Professional Documents
Culture Documents
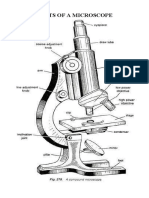
Mirror:: Eyepiece or Ocular Lens: Tube: Resolving Nosepiece: Objective Lenses
Uploaded by
Jny An Aparente0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
78 views1 pageHS File
Original Title
Eyepiece or Ocular Lens
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentHS File
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
78 views1 pageMirror:: Eyepiece or Ocular Lens: Tube: Resolving Nosepiece: Objective Lenses
Uploaded by
Jny An AparenteHS File
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
Eyepiece or ocular lens: Eyepiece is the lens, present at the top and is used to see the objects under
study. Eyepiece lens contains a magnification of 10X or 15X.
Tube: Tube or the body tube, connects the eyepiece to the objective lenses.
Resolving nosepiece: It is also known as the Turret. Resolving nosepiece has holders for the different
objective lenses. It allows the rotation of the lenses while viewing.
Objective lenses: Generally, three or four objective lenses are found on a microscope, with ranges of 10X,
40X, 100X powers. Lenses are colour coded, the shortest lens is of the lowest power, and the longest lens is
high power lenses.
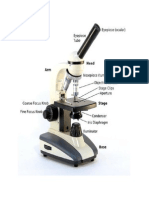
Diaphragm: Diaphragm helps in controlling the amount of light that is passing through the opening of the
stage. It is helpful in the adjustment of the control of light that enters.
Coarse adjustment knob: Used for focus on scanning. Usually the low power lens is used enabling the
movement of the tube.
Fine adjustment knob: Used for focus on oil. Moves the body tube for focussing the high power lens.
Arm: It supports the tube of the microscope and connects to the base of the microscope.
Stage: The platform that is flat used for placing the slides under observation.
Stage clip: Stage clips hold the slides in proper place.
Condensor: The main function of condenser lens is focussing the light on the specimen under observation.
When very high powers of 400X are used, condenser lenses are very important. Presence of condenser lens
gives a sharper image as compared to the microscope with no condenser lens.
Base: Provides basal support for the microscope.
Power switch: The main power switch that turns the illumination on or off.
Mirror: shines light through the sample
You might also like
- Parts of A Microscope and Their FunctionsDocument1 pageParts of A Microscope and Their FunctionsThess Tecla Zerauc Azodnem0% (1)
- Parts of Microscope and Their FunctionsDocument3 pagesParts of Microscope and Their Functionsiammiiie0150% (2)
- Microscope Parts and FunctionsDocument2 pagesMicroscope Parts and FunctionsKenneth P PablicoNo ratings yet
- Eyepiece or Ocular Lens: Tube: Resolving Nosepiece:: MirrorDocument1 pageEyepiece or Ocular Lens: Tube: Resolving Nosepiece:: MirrorJny An AparenteNo ratings yet
- Simple Microscope: Luna, Zyrah Angelic L. BSBA-3 MWF 4:00-5:00pmDocument2 pagesSimple Microscope: Luna, Zyrah Angelic L. BSBA-3 MWF 4:00-5:00pmJerald LunaNo ratings yet
- Eyepiece and Objective Lenses: Key Parts of a MicroscopeDocument4 pagesEyepiece and Objective Lenses: Key Parts of a MicroscopeChristine Joy ArisgarNo ratings yet
- Eyepiece: The Lens The Viewer Looks Through To See TheDocument4 pagesEyepiece: The Lens The Viewer Looks Through To See TheKemuel LozadaNo ratings yet
- Microscope Parts and Functions GuideDocument3 pagesMicroscope Parts and Functions GuideJovelyn Avila100% (1)
- สี่โมงเย็น si-mong-yen วันอาทิตย์ wan-atit: Objective lensesDocument3 pagesสี่โมงเย็น si-mong-yen วันอาทิตย์ wan-atit: Objective lenseskim myungyNo ratings yet
- Microscope Parts and FunctionsDocument3 pagesMicroscope Parts and FunctionsAntonov VodkaNo ratings yet
- Parts of Microscope and Their FunctionsDocument3 pagesParts of Microscope and Their FunctionsAlfina SafiraNo ratings yet
- FagdhfDocument2 pagesFagdhfRachel Ann PangilinanNo ratings yet
- Layka M. SabdaniDocument4 pagesLayka M. SabdaniRaniaNo ratings yet
- Microscope DefinitionsDocument3 pagesMicroscope DefinitionsJessica ThomasNo ratings yet
- Function of Each Microscope PartDocument6 pagesFunction of Each Microscope PartDavid W ReynosoNo ratings yet
- Parts of A Microscope and Their FunctionsDocument3 pagesParts of A Microscope and Their FunctionsJessica Cordis100% (1)
- EyepieceDocument2 pagesEyepieceOzner WanijimaNo ratings yet
- The Microscope - Parts and FunctionsDocument2 pagesThe Microscope - Parts and FunctionsLhynne Riano Salando100% (1)
- Compound Microscope Parts and Functions GuideDocument2 pagesCompound Microscope Parts and Functions Guidemydiamondstar17No ratings yet
- Parts of A MicroscopeDocument5 pagesParts of A MicroscopeShankey Faith BediaNo ratings yet
- Compound Microscope Definitions For LabelsDocument9 pagesCompound Microscope Definitions For LabelsDURANO, ROSELLE Z.SCINo ratings yet
- Parts of The Microscope and Their Uses (Compilation From Diff. Site.)Document5 pagesParts of The Microscope and Their Uses (Compilation From Diff. Site.)ivoryshin daluroNo ratings yet
- Compound Microscope Definitions For LabelsDocument3 pagesCompound Microscope Definitions For LabelsRonalee PeralesNo ratings yet
- Head/Body Houses The Optical Parts in The Upper Part of The MicroscopeDocument2 pagesHead/Body Houses The Optical Parts in The Upper Part of The MicroscopeNica Bautista BarsolasoNo ratings yet
- Ekaterina 6b MicroscopesDocument19 pagesEkaterina 6b Microscopesapi-269598196No ratings yet
- 1 Microscope (23-09-2020)Document22 pages1 Microscope (23-09-2020)Maaz GulNo ratings yet
- MicroscopeDocument3 pagesMicroscopeJoun Erica TalinguezNo ratings yet
- Compound MicroscopeDocument2 pagesCompound MicroscopeditucalanshanmichaelvNo ratings yet
- The Microscope: Parts and SpecificationsDocument3 pagesThe Microscope: Parts and SpecificationsfitrianiNo ratings yet
- The Microscope GuideDocument9 pagesThe Microscope GuideSheryl Reyes100% (1)
- MicroscopeDocument8 pagesMicroscopeamanda_orbe8504No ratings yet
- Microscope Parts and FunctionsDocument4 pagesMicroscope Parts and FunctionsChris ChanNo ratings yet
- MICROSCOPEDocument1 pageMICROSCOPEBotzBotzBotzNo ratings yet
- The MicroscopeDocument3 pagesThe MicroscopeShaira RubanteNo ratings yet
- The key parts of the microscope explainedDocument2 pagesThe key parts of the microscope explainedArnolfo S. CaladreNo ratings yet
- Microscope Parts and Functions GuideDocument3 pagesMicroscope Parts and Functions GuideJhonLloyd DomingoNo ratings yet
- Microscope Parts and FunctionsDocument2 pagesMicroscope Parts and FunctionsLileth Anne Panghulan ViduyaNo ratings yet
- Microscopes Parts and FunctionDocument3 pagesMicroscopes Parts and Functionweng100% (6)
- Microscope Handouts G7Document3 pagesMicroscope Handouts G7Gloriefe QuitongNo ratings yet
- Parts and Function of The MicroscopeDocument3 pagesParts and Function of The MicroscopeStephen GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Compound Microscope PartsDocument3 pagesCompound Microscope PartsMimi MonteNo ratings yet
- Histology Assignment 1Document3 pagesHistology Assignment 1Kristine Pangahin100% (1)
- Microscope: Microscope Is An Instrument Used For Viewing Objects That Are Too Small To Be Seen by The Nacked EyeDocument23 pagesMicroscope: Microscope Is An Instrument Used For Viewing Objects That Are Too Small To Be Seen by The Nacked Eyeشاجوان عباس محمد احمدNo ratings yet
- The Compound Light MicroscopeDocument2 pagesThe Compound Light MicroscopeIsabela MartinezNo ratings yet
- The Functions and Parts of A MicroscopeDocument1 pageThe Functions and Parts of A Microscopejayr ludoviceNo ratings yet
- Structural Parts of The Microscope (Biology)Document4 pagesStructural Parts of The Microscope (Biology)Nemie VelascoNo ratings yet
- Parts of A Compound MicroscopeDocument5 pagesParts of A Compound MicroscopeKim Ashley BallesterosNo ratings yet
- Introduction To The Microscope: - History - Types - Care - Parts & Functions - FocusingDocument40 pagesIntroduction To The Microscope: - History - Types - Care - Parts & Functions - FocusingMegalexNo ratings yet
- Parts of MicroscopeDocument6 pagesParts of MicroscopeKHEARALLAHNo ratings yet
- Parts of a Compound MicroscopeDocument4 pagesParts of a Compound MicroscopeShania Guillermo GallardoNo ratings yet
- Microscope: - History - Types - Care - Parts & Functions - FocusingDocument38 pagesMicroscope: - History - Types - Care - Parts & Functions - Focusingabdikafi sugeNo ratings yet
- Parts of a Microscope ExplainedDocument2 pagesParts of a Microscope ExplainedJulie Anne TanNo ratings yet
- Microscopy LectureDocument39 pagesMicroscopy LecturesjoerjenNo ratings yet
- The science of investigating small objects using microscopesDocument6 pagesThe science of investigating small objects using microscopeslarry machonNo ratings yet
- There Are Three Structural Parts of The Microscope IDocument3 pagesThere Are Three Structural Parts of The Microscope Ijoshladac94No ratings yet
- The MicroscopeDocument3 pagesThe MicroscopethereseNo ratings yet
- More History Here: The Functions & Parts of A MicroscopeDocument3 pagesMore History Here: The Functions & Parts of A MicroscopeKezhia ShaneNo ratings yet
- Parts of MicroscopeDocument4 pagesParts of MicroscopeJohn Rey F. CastroNo ratings yet
- Shop Rental Payment History 2014-2017Document1 pageShop Rental Payment History 2014-2017Jny An AparenteNo ratings yet
- KodalyDocument2 pagesKodalyJny An AparenteNo ratings yet
- Understanding Discrimination and its EffectsDocument6 pagesUnderstanding Discrimination and its EffectsJny An AparenteNo ratings yet
- Kindergarten Class ProgramDocument2 pagesKindergarten Class ProgramJny An AparenteNo ratings yet
- Organ SystemDocument2 pagesOrgan SystemJny An AparenteNo ratings yet
- Thank Teachers for Education's FutureDocument1 pageThank Teachers for Education's FutureJny An AparenteNo ratings yet
- Report On Learning Progress and Achievement Report On Learner'S Observed ValuesDocument1 pageReport On Learning Progress and Achievement Report On Learner'S Observed ValuesJny An AparenteNo ratings yet
- Steamed Moist Banana CakeDocument1 pageSteamed Moist Banana CakeJny An AparenteNo ratings yet
- The Influential Effect of All StudentsDocument1 pageThe Influential Effect of All StudentsJny An AparenteNo ratings yet
- FederalismDocument3 pagesFederalismJny An AparenteNo ratings yet
- Maanahao Es: Adviser Tagalog, Evelyn Adviser Guk-Ong, RosejeanDocument1 pageMaanahao Es: Adviser Tagalog, Evelyn Adviser Guk-Ong, RosejeanJny An AparenteNo ratings yet
- School Readiness Year-End Assessment (Sreya) For Kinder: Pupil'S NameDocument1 pageSchool Readiness Year-End Assessment (Sreya) For Kinder: Pupil'S NameJny An Aparente100% (1)
- Understanding Discrimination and its EffectsDocument6 pagesUnderstanding Discrimination and its EffectsJny An AparenteNo ratings yet
- Oldies MedleyDocument5 pagesOldies MedleyJny An AparenteNo ratings yet
- Accomplishment Report in EPPDocument2 pagesAccomplishment Report in EPPJny An AparenteNo ratings yet
- EPP District Festival and Regional Contest AccomplishmentsDocument2 pagesEPP District Festival and Regional Contest AccomplishmentsJny An AparenteNo ratings yet
- Special Power of Attorney: Know All Men by These PresentsDocument2 pagesSpecial Power of Attorney: Know All Men by These PresentsJny An AparenteNo ratings yet
- InkDocument1 pageInkJny An AparenteNo ratings yet
- Word MeaningDocument4 pagesWord MeaningJny An AparenteNo ratings yet
- Retention RequestDocument1 pageRetention RequestJny An AparenteNo ratings yet
- 1Document2 pages1Jny An AparenteNo ratings yet
- Retention RequestDocument1 pageRetention RequestJny An AparenteNo ratings yet
- Special Power of Attorney: Know All Men by These PresentsDocument1 pageSpecial Power of Attorney: Know All Men by These PresentsJny An AparenteNo ratings yet
- 20% 30% Snacks Print and Xerox Other ExpensesDocument1 page20% 30% Snacks Print and Xerox Other ExpensesJny An AparenteNo ratings yet
- Rona Paz LabelDocument1 pageRona Paz LabelJny An AparenteNo ratings yet
- ScienceDocument2 pagesScienceJny An AparenteNo ratings yet
- Speaking Reading Listening LongDocument4 pagesSpeaking Reading Listening LongJny An AparenteNo ratings yet
- ADocument1 pageAJny An AparenteNo ratings yet
- Leave Form 6Document2 pagesLeave Form 6Jny An AparenteNo ratings yet
- Aral. Pan. Dinastiyang Balhae Sa KoreaDocument5 pagesAral. Pan. Dinastiyang Balhae Sa KoreaJny An AparenteNo ratings yet