Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lecture 8a Electric Potential
Lecture 8a Electric Potential
Uploaded by
johndoe217180 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views9 pageselectric potential
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentelectric potential
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views9 pagesLecture 8a Electric Potential
Lecture 8a Electric Potential
Uploaded by
johndoe21718electric potential
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 9
Batteries and Potential Difference.
A battery is a device that stores positive charge on one
of its terminals and negative charge on the other
terminal.
Electric Potential Energy.
Potential energy can be defined as the capacity for
doing work which arises from position.
In the electrical case, a charge will exert a force on any
other charge and potential energy arises from any
collection of charges.
For example, if a positive charge Q
1
is fixed at some
point in space, any other positive charge which is
broght close to it will experience a replsive force
and will therefore have potential energy. !he potential
energy of a test charge Q
"
in the vicinity of this sorce
charge will be#
r
Q Q
k x Force Energy
" 1
distance = =
Electric Potential.
At a point in space, the electric potential is the
potential energy per nit of charge that is associated
with a static electric field. It is a scalar $antity,
typically measred in volts.
r
Q
k
Q
r
Q Q
k
P
"
" 1
%harge
&nergy Potential
point a at otential = =
Potential at a point is defined as the work done in
moving a charge of 1 colomb from infinity to that
point. 'ymbol for potential at the point A is
(
A
!he difference in electrical potential between two
points is known as the potential difference or voltage.
Potential Difference between two charged metal
plates A and B
A )
* +
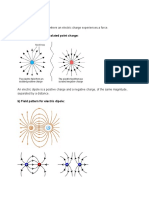
!he electric field that exists between two metal plates
is niform except at the edges. %heck the diagrams for
the electric field lines.
If an electron , +ve charge - were moved from the
positive plate A to the negative plate ), work wold
have to be done to overcome the force of replsion
between the +ve electron and the +vely charge metal
plate at ).
!his work wold be stored in the election as potential
energy as long as the election remains at plate ). !his
is also tre if a *ve charge is moved from plate ) to A.
)ecase of this change in potential energy we say that
there is a difference in potential or potential difference
, p.d. - between the plates.
!he potential difference in this context is an indication
of the amont of work that wold be done in moving a
charge between two points.
!he '.I. nit of potential difference is called the (olt
and the potential difference is also called voltage.
!he nit (olt is defined as follows # !here is a
potential difference of 1 (olt between two points when
1 .ole of work has to be done to move 1 %olomb of
charge between the two points.
(
A )
is symbol for the potential difference between A
and )
/ote also (
A)
0 (
A
+ (
)
1elationship between potential difference ( and work
done ,energy- is given by
2314 53/& 0 Q . (.
1elationship between &lectric Field Intensity , & - and
Potential ( at a distance of r,m- from a point charge is
given by
r E V . =
1elationship between &lectric Field Intensity , & - and
Potential difference ( between two parallel charge
metal plates a distance d ,m- apart is given by
d E V . =
Also it is important to note that Potential or Potential
difference is a scalar $antity and this is always the
case the
if Q is +ve then the potential is negative and
if Q is *ve then the potential is positive.
&lectric 5ipole# &$al and opposite point charges a
distance r ,m- apart.
Q
1
Q
"
r ,m-
&xample 1.An electric dipole has a positive charge of
"6% and a length of 6.7mm.
%alclate ,i- the electric force between the two
charges
,ii- &lectric field intensity at the midpoint ,A- of the
dipole.
,iii- !he potential at the midpoint.
Q
1
A Q
"
r ,m-
Q
1
0 * "6x16
+8
% Q
"
0 + "6x16
+8
%
,i- 9se %olomb:s ;aw to calclate the vale of the
force i.e. magnitde
F 0 1 |Q
1
| |Q
"
|
< r
"
0 = x 16
=
"6 x 16
+8
x "6 x 16
+8
,7 x 16
+<
-
"
0 1.<< x 16
>
/
,ii- !o calclate the total electric field intensity at the
midpoint of the dipole we will calclate the field
strength de to each point charge individally first and
then calclate the total by adding the two vales
together remembering that there are each vectors and
so they have to be added as sch.
&
1A
0 !he electric field intensity at the midpoint A of
the dipole de to the charge Q
1
a distance
".7 mm from A
&
"A
0 !he electric field intensity at the midpoint A of
the dipole de to the charge Q
"
a distance
".7 mm from A
As & is a vector $antity we need to calclate its
magnitde and its direction
|& | 0 k |Q|
r
"
|&
1A
| 0 k |Q
1
|
r
"
0 =x16
=
,"6 x16
+8
-
,".7 x16
+<
-
"
0 ".?? x 16
1"
/ %
+1
Acting Away from Q
1
|&
"A
| 0 k |Q
"
|
r
"
0 =x16
=
,"6 x16
+8
-
,".7 x16
+<
-
"
0 ".?? x 16
1"
/ %
+1
Acting towards Q
"
'o the directions of &
1A
and &
"A
are the same i.e. away
from Q
1
and towards Q
"
are the same direction so the
total vale of
&
A
0 ".?? x 16
1"
/ %
+1
* ".?? x 16
1"
/ %
+1
&
A
0 7.88 x 16
1"
/ %
+1
!owards Q
"
1ecall adding two vectors in the same direction.
,iii- !o calclate the potential at A
since Q
1
is a positive charge it cases a positive
potential
(
1A
0 &
1A
. r 0 ".?? x 16
1"
, ".7 x16
+<
-
0 >." x 16
?
(olts
As Q
"
is a negative charge it cases a negative
potential.
(
"A
0 &
"A
. r 0 + ".?? x 16
1"
,".7 x16
+<
-
0 + >." x 16
?
(olts
(
A
0 (
1A
* (
"A
0 6 (
Problem 'heet &lectrostatics.
1. %alclate ,a- !he electric field intensity in air at a
distance of @6 cm from a point charge of 7 n%. ,b-
!he force acting on a charge of <66% placed at @6cm
from the original charge.
". A dipole has a positive charge of 8% and a length
of 6."mm
%alclate ,a- !he force acting on the +ve charge ,b-
!he electric field intensity and the electric potential at
the midpoint of the dipole. ,c- !he electric field
intensity at a distance of 6.7mm beyond the *ve
charge.
@. !wo parallel plates have a p.d. of 766 k( placed
across them. !he plates are "6cm apart. %alclate ,a-
!he electric field intensity between the plates ,b- !he
force acting on an electron placed between the plates
given that e 0 1.8 x 16
+1=
%.
,c- Aow long will it take an electron starting from one
plate to reach the other plate m
e
, mass of electron - 0
= x 16
+@1
kg.
<. A dipole has a positive charge of 1.8 x 16
+1=
% and a
length of " x
16
+16
m
%alclate ,a- !he force acting on the +ve charge ,b-
!he electric field intensity and the electric potential at
the midpoint of the dipole , point A -. ,c- !he electric
field intensity and the electric potential at a distance of
16 x 16
+16
m beyond the *ve charge , point ) -.
7. An electric field is maintained between two parallel
metal plates by a p.d. of 1666 (. A charge of 1 x 16
+17
% is moved between the plates by the forces of the
field which exists between the plates. !he plates are
"6 mm apart.
,a- Aow mch work is done in moving the charge
from one plate to another
,b- %alclate the field strength in / %
+1
,c- %alclate the field strength in ( m
+1
You might also like
- AP Physics Question BankDocument99 pagesAP Physics Question BankElianne Gabbay100% (2)
- Chapter 25 PDFDocument25 pagesChapter 25 PDFRayyan SalmanNo ratings yet
- LawDocument30 pagesLawrogelio1234567100% (1)
- Electricity and Magnetism: Problems in Undergraduate PhysicsFrom EverandElectricity and Magnetism: Problems in Undergraduate PhysicsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- g485 5 1 1 Electric FieldsDocument10 pagesg485 5 1 1 Electric Fieldsapi-236179294No ratings yet
- g485 5.1.1 Electric Fields OCR A Physics NOTES For Revision or LearningDocument10 pagesg485 5.1.1 Electric Fields OCR A Physics NOTES For Revision or Learningviyas07No ratings yet
- Chapter1 Electrostatic 2016 ReviewedDocument98 pagesChapter1 Electrostatic 2016 ReviewedSyaza IzzatyNo ratings yet
- Electric Field Is A Region Where An Electric Charge Experiences A ForceDocument6 pagesElectric Field Is A Region Where An Electric Charge Experiences A ForceTeow JeffNo ratings yet
- Electric Field Is A Region Where An Electric Charge Experiences A ForceDocument6 pagesElectric Field Is A Region Where An Electric Charge Experiences A Force加卡内-张进哲No ratings yet
- Chapter 22 (1) .ElectDocument28 pagesChapter 22 (1) .ElectOsama HassanNo ratings yet
- Physics 12thDocument119 pagesPhysics 12thAbhijith Ramachandran100% (1)
- CH 22Document32 pagesCH 22هشام المالكيNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics: Two Kinds of ChargesDocument37 pagesElectrostatics: Two Kinds of ChargesShajjadul HoqueNo ratings yet
- 10a-Electrostatics MC Practice ProblemsDocument38 pages10a-Electrostatics MC Practice ProblemsJanel EdwardsNo ratings yet
- New Topic 18 ELECTRIC FIELDSDocument8 pagesNew Topic 18 ELECTRIC FIELDSnadiamuhorakeye29No ratings yet
- Grade 11 TS Exercise 14 Page 174Document20 pagesGrade 11 TS Exercise 14 Page 174Priyanka KanaNo ratings yet
- 1 Electrostatics LPDocument61 pages1 Electrostatics LPtumiNo ratings yet
- Topic 6 Fields and Forces and Topic 9 Motion in FieldsDocument30 pagesTopic 6 Fields and Forces and Topic 9 Motion in Fieldsgloria11111No ratings yet
- Cbse Class Xii PhysicsDocument30 pagesCbse Class Xii PhysicskumarnpccNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Physics Chapter 1Document11 pagesClass 12 Physics Chapter 1Garry BroNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics I Electric Charges and Coulomb's Law: (Important Formulae and Concepts)Document24 pagesElectrostatics I Electric Charges and Coulomb's Law: (Important Formulae and Concepts)Sankar KumarasamyNo ratings yet
- Physics Study MaterialDocument150 pagesPhysics Study Materialsiya sharmaNo ratings yet
- Previous Year Questions CH 1Document26 pagesPrevious Year Questions CH 1MickuNo ratings yet
- Electrostatic PotentialDocument20 pagesElectrostatic PotentialhiranmayeeNo ratings yet
- Electric Fields IB HandoutDocument57 pagesElectric Fields IB HandoutBakuByronNo ratings yet
- Electrostatic Potential and CapascitanceDocument9 pagesElectrostatic Potential and CapascitancemapuclouddigitalworldNo ratings yet
- Efields PDFDocument73 pagesEfields PDFsydonai416No ratings yet
- 2023-2024-Class XII-Physics-Part 1-AWDocument24 pages2023-2024-Class XII-Physics-Part 1-AWsafaaNo ratings yet
- Physics Study Material 12Document220 pagesPhysics Study Material 12Ramesh PaikNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Chapterwise PYQs Shobhit NirwanDocument65 pagesClass 12 Chapterwise PYQs Shobhit NirwanHimanshu92% (13)
- XII CH - 1&2 AsssignmentDocument2 pagesXII CH - 1&2 AsssignmentYash KumarNo ratings yet
- ElectrostaticsDocument9 pagesElectrostaticsapi-283216587No ratings yet
- 18 - Electric FieldsDocument79 pages18 - Electric Fieldsnathanbushe1638No ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument17 pagesPhysicspaninikumar0000No ratings yet
- ElectrostaticsDocument28 pagesElectrostaticssonaliswain2345No ratings yet
- Electric Field IntensityDocument11 pagesElectric Field IntensityDeeNo ratings yet
- Electric Potential Energy and Electric PotentialDocument12 pagesElectric Potential Energy and Electric PotentialMarquee Mae EnriquezNo ratings yet
- Thread 3-1 (Electeic Potential+electric Current)Document11 pagesThread 3-1 (Electeic Potential+electric Current)srian551No ratings yet
- Module 4 - Electric Potential and CapacitanceDocument9 pagesModule 4 - Electric Potential and CapacitancePatrick CruzNo ratings yet
- Electric Charges FieldsDocument19 pagesElectric Charges FieldsSridevi KamapantulaNo ratings yet
- K Uwhr 3 RSi 2 Js PMP MJK WKDocument47 pagesK Uwhr 3 RSi 2 Js PMP MJK WKMystry FactNo ratings yet
- Physics: Aurora ClassesDocument21 pagesPhysics: Aurora ClassesxentrixxNo ratings yet
- 17 - Electric FieldsDocument32 pages17 - Electric FieldsBONGLAV JemasonNo ratings yet
- A2 43 ElectricfieldsDocument37 pagesA2 43 ElectricfieldsHany ElGezawyNo ratings yet
- Electric Potential and CapacitanceDocument8 pagesElectric Potential and CapacitanceCyrelle GuzmanNo ratings yet
- 29 - Electric Field and PotentialDocument8 pages29 - Electric Field and PotentialPankaj Mishra0% (1)
- Electrostatics ProblemsDocument8 pagesElectrostatics ProblemsBadamNo ratings yet
- Coloumb Law....Document16 pagesColoumb Law....JayeNo ratings yet
- Electrostatic For MurniDocument55 pagesElectrostatic For MurniAnonymous RMXuPuNo ratings yet
- Week 2Document36 pagesWeek 2GeminiNo ratings yet
- Thread 3-2 Electric Potential and CapacitorDocument5 pagesThread 3-2 Electric Potential and CapacitorheroNo ratings yet
- Versatile Notes PHYSICS XII Chapter 01Document36 pagesVersatile Notes PHYSICS XII Chapter 01ShaheerNo ratings yet
- Versatile Notes PHYSICS XIIDocument209 pagesVersatile Notes PHYSICS XIIShaheerNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 Electric Field and Electric FluxDocument17 pagesTopic 2 Electric Field and Electric FluxSmk Abdul Rahim Dua100% (1)
- SP025 Modul Chapter 1Document33 pagesSP025 Modul Chapter 1naderaqistina23No ratings yet
- Physics ProjectDocument16 pagesPhysics ProjectAbishek KumarNo ratings yet
- Phy ProjectDocument16 pagesPhy ProjectAbishek KumarNo ratings yet
- Electrostatics Xii HDHW Vsa &VS 2023Document6 pagesElectrostatics Xii HDHW Vsa &VS 2023mishra.sanskar12345No ratings yet
- Feynman Lectures Simplified 2B: Magnetism & ElectrodynamicsFrom EverandFeynman Lectures Simplified 2B: Magnetism & ElectrodynamicsNo ratings yet