Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Problem Recognition & Information Search
Uploaded by
rincse0%(1)0% found this document useful (1 vote)
441 views19 pagesThe document discusses consumer decision making and information search. It describes the stages of problem recognition, information search, alternative evaluation, choice, and outcomes. It covers types of information search like prepurchase, post-purchase, and ongoing searches. Sources of information can be internal memory or external impersonal sources like advertising. Consumers form consideration sets of brands or options they will evaluate.
Original Description:
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses consumer decision making and information search. It describes the stages of problem recognition, information search, alternative evaluation, choice, and outcomes. It covers types of information search like prepurchase, post-purchase, and ongoing searches. Sources of information can be internal memory or external impersonal sources like advertising. Consumers form consideration sets of brands or options they will evaluate.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0%(1)0% found this document useful (1 vote)
441 views19 pagesProblem Recognition & Information Search
Uploaded by
rincseThe document discusses consumer decision making and information search. It describes the stages of problem recognition, information search, alternative evaluation, choice, and outcomes. It covers types of information search like prepurchase, post-purchase, and ongoing searches. Sources of information can be internal memory or external impersonal sources like advertising. Consumers form consideration sets of brands or options they will evaluate.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as PPT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 19
Chapter 2
Problem Recognition &
Information Search
Chapter Spotlights
Consumer decision process action options
Problem recognition: actual state versus
desired state and motivation arousal
Pre-purchase, post-purchase, and ongoing
information search
Internal and external information search
Consideration sets
Sources of marketplace information
Consumer Decision
Process Action Options
Start through steps and complete them in
order
Start, stop, start, stop, etc. and complete
steps in order
Start steps and “loop back” as needed based
on what happens and complete process
Start into the process then stop somewhere
along the way and never finish
Do not start the process
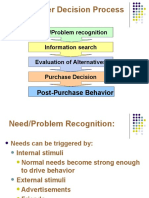
Problem Recognition
When consumers realize that they need
something!
It is the first step in the decision-making
process:
Problem recognition
Information search
Alternative evaluation
Choice
Outcomes
Motivational Arousal
Different people have different benefit
motivations for purchasing different
products or services.
Types of benefit motives:
To optimize satisfaction
To prevent possible future problems
To escape from a problem
To resolve a conflict
To maintain the status quo or satisfaction
Problem Recognition:
Actual State versus
Desired State
It is the psychological process used
to determine the difference
between the consumer’s actual
benefits state (where you are) and
the desired benefits state (where
you want to be).
Opportunity (vs. problem) recognition
Problem Recognition
Influences
Situational influences
Consumer influences
Marketing influences
Situational Influences
Product consumption (e.g., running
out of gas)
Product acquisition (e.g., purchasing
a new home may stimulate other
purchases)
Changed circumstances (e.g., moving
away from home to college)
Consumer Influences
Actual state consumers: those who
look to existing products to solve
their problems.
Desired state consumers: those
who shop for new products to
address their problems.
They enjoy the shopping experience
Marketing Influences
Marketing mix
changes and/or
promotion actions
may help stimulate
problem
recognition:
Advertising
Coupons
Free offers
sweepstakes
Information Search
Information collected by
consumers is the basis
for evaluation and
choice behavior.
It is important for
marketers to know:
Why consumers are
searching for information
Where will they look
What information
consumers seek
How extensively they are
willing to search
Types of Information
Search
Prepurchase search:
Directed searches: consumer searches for
information that will help solve a specific problem.
Browsing: consumer is “just looking” with no
immediate intent to buy.
Accidental search: consumer is not actively looking
for information, but takes note of information that is
formally presented or inadvertently encountered.
Post-purchase search: gathering information
on choice made after the purchase.
Ongoing search: continuous information
gathering to stay “marketplace-current.”
Internal and External
Information Search
Internal search: search based on existing
information in memory.
Information quantity, quality, relevance, currency
Experts vs. novices
External search: the search of information
beyond one’s memory.
Personal sources: friends, experts, salespeople
Impersonal sources: advertising, in-store displays,
trade reports, the Internet.
Experts vs. novices
Why Do Consumers
Engage in External
Information Search?
High perceived value versus perceived cost of search
Need to acquire information
Ease of acquiring and using information
Confidence in decision-making ability
Locus of control (internals vs. externals)
Actual or perceived risk
Costs of external search
Types of products sought
Characteristics of the purchase decision
Types of Risk
Functional or
performance
Financial
Psychological
Social
Physiological
Time
Linked-decision
Costs of External Search
Financial
Time
Decision delay
(opportunity cost)
Physical cost
Psychological cost
Information
overload
Type of Product Sought
Specialty goods: search willingness is high
when consumer has developed strong
preferences
Shopping goods: less search willingness for
products that the consumer must devote
time and effort to compare and contrast.
Convenience goods: consumer is reluctant to
spend any time and effort in search and
evaluation before purchase.
Characteristics of
Purchase Decision
If number of possible
solutions is limited –
extensive search is
acceptable
If need for trial is high
– more likely to
search
Difficulty of trial high
– search is for quality
supplier
External Search Strategy
Consideration set: those brands, outlets, etc.
that have front-of-mind presence and from
among which there is intention to choose.
Which brands of computers would you consider
purchasing?
Also called “evoked set” or “relevant set”
Marketplace information sources:
General (face-to-face or mass media)
Marketer-controlled (face-to-face or mass media)
You might also like
- Milk Tea StudyDocument111 pagesMilk Tea StudyAndrea Nicole Rocafort45% (29)
- Ahead of the Curve: Using Consumer Psychology to Meet Your Business GoalsFrom EverandAhead of the Curve: Using Consumer Psychology to Meet Your Business GoalsNo ratings yet
- Impact of Social Media On Consumer Behaviour: Duangruthai VoramontriDocument25 pagesImpact of Social Media On Consumer Behaviour: Duangruthai VoramontriAnand ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Marketing AssignmentDocument12 pagesMarketing AssignmentTabassumAkhterNo ratings yet
- Consumer Behaviour BookDocument59 pagesConsumer Behaviour BookPriyanka BatishNo ratings yet
- The Encyclopaedic Dictionary of Marketing PDFDocument597 pagesThe Encyclopaedic Dictionary of Marketing PDFSorin NastasNo ratings yet
- A COMPARATIVE STUDY ON BUYING BEHAVIOUR OF CONSUMER FOR INDIGENOUS PRODUCT Vis-À-Vis INTERNATIONAL PRODUCTDocument61 pagesA COMPARATIVE STUDY ON BUYING BEHAVIOUR OF CONSUMER FOR INDIGENOUS PRODUCT Vis-À-Vis INTERNATIONAL PRODUCTPunit Chopra100% (1)
- Individual Decision Making CmaDocument38 pagesIndividual Decision Making CmaFatimah Binte AtiqNo ratings yet
- Consumer Behavior IntroductionDocument121 pagesConsumer Behavior IntroductionLovely MongaNo ratings yet
- Problem Recognition & Information SearchDocument19 pagesProblem Recognition & Information Searchrajendra91No ratings yet
- Consumer Behaviour: DR Ajitabh DashDocument33 pagesConsumer Behaviour: DR Ajitabh DashDevasish PandaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document24 pagesUnit 2Pranay ChhetriNo ratings yet
- The Buyer Decision Process: Post-Purchase BehaviorDocument12 pagesThe Buyer Decision Process: Post-Purchase BehaviorAditya KumarNo ratings yet
- Distribution ManagementDocument49 pagesDistribution ManagementCarlisle ParkerNo ratings yet
- The Consumer Decision Making Process Consists of The Following StagesDocument29 pagesThe Consumer Decision Making Process Consists of The Following StagesSHIVPRATAPNo ratings yet
- Decision Making Process: Consumer Psychology Instructor: Miss Zara HaroonDocument33 pagesDecision Making Process: Consumer Psychology Instructor: Miss Zara HaroonAyesha MasoodNo ratings yet
- Consumer Behaviour The Purchasing ProcessDocument14 pagesConsumer Behaviour The Purchasing ProcessNeggaz D MapeleNo ratings yet
- CB Assignment01Document8 pagesCB Assignment01Hira RazaNo ratings yet
- Consumer Decision Process: Session 7 Prof: YasminDocument38 pagesConsumer Decision Process: Session 7 Prof: YasminmayurgharatNo ratings yet
- Consumer BehaviourDocument27 pagesConsumer BehaviourRahul SharmaNo ratings yet
- 4 PDFDocument5 pages4 PDFHani Bin Faisal AhammadNo ratings yet
- Consumer Buying Behavior: Presented By: Nidhi SharmaDocument28 pagesConsumer Buying Behavior: Presented By: Nidhi SharmaGaurav GandhiNo ratings yet
- Consumer Behaviour Towards Readymade Garments With Reference To ITCDocument96 pagesConsumer Behaviour Towards Readymade Garments With Reference To ITCchunnu12345678980% (5)
- Consumer Decision Making ProcessDocument69 pagesConsumer Decision Making ProcessROHAN DESAINo ratings yet
- Consumer Behavior Is The Study of How People Buy, What They BuyDocument9 pagesConsumer Behavior Is The Study of How People Buy, What They BuyPushpendra Trivedi100% (1)
- How Do Customers Buy?Document5 pagesHow Do Customers Buy?Vikas KhobragadeNo ratings yet
- By DR - Genet Gebre: 5. Consumer Decision Making Process (Mbam 641)Document32 pagesBy DR - Genet Gebre: 5. Consumer Decision Making Process (Mbam 641)Legesse Gudura MamoNo ratings yet
- The Consumer Buying Decision Process Looks at How Consumers Make Buying DecisionsDocument4 pagesThe Consumer Buying Decision Process Looks at How Consumers Make Buying DecisionsKunal ChauhanNo ratings yet
- CBAssignment HoangThuyLinhDocument6 pagesCBAssignment HoangThuyLinhlinhcindyNo ratings yet
- Course 3 - Consumer BehaviorDocument41 pagesCourse 3 - Consumer BehaviorRGN 11E 6 ANANYA GARGNo ratings yet
- Definition of Consumer BehaviourDocument2 pagesDefinition of Consumer BehaviourHeenaNo ratings yet
- Roxas, Dan - POM - Assignment3Document6 pagesRoxas, Dan - POM - Assignment3DAN CARLO ROXASNo ratings yet
- Buying Decision ProcessDocument3 pagesBuying Decision ProcessUsman KhizarNo ratings yet
- Principles of Marketing: BY William Asamoah-AppiahDocument64 pagesPrinciples of Marketing: BY William Asamoah-AppiahDaniel RizviNo ratings yet
- Decision Making: Consumer Behavior, 9EDocument21 pagesDecision Making: Consumer Behavior, 9ELya GayiNo ratings yet
- BOM Unit 4 - Consumer BehaviourDocument27 pagesBOM Unit 4 - Consumer BehaviourKaushal SabalNo ratings yet
- HW 26526 14Document10 pagesHW 26526 14Harshita MarmatNo ratings yet
- Purchase Proccess & Post Purchase BehaviourDocument32 pagesPurchase Proccess & Post Purchase Behaviourprtyushsolanki67% (3)
- Unit 2 Consumer BehaviourDocument23 pagesUnit 2 Consumer BehaviourDr Priyanka TripathyNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document23 pagesUnit 2Bhuvaneswari ANo ratings yet
- FREE Online Courses On Consumer Behaviour and Motivation - Meaning of Motivation ResearchDocument7 pagesFREE Online Courses On Consumer Behaviour and Motivation - Meaning of Motivation Researchpwd001No ratings yet
- Retail Management U-II BBA VI SEMDocument32 pagesRetail Management U-II BBA VI SEMakshi guptaNo ratings yet
- My FinalDocument67 pagesMy FinalkaurpreetgillNo ratings yet
- Mar BuyingDocument39 pagesMar BuyingMohan SavadeNo ratings yet
- Patronage Motives: Patronage Motives May Be Defined As Consideration or Impulses Emotional Patronage Motives: Emotional Patronage Motives Those ThatDocument3 pagesPatronage Motives: Patronage Motives May Be Defined As Consideration or Impulses Emotional Patronage Motives: Emotional Patronage Motives Those ThatThe State AcademyNo ratings yet
- The Buying Decision ProcessDocument7 pagesThe Buying Decision ProcessBirhanu DesalegnNo ratings yet
- Consumer and Business Buyer Behaviour NotesDocument7 pagesConsumer and Business Buyer Behaviour NotesSavannah Simone PetrachenkoNo ratings yet
- Customer SegmentationDocument33 pagesCustomer Segmentationlina100No ratings yet
- Lecture 3, Consumer Behaviour RefinedDocument23 pagesLecture 3, Consumer Behaviour RefinedShiro WanjiruNo ratings yet
- Ekb ModelDocument2 pagesEkb ModelManas Saha0% (1)
- Consumer Decision Making AdditionalDocument2 pagesConsumer Decision Making Additionalking hoboNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 MarketingDocument18 pagesChapter 3 MarketingNabin GhimireNo ratings yet
- Basic Model of Consumer BehaviorDocument41 pagesBasic Model of Consumer BehaviorRohit Kumar100% (1)
- How Do Customers BuyDocument3 pagesHow Do Customers BuyAkshai NayakNo ratings yet
- Consumer BehaviorDocument16 pagesConsumer Behaviorusama juttNo ratings yet
- Buyer BehaviourDocument15 pagesBuyer BehaviourLeo LeiroNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15 - PreparationDocument3 pagesChapter 15 - PreparationTu Thanh Quang NguyenNo ratings yet
- Consumer Decision Making: by Rachita Jayswal, LecturerDocument46 pagesConsumer Decision Making: by Rachita Jayswal, Lecturerrachita1112100% (1)
- MBA MK 1 Unit 2Document42 pagesMBA MK 1 Unit 2Mayank SinghNo ratings yet
- Chap 3 Problem Regconition (AutoRecovered)Document9 pagesChap 3 Problem Regconition (AutoRecovered)s4023247No ratings yet
- MM Unit - IIDocument18 pagesMM Unit - IIHecbjtbbvNo ratings yet
- Consumer Behaviour (PAPER CODE: MM-3202)Document23 pagesConsumer Behaviour (PAPER CODE: MM-3202)Bristi SonowalNo ratings yet
- Consumer Research Process & Consumer Decision MakingDocument50 pagesConsumer Research Process & Consumer Decision MakingGazal Atul SharmaNo ratings yet
- Decision MakingDocument3 pagesDecision MakingjassimranNo ratings yet
- Think and Supply Any Product: Unlocking Success Through Strategic Product SourcingFrom EverandThink and Supply Any Product: Unlocking Success Through Strategic Product SourcingNo ratings yet
- Consumer Behaviour Model of Philip KotlerDocument13 pagesConsumer Behaviour Model of Philip KotlerQuelNo ratings yet
- A Project Report On Big BazarDocument183 pagesA Project Report On Big BazarSourav Roy100% (1)
- A Study in Role of Celebrity Endorsements On Consumer Buying BehaviourDocument7 pagesA Study in Role of Celebrity Endorsements On Consumer Buying Behaviourwaqas farooqNo ratings yet
- Principles of Marketing - Quarter 3 - Module 5 (For Print)Document10 pagesPrinciples of Marketing - Quarter 3 - Module 5 (For Print)Stephanie MinorNo ratings yet
- What Is Marketed?: Chapter 1 Defining Marketing For The New RealitiesDocument9 pagesWhat Is Marketed?: Chapter 1 Defining Marketing For The New RealitiesRhobie TorresNo ratings yet
- Marketing Management Assignment: Jewellery Buying BehaviourDocument16 pagesMarketing Management Assignment: Jewellery Buying BehaviourmechatronicsmkNo ratings yet
- Major Research Project: Submitted To DAVV (Indore) in Partial Fulfillment of The Degree ofDocument70 pagesMajor Research Project: Submitted To DAVV (Indore) in Partial Fulfillment of The Degree ofRohanNo ratings yet
- Muni-Awudu, G., Kwon, H. 2017Document143 pagesMuni-Awudu, G., Kwon, H. 2017nithyaNo ratings yet
- Literature Review On Consumer Purchase DecisionDocument7 pagesLiterature Review On Consumer Purchase Decisionzeiqxsbnd100% (1)
- Impact of Humor in Advertisements On The Selection and Brand Recall AspectsDocument13 pagesImpact of Humor in Advertisements On The Selection and Brand Recall AspectsPratyush BaruaNo ratings yet
- A Study On Consumer Buying BehaviourDocument66 pagesA Study On Consumer Buying BehaviourharshNo ratings yet
- The Times of IndiaDocument66 pagesThe Times of Indiaakshaykumar2No ratings yet
- Thesis Revise 5Document18 pagesThesis Revise 5Niala AlmarioNo ratings yet
- Consumer Awareness, Motivations and BuyingDocument17 pagesConsumer Awareness, Motivations and BuyingJARVIZNo ratings yet
- Personal Selling - Session 2Document61 pagesPersonal Selling - Session 2ak3098088No ratings yet
- MM - IDocument5 pagesMM - ISameer SamNo ratings yet
- Shashankgprollno112 130507091013 Phpapp01Document62 pagesShashankgprollno112 130507091013 Phpapp01Dola SahaNo ratings yet
- MR TitleDocument6 pagesMR Title202120609No ratings yet
- CB-Unit 04-Organizational Buying Process PDFDocument12 pagesCB-Unit 04-Organizational Buying Process PDFVivek Lal Karna100% (1)
- A Study On Product Packaging Impact On Consumer Buying BehaviourDocument9 pagesA Study On Product Packaging Impact On Consumer Buying BehaviourNovelty JournalsNo ratings yet
- 1 Tto 5Document67 pages1 Tto 5DhavalNo ratings yet
- RM ProjectDocument75 pagesRM ProjectNazia Zabin Memon100% (1)
- Answers To Applying Marketing Knowledge Questions PDFDocument67 pagesAnswers To Applying Marketing Knowledge Questions PDFUtkarsh Gupta100% (1)
- Bonn BiscuitsDocument71 pagesBonn Biscuitssonabeta07No ratings yet