Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Fracture Collum Femoris
Uploaded by
Ganis Panji Yahya0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
38 views12 pagesThis document discusses fractures of the femoral neck, which occur most commonly in elderly patients due to osteoporosis and falls. It describes the anatomy and epidemiology of femoral neck fractures, which are increasing in incidence. Classification systems for femoral neck fractures including the Garden classification are presented. The clinical features, diagnosis using x-rays and scans, and management including internal fixation and hip replacement surgery are summarized. Potential complications of femoral neck fractures including avascular necrosis, non-union, and osteoarthritis are also mentioned.
Original Description:
coass bedah orthopedi
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses fractures of the femoral neck, which occur most commonly in elderly patients due to osteoporosis and falls. It describes the anatomy and epidemiology of femoral neck fractures, which are increasing in incidence. Classification systems for femoral neck fractures including the Garden classification are presented. The clinical features, diagnosis using x-rays and scans, and management including internal fixation and hip replacement surgery are summarized. Potential complications of femoral neck fractures including avascular necrosis, non-union, and osteoarthritis are also mentioned.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
38 views12 pagesFracture Collum Femoris
Uploaded by
Ganis Panji YahyaThis document discusses fractures of the femoral neck, which occur most commonly in elderly patients due to osteoporosis and falls. It describes the anatomy and epidemiology of femoral neck fractures, which are increasing in incidence. Classification systems for femoral neck fractures including the Garden classification are presented. The clinical features, diagnosis using x-rays and scans, and management including internal fixation and hip replacement surgery are summarized. Potential complications of femoral neck fractures including avascular necrosis, non-union, and osteoarthritis are also mentioned.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 12
Ganis Panji Yahya 12100113033
Preceptor : dr. Deny Hermawan, Sp.OT, FICS
SMF Bedah RSAI FK UNISBA
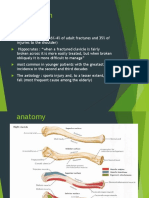
Anatomy
Fracture neck of femur
The femoral neck is the
commonest site of fractures
in the elderly.
age-related osteoporosis
bone-losing or bone-
weakening
disorders such as
osteomalacia, diabetes,
stroke (disuse), alcoholism
and chronic debilitating
disease.
Weak muscles and poor
balance
Epidemiology &
mechanisme
The incidence of
femoral neck fractures
is set to double over the
next 30 years;
beyond 65 years
simple fall;
osteoporotic people,
less force is required
twisting the hip into
external rotation.
In younger fall from
a height or a blow
sustained in a road
accident.
Multiple injury 20%
runners or military
personnel.
Classification
Garden :
Stage I is an incomplete
Stage II is a complete but undisplaced fracture.
Stage III is a complete fracture with moderate
displacement. And
Stage IV is a severely displaced fracture.
X-ray : garden
classification
Clinical feature
usually a history of a
fall, followed by pain in
the hip.
lateral rotation and the
leg looks short.
patient may still be able
to walk, and debilitated
or mentally
handicapped
young adults road
traffic accidents or falls
from heights &
multiple injuries.
Diagnosis
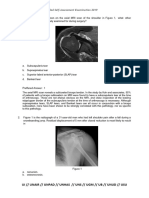
Fractures of the femoral neck diagnosis (a) An elderly woman
tripped on the pavement and complained of
pain in the left hip. The plain x-ray showed no abnormality. Two
weeks later she was still in pain; (b) a bone scan showed a
hot area medially at the base of the femoral neck. MRI, if available,
is an alternative investigation to confirm suspicions of
a femoral neck fracture (c).
Management
Femoral neck injuries treatment (a,b) This Garden stage II fracture has
been stabilized with 3 cannulated
screws. (c,d) An optimum position for the screws is: one to support the
inferior portion of the neck (centrally); and another
two, central in level, skirting the anterior and posterior cortices of the
femoral neck on the lateral x-ray. It is important the
most inferior screw enters the lateral cortex of the femur proximal to the
level of the inferior margin of the lesser
trochanter.
Fracture of the femoral neck treatment (a) A fracture as severely displaced
as this (Stage IV), if treated by
reduction and internal fixation, will probably end up needing revision
surgery; instead it could be treated by performing a
hemiarthroplasty using a cemented femoral prostheses (b). A total hip
replacement (c) provides a better outcome for
younger patients (5060 year olds) with this type of fracture.
Complication
General
complication
Avascular
necrosis
Non-union
osteoarthritis
Thanks
You might also like
- Lumbar Spine Trauma Imaging - Overview, Radiography, Computed TomographyDocument36 pagesLumbar Spine Trauma Imaging - Overview, Radiography, Computed TomographyAchmadRizaNo ratings yet
- Ortho - Surgery PDFDocument15 pagesOrtho - Surgery PDFIC BNo ratings yet
- Sports Medicine Scored and Recorded Self-Assessment ExaminationDocument71 pagesSports Medicine Scored and Recorded Self-Assessment ExaminationZia Ur RehmanNo ratings yet
- Spinal Injury HockeyDocument65 pagesSpinal Injury HockeyTaniaR.BernalNo ratings yet
- Kamars RadiologyDocument135 pagesKamars RadiologyNayantara Nair100% (1)
- Frienchzel Joy A. Asis Group 3 BSN 3-ADocument14 pagesFrienchzel Joy A. Asis Group 3 BSN 3-AKenneth Louis GalizaNo ratings yet
- C14 - Coloana Vertebrala Engleza 2Document109 pagesC14 - Coloana Vertebrala Engleza 2Andreea DanielaNo ratings yet
- I. X-Ray Image: Hindfoot Fractures By: Jeremy Tan and Sarah HillDocument8 pagesI. X-Ray Image: Hindfoot Fractures By: Jeremy Tan and Sarah HillSheril MarekNo ratings yet
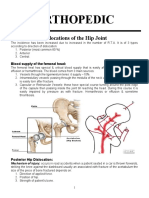
- Orthopedic: Dislocations of The Hip JointDocument16 pagesOrthopedic: Dislocations of The Hip JointAnmarNo ratings yet
- Cervical Spine InjuryDocument26 pagesCervical Spine InjuryNufit Haruna100% (1)
- Spinal Cord InjuryDocument91 pagesSpinal Cord InjuryPrabaningrum DwidjoasmoroNo ratings yet
- Cervical Spine FracturesDocument74 pagesCervical Spine FracturessrhubanbabuNo ratings yet
- Aaos 2019Document283 pagesAaos 2019alealer2708No ratings yet
- Ortho Review 1Document67 pagesOrtho Review 1mark tNo ratings yet
- Fracture FemurDocument28 pagesFracture FemurKulsoom ShahNo ratings yet
- 05 - Spinal Cord InjuryDocument92 pages05 - Spinal Cord InjurywaqarsuparcoNo ratings yet
- Trauma CervicalDocument36 pagesTrauma Cervicalesterhs100% (1)
- Ilmiah Radilogi Dr. YuyunDocument59 pagesIlmiah Radilogi Dr. YuyunMia Pradana NingtyasNo ratings yet
- Pathology Mechanism: Jefferson Fracture Is The Eponymous Name Given To A Burst Fracture ofDocument25 pagesPathology Mechanism: Jefferson Fracture Is The Eponymous Name Given To A Burst Fracture ofAtikah FairuzNo ratings yet
- Fracture of Neck of FemurDocument13 pagesFracture of Neck of FemurRosemarie AbelaNo ratings yet
- Hip Joint DislocationDocument19 pagesHip Joint Dislocationshaoib.grandyNo ratings yet
- AAOS2003 SpineDocument61 pagesAAOS2003 SpineHizkyas KassayeNo ratings yet
- LBM 4 Step 1 1. ATLS Protocol Step 2 1. How Is The Biomechanic of Trauma? 2. How Is The Anatomical Structure of Hip and Leg?Document6 pagesLBM 4 Step 1 1. ATLS Protocol Step 2 1. How Is The Biomechanic of Trauma? 2. How Is The Anatomical Structure of Hip and Leg?indahsariNo ratings yet
- Intertrochanter Femur Fracture: M.Akhyar Baharuddin 20194010011Document23 pagesIntertrochanter Femur Fracture: M.Akhyar Baharuddin 20194010011Muhammad AkhyarNo ratings yet
- Spinal Cord Compression Due To Undiagnosed Thoracic Meningioma Following Lumbar Surgery in An Elderly Patient: A CaseDocument4 pagesSpinal Cord Compression Due To Undiagnosed Thoracic Meningioma Following Lumbar Surgery in An Elderly Patient: A CaseLuwiNo ratings yet
- Upper Cervical InjuriesDocument46 pagesUpper Cervical InjuriesmushyhuzNo ratings yet
- SportDocument79 pagesSportMohamed Abdulgader MorganNo ratings yet
- Hangmans Fracture and Its ManagementDocument1 pageHangmans Fracture and Its ManagementPeko PekoNo ratings yet
- Lisfranc InjuryDocument99 pagesLisfranc InjurySubodh PathakNo ratings yet
- Manejo de Fracturas Mediales de Cadera 2015 Femoral Neck Fractures - Current ManagementDocument9 pagesManejo de Fracturas Mediales de Cadera 2015 Femoral Neck Fractures - Current ManagementSergio Tomas Cortés MoralesNo ratings yet
- Spastic Quadraparesis Following A Relatively Minor Injury - The Os Odontoideum'Document3 pagesSpastic Quadraparesis Following A Relatively Minor Injury - The Os Odontoideum'Stefan StanciuNo ratings yet
- Moteggia Fracture and Dislocation: Presented By: Dr. Siddharth Dubey Moderator: Prof. H.L. Nag Co-Moderator: Dr. VaibhavDocument70 pagesMoteggia Fracture and Dislocation: Presented By: Dr. Siddharth Dubey Moderator: Prof. H.L. Nag Co-Moderator: Dr. VaibhavdidiNo ratings yet
- Traumatic Hip Dislocation: A ReviewDocument6 pagesTraumatic Hip Dislocation: A ReviewAna HurtadoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Spinal CordDocument43 pagesAnatomy of Spinal CordGargi MPNo ratings yet
- Iatrogenic Vertebral Fracture During Intramedullary Nailing For Femoral FractureDocument8 pagesIatrogenic Vertebral Fracture During Intramedullary Nailing For Femoral FractureCristian ZepitaNo ratings yet
- F - Proximal Ulnar Nerve Injury Correct AnswerDocument26 pagesF - Proximal Ulnar Nerve Injury Correct AnswerMehdi Hasan MazumderNo ratings yet
- Fractures in Brief Intertrochanteric Hip FracturesDocument3 pagesFractures in Brief Intertrochanteric Hip FracturesikhwanNo ratings yet
- Upper Limb FracturesDocument3 pagesUpper Limb FracturesNikhil junejaNo ratings yet
- Fracturas SubtrocantericasDocument9 pagesFracturas SubtrocantericasPedro Fernando GiraldoNo ratings yet
- Case Report Traumatic Fracture: Dislocation of Cervicothoracic Junction - Grand Round Presentation of C7-T1 Instabilities and Different Instrumentation TechniquesDocument6 pagesCase Report Traumatic Fracture: Dislocation of Cervicothoracic Junction - Grand Round Presentation of C7-T1 Instabilities and Different Instrumentation TechniquesMohammad Al-SofyaniNo ratings yet
- Fractures of The Elbow Joint 2Document41 pagesFractures of The Elbow Joint 2Noor Al Zahraa AliNo ratings yet
- Trauma - Intertrochanteric Fracture - RustiniDocument7 pagesTrauma - Intertrochanteric Fracture - Rustinidedyalkarni08No ratings yet
- Fractura de CaderaDocument5 pagesFractura de CaderaalejandraNo ratings yet
- Fractura Columnae VertebralisDocument4 pagesFractura Columnae VertebralisTheo DapamedeNo ratings yet
- Surgical Treatment of Neglected Malunion of Shaft Femur: Case ReportDocument13 pagesSurgical Treatment of Neglected Malunion of Shaft Femur: Case ReportNando OktariNo ratings yet
- C2 (Axis) FracturesDocument12 pagesC2 (Axis) FracturesSetyo Budi Premiaji WidodoNo ratings yet
- Jurding Fraktur Caput FemurDocument17 pagesJurding Fraktur Caput FemurWildan AfrNo ratings yet
- ClaviculaDocument24 pagesClaviculaoktavia indahNo ratings yet
- Elbow Dislocation: Severe Dislocations, The Blood Vessels and Nerves That Travel Across The Elbow May Be Injured. IfDocument15 pagesElbow Dislocation: Severe Dislocations, The Blood Vessels and Nerves That Travel Across The Elbow May Be Injured. IftelefixeroNo ratings yet
- Thoracolumbarfractures 150817055817 Lva1 App6891Document75 pagesThoracolumbarfractures 150817055817 Lva1 App6891Pap PipNo ratings yet
- Spinal Injuries: DR Abdelmoniem SaeedDocument44 pagesSpinal Injuries: DR Abdelmoniem SaeedYousef Al-AmeenNo ratings yet
- Foot Calcaneal Fracture - Rehabilitation ProtocolDocument7 pagesFoot Calcaneal Fracture - Rehabilitation ProtocolAdmirNo ratings yet
- Svoa Ne 02 020Document10 pagesSvoa Ne 02 020Trina ViskhawatNo ratings yet
- Bilateral Traumatic Anterior Dislocation of The Hip With An Unstable Lumbar Burst FractureDocument4 pagesBilateral Traumatic Anterior Dislocation of The Hip With An Unstable Lumbar Burst FractureFadhli Aufar KasyfiNo ratings yet
- MRCS-A - Orthopaedics & Hand Disorder - Mock Test - DR Akter Hossain - Feb2023 - d501-22078 DR RobinDocument24 pagesMRCS-A - Orthopaedics & Hand Disorder - Mock Test - DR Akter Hossain - Feb2023 - d501-22078 DR RobinAminur Rahman AlifNo ratings yet
- Fraktur Patologis FemurDocument32 pagesFraktur Patologis FemurPanji Dify AkbarNo ratings yet
- 36 Knee Conditions: EMQ Answers 87Document10 pages36 Knee Conditions: EMQ Answers 87Eunice LimNo ratings yet
- Talar Body Fracture in A 10-Year-Old Boy. Case Presentation: Tamara Rodríguez-López, Alberto Núñez MedinaDocument6 pagesTalar Body Fracture in A 10-Year-Old Boy. Case Presentation: Tamara Rodríguez-López, Alberto Núñez MedinaPoliceNo ratings yet
- Neck Trauma, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandNeck Trauma, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet