assistant Professor Dept - of Microbiology Ipgme&Rbook keedaNo ratings yet