Professional Documents
Culture Documents
XML Example
XML Example
Uploaded by
etcoolswiss0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views11 pagesInformation regarding XML
Original Title
XML
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentInformation regarding XML
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views11 pagesXML Example
XML Example
Uploaded by
etcoolswissInformation regarding XML
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 11
XML EXAMPLE
XML Example: test.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="iso-8859-1"?>
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1" >
<head>
<title> Title of text XHTML Document </title>
</head>
<body>
<div class="myDiv">
<h1> Heading of Page </h1>
<p> here is a paragraph of text. I will include inside this paragraph a bunch of
wonky text so that it looks fancy. </p>
<p>Here is another paragraph with <em>inline emphasized</em> text, and
<b> absolutely no</b> sense of humor. </p>
<p>And here is another paragraph, this one containing an <img src="image.gif"
alt="waste of time" /> inline image, and a <br /> line break. </p>
</div>
</body></html>
Example Message
<partorders xmlns=http://myco.org/Spec/partorders.desc>
<order ref=x23-2112-2342 date=25aug1999-12:34:23h>
<desc> Gold sprockel grommets, with matching hamster</desc>
<part number=23-23221-a12 />
<quantity units=gross> 12 </quantity>
<delivery-date date=27aug1999-12:00h>
</order>
<order ref=x23-2112-2342 date=25aug1999-12:34:23h>
. Order something else ..
</order>
</partorders>
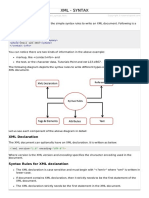
XML Parsers
An XML parser is a program that can read an XML
document and provide programmatic access to the
document
Two types of parsers:
1) DOM based Document Object Model
Constructs a tree that represents the
document
2) SAX based Simple API for XML
Generates events when parts of the
document are encountered.
Can also be classified as push or pull parsers
XML Characters
Consist of carriage returns, line feeds
and Unicode characters
XML is either markup or text
Markup is enclosed in < and >
Character text is the text between a
start and end tag
Child elements are considered markup
White Space
Parsers consider whitespace inside
text data to be significant and must
pass it to an application
An application can consider
whitespace significant or insignificant.
Normalization is the process in which
whitespace is collapsed or removed
Entities
&, <, >, (apostrophe), and (double
quote) are special characters and may
not be used in character data directly
To use these characters we code
entity references which begin with an
ampersand and end with a semicolon
& < > '
"
<mytag>David's
Tag</mytag>
Root Element
<?xml version="1.0"?>
<xs:schema>
...
...
</xs:schema>
Some Simple Data Types
XML Schema has a lot of built-in data
types, including:
xs:string
xs:decimal
xs:integer
xs:boolean
xs:date
xs:time
Simple Elements
Here are some XML elements:
<lastname>Refsnes</lastname>
<age>36</age>
<dateborn>1970-03-27</dateborn>
And here are the corresponding
simple element definitions:
<xs:element name="lastname" type="xs:string"/>
<xs:element name="age" type="xs:integer"/>
<xs:element name="dateborn" type="xs:date"/>
Default and Fixed Values for Simple
Elements
Simple elements may have a default value OR a
fixed value specified.
A default value is automatically assigned to the
element when no other value is specified.
In the following example the default value is "red":
<xs:element name="color" type="xs:string"
default="red"/>
A fixed value is also automatically assigned to the
element, and you cannot specify another value.
In the following example the fixed value is "red":
<xs:element name="color" type="xs:string"
fixed="red"/>
You might also like
- What Is HTML?Document36 pagesWhat Is HTML?Anand TiwariNo ratings yet
- Document - Repository and Search Engine For Alumni of CollegeDocument110 pagesDocument - Repository and Search Engine For Alumni of CollegeSminfo Mdu67% (3)
- XML and Web Technologies For Data Sciences With R-Springer-Verlag New York (2014)Document677 pagesXML and Web Technologies For Data Sciences With R-Springer-Verlag New York (2014)Carlos Barco100% (1)
- Sap Pi Xi NotesDocument28 pagesSap Pi Xi Notessryalla100% (4)
- 3 Create XML File and Explain About Web ServersDocument14 pages3 Create XML File and Explain About Web ServersArunNo ratings yet
- Generating XML Data: Defining The Root ElementDocument5 pagesGenerating XML Data: Defining The Root ElementMaheshNo ratings yet
- XML JavascriptDocument62 pagesXML Javascriptanon-506495No ratings yet
- Sabyasachi MoitraDocument26 pagesSabyasachi MoitraSabyasachi MoitraNo ratings yet
- Web Technologies: Prepared byDocument66 pagesWeb Technologies: Prepared bygrchandraNo ratings yet
- Adding HTML-Style Text: XHTMLDocument5 pagesAdding HTML-Style Text: XHTMLgovindneoNo ratings yet
- HTML and CSSDocument93 pagesHTML and CSSHimanshu SachdevaNo ratings yet
- XMLDocument27 pagesXMLVivekNo ratings yet
- XML Document Rule, XML Structuring, XML Presentation TechnologiesDocument53 pagesXML Document Rule, XML Structuring, XML Presentation TechnologieshariniNo ratings yet
- Tutorial XHTMLDocument22 pagesTutorial XHTMLirsyad rahmanNo ratings yet
- HTML NotesDocument21 pagesHTML Notesiwillkeeplovingu08No ratings yet
- Editors: Write HTML Using Notepad or TexteditDocument53 pagesEditors: Write HTML Using Notepad or Texteditamirgholami1No ratings yet
- XML SyntaxDocument3 pagesXML Syntaxpulkit GargNo ratings yet
- HTML w3 SchoolsDocument30 pagesHTML w3 Schoolsmohit123ashuNo ratings yet
- Line Break TagDocument23 pagesLine Break TagJalla Sudharshan ReddyNo ratings yet
- HTML Form Controls: ActionDocument14 pagesHTML Form Controls: ActionManish Singh SuryavanshiNo ratings yet
- What Is HTML????Document12 pagesWhat Is HTML????naushinaliNo ratings yet
- HTML Basic - : 4 ExamplesDocument13 pagesHTML Basic - : 4 ExamplesjalalkhalilNo ratings yet
- Basic HTML TutorialDocument13 pagesBasic HTML TutorialkeshavpoudelNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Pemrograman WebDocument77 pagesTutorial Pemrograman WebAan Kristanto NugrohoNo ratings yet
- HTML LectDocument6 pagesHTML LectJoe AymanNo ratings yet
- Write HTML Using Notepad or Textedit: ExampleDocument23 pagesWrite HTML Using Notepad or Textedit: ExamplemumstelNo ratings yet
- Example Explained: This Is My Main PageDocument22 pagesExample Explained: This Is My Main PageBhavin PanchalNo ratings yet
- MicrosoftDocument20 pagesMicrosoftIvm IvmNo ratings yet
- Examples of XMLDocument6 pagesExamples of XMLkrishitha aravindNo ratings yet
- Markup Language (HTML) Is The Predominant: HypertextDocument11 pagesMarkup Language (HTML) Is The Predominant: HypertextAnurag ChahalNo ratings yet
- IWP MQP SolpdfDocument49 pagesIWP MQP Solpdfiamsurya195No ratings yet
- XML and JSPDocument27 pagesXML and JSPsumit tripathyNo ratings yet
- Introduction To HTMLDocument21 pagesIntroduction To HTMLJayachandra VenkataramanappaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To XMLDocument8 pagesIntroduction To XMLNITESH RAWALNo ratings yet
- HTMLDocument104 pagesHTMLKrishno Jeet Sutra DharNo ratings yet
- HTML Basics Guide Pythonista PlanetDocument16 pagesHTML Basics Guide Pythonista Planetproject satuNo ratings yet
- UNIT 4 HTMLDocument7 pagesUNIT 4 HTMLDhruv DankharaNo ratings yet
- XML FMTDocument8 pagesXML FMTBharathi Krishna LNo ratings yet
- HTML Tags: Prepared by Shahzeb KhanDocument18 pagesHTML Tags: Prepared by Shahzeb KhanpariNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 XML IntroductionDocument64 pagesLecture 1 XML IntroductionVinit Vini JainNo ratings yet
- HTML Course Introduction For IgcseDocument36 pagesHTML Course Introduction For IgcseChu ChilliesNo ratings yet
- Jquery 1 4 2 SdocmlDocument175 pagesJquery 1 4 2 SdocmlArno CornetteNo ratings yet
- HTML Cha1Document49 pagesHTML Cha1အောင်ပိုင် ဖြိုးNo ratings yet
- HTML Course NotesDocument9 pagesHTML Course Notesradwa.talaatNo ratings yet
- UNIT-4 Web AuthoringDocument32 pagesUNIT-4 Web Authoringbeki.ad10No ratings yet
- HTMLDocument68 pagesHTMLKumar GauravNo ratings yet
- Write The Standard HTML Documents and Discuss The Various Basic Tags With Code ExamplesDocument7 pagesWrite The Standard HTML Documents and Discuss The Various Basic Tags With Code Examplessmartclass2022jknNo ratings yet
- HTMLDocument26 pagesHTMLPrathapNo ratings yet
- 70-480 Exam NotesDocument19 pages70-480 Exam NotesFreedom SpiritNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Advanced Java JSPDocument12 pagesModule 2 Advanced Java JSPRithvik DadapuramNo ratings yet
- XML Document Rule, XML Structuring, XML Presentation TechnologiesDocument53 pagesXML Document Rule, XML Structuring, XML Presentation TechnologiesRamya MaryNo ratings yet
- HTML - ListsDocument47 pagesHTML - ListsManish Singh SuryavanshiNo ratings yet
- Lab #9Document8 pagesLab #9aamirali1061aNo ratings yet
- HTMLDocument31 pagesHTMLmanasailla666No ratings yet
- Htmlcourse 2Document31 pagesHtmlcourse 2manar mohamedNo ratings yet
- Html5: Writing HTML Using Notepad or TexteditDocument7 pagesHtml5: Writing HTML Using Notepad or TexteditThangadurai PonnusamyNo ratings yet
- E Tensible Arkup Anguage Unit-3: Basic XML DTD XML Schema Dom Vs Sax Presenting XMLDocument39 pagesE Tensible Arkup Anguage Unit-3: Basic XML DTD XML Schema Dom Vs Sax Presenting XMLGODDU NAVVEN BABUNo ratings yet
- XML Subjective Questions and AnswersDocument6 pagesXML Subjective Questions and AnswersSaravanan SanthoshNo ratings yet
- JSP PrgmsDocument13 pagesJSP PrgmsMohammed JeelanNo ratings yet
- Build Simple Websites Using Commercial ProgramsDocument51 pagesBuild Simple Websites Using Commercial ProgramsIsrael EyasuNo ratings yet
- Mastering JavaScript: The Complete Guide to JavaScript MasteryFrom EverandMastering JavaScript: The Complete Guide to JavaScript MasteryRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- SAP PI 7.3 Training MaterialDocument153 pagesSAP PI 7.3 Training MaterialUrloNegro50% (4)
- XMLDocument23 pagesXMLsankarcptNo ratings yet
- Sharp Interview QuestionsDocument133 pagesSharp Interview Questionsparit_qa8946No ratings yet
- Benjamin Gan (Bengan@iss - Nus.edu - SG) Institute of Systems Science National University of SingaporeDocument89 pagesBenjamin Gan (Bengan@iss - Nus.edu - SG) Institute of Systems Science National University of SingaporeJitendra ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- Web Data: XMLDocument13 pagesWeb Data: XMLAshokNo ratings yet
- Interfacing PB With The Web 1 2 PDFDocument4 pagesInterfacing PB With The Web 1 2 PDFbhutengsNo ratings yet
- Asm4 Guide PDFDocument154 pagesAsm4 Guide PDFTRAN Tuan HiepNo ratings yet
- Unit - 1 SAXDocument8 pagesUnit - 1 SAX4048 Sivashalini.GNo ratings yet
- ENOVIA Program Central Administrator's Guide (V6R2011)Document136 pagesENOVIA Program Central Administrator's Guide (V6R2011)蔡佳純No ratings yet
- Dice Resume CV ABHISHEK SINHADocument4 pagesDice Resume CV ABHISHEK SINHADave JonesNo ratings yet
- XML Processing With PythonDocument447 pagesXML Processing With Pythonpjf54100% (1)
- AbbreviationDocument3 pagesAbbreviation0796105632No ratings yet
- Import XML Data To Google App EngineDocument25 pagesImport XML Data To Google App EngineKristian ArjiantoNo ratings yet
- CS311 Midterm Papers-1Document22 pagesCS311 Midterm Papers-1asimtoqeer458No ratings yet
- Unit Iv: PHP and XMLDocument163 pagesUnit Iv: PHP and XMLSENTHIL RNo ratings yet
- 9ib XMLDocument51 pages9ib XMLapi-3831209100% (1)
- Unit 2Document11 pagesUnit 2Kavya AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Question Bank Subject: IT8501 Web Technology Sem / Year: V Sem/ Iii YearDocument11 pagesQuestion Bank Subject: IT8501 Web Technology Sem / Year: V Sem/ Iii YearVarsha BhuviNo ratings yet
- iOS Interview Questions With Answers PDFDocument12 pagesiOS Interview Questions With Answers PDFmani0% (1)
- 3 4 Anton Gerasimov OTADocument49 pages3 4 Anton Gerasimov OTAsaika_1982No ratings yet
- GJava DocsDocument743 pagesGJava DocsChakka Ramesh GuptaNo ratings yet
- SAX DOM: 1. Which Parser Can Get Better Speed, DOM or SAX Parsers?Document51 pagesSAX DOM: 1. Which Parser Can Get Better Speed, DOM or SAX Parsers?Anonymous rcmeSfj5No ratings yet
- CACS 205: Web Technology XML: Prepared by Krishna Pd. Acharya (Mechi Multiple Campus)Document67 pagesCACS 205: Web Technology XML: Prepared by Krishna Pd. Acharya (Mechi Multiple Campus)Dipesh GuptaNo ratings yet
- 2082 - Unit 4 Notes WT (BCA 204)Document26 pages2082 - Unit 4 Notes WT (BCA 204)DhananjayKumarNo ratings yet
- XML Subjective Questions and AnswersDocument6 pagesXML Subjective Questions and AnswersSaravanan SanthoshNo ratings yet
- XML, COBOL and ApplicationDocument51 pagesXML, COBOL and ApplicationpsavazNo ratings yet