Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Organic Chemistry Midterm Exam 1 Study Guide - Information To Memorize
Organic Chemistry Midterm Exam 1 Study Guide - Information To Memorize
Uploaded by
Teddy LarkinOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Organic Chemistry Midterm Exam 1 Study Guide - Information To Memorize
Organic Chemistry Midterm Exam 1 Study Guide - Information To Memorize
Uploaded by
Teddy LarkinCopyright:
Available Formats
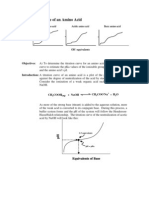
pKa Values Acids
- The smaller the value of the pKa the more acidic the acid (stronger acid)
- The more Acidic an acid is the more stable its conjugate base.
- The less Acidic an acid is the less stable its conjugate base.
- A more stable base (a weaker base) has a more acidic conjugate acid
relative to a less stable base.
n Name Formula
1 Methane CH
4
2 Ethane CH
3
CH
3
3 Propane CH
3
CH
2
CH
3
4 Butane CH
3
CH
2
CH
2
CH
3
5 Pentane CH
3
(CH
2
)
3
CH
3
6 Hexane CH
3
(CH
2
)
4
CH
3
7 Heptane CH
3
(CH
2
)
5
CH
3
8 Octane CH
3
(CH
2
)
6
CH
3
9 Nonane CH
3
(CH
2
)
7
CH
3
10 Decane CH
3
(CH
2
)
8
CH
3
11 Undecane CH
3
(CH
2
)
9
CH
3
12 Dodecane CH
3
(CH
2
)
10
CH
3
13 Tridecane CH
3
(CH
2
)
11
CH
3
14 Tetradecane CH
3
(CH
2
)
12
CH
3
15 Pentadecane CH
3
(CH
2
)
13
CH
3
16 Hexadecane CH
3
(CH
2
)
14
CH
3
17 Heptadecane CH
3
(CH
2
)
15
CH
3
18 Octadecane CH
3
(CH
2
)
16
CH
3
19 Nonadecane CH
3
(CH
2
)
17
CH
3
20 Icosane CH
3
(CH
2
)
18
CH
3
Branched Alkyl Groups
You might also like
- Mineralogy MCQs With AnswerDocument11 pagesMineralogy MCQs With Answerkumar Harsh100% (6)
- Biochem - C3 Lab Con 02 - Titration of Amino AcidsDocument66 pagesBiochem - C3 Lab Con 02 - Titration of Amino AcidsErnesto V. Ignacio Jr.No ratings yet
- Acids and Bases1Document12 pagesAcids and Bases1mttlaNo ratings yet
- Amine Basicity Is Measued by The PKa of Its Conjugate Acid PKaHDocument7 pagesAmine Basicity Is Measued by The PKa of Its Conjugate Acid PKaHRecky Jedianta RiadyNo ratings yet
- Titration CurveDocument12 pagesTitration Curveoguztop10No ratings yet
- 10.b Acid and Base Equilbria Part II-Chemistry Unit IDocument4 pages10.b Acid and Base Equilbria Part II-Chemistry Unit Imcleodtravis14No ratings yet
- Chapter 15Document50 pagesChapter 15陈希尧No ratings yet
- LAB 03 - PH and BuffersDocument23 pagesLAB 03 - PH and Bufferseliza makNo ratings yet
- Answers: Acids and Bases. Additional ProblemsDocument19 pagesAnswers: Acids and Bases. Additional ProblemsAnand Utsav KapoorNo ratings yet
- GTP in PharmaDocument34 pagesGTP in PharmaNdra PompomorinNo ratings yet
- Curs 11, 12Document29 pagesCurs 11, 12didibutterflyNo ratings yet
- Determination of Ka Value of Weak ADetermination of Ka Value of Weak AcidDocument6 pagesDetermination of Ka Value of Weak ADetermination of Ka Value of Weak Acidainmirsya100% (4)
- Week 1Document31 pagesWeek 1Najmedin AziziNo ratings yet
- Say My Name (Organichem) Phase 1.0Document115 pagesSay My Name (Organichem) Phase 1.0Dinesh RamaNo ratings yet
- Comparing Acidity and BasicityDocument1 pageComparing Acidity and BasicitybhartiyaanujNo ratings yet
- PH - Log (H O)Document26 pagesPH - Log (H O)UMAIR ASHFAQNo ratings yet
- Ka Lab RubenDocument3 pagesKa Lab Rubenrubenq270% (10)
- Moderator: Dr. R. K. Yadav (MD) Presented By: Ashish JaisawalDocument47 pagesModerator: Dr. R. K. Yadav (MD) Presented By: Ashish Jaisawalimranqazi11No ratings yet
- Identifying An Unknown Weak Acids ExperimentDocument18 pagesIdentifying An Unknown Weak Acids Experimentgeek3112100% (5)
- ) Iupac (International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry) - Is Used To Name OrganicDocument11 pages) Iupac (International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry) - Is Used To Name OrganicPkrajen PillaiNo ratings yet
- 3 - Acid Base Titration in Nonaqueous - DSWDocument27 pages3 - Acid Base Titration in Nonaqueous - DSWbrianNo ratings yet
- Determine Net Charge of Amino Acid With Different PH ValueDocument5 pagesDetermine Net Charge of Amino Acid With Different PH Valuetheodore_estradaNo ratings yet
- Acid Ba See QuilDocument48 pagesAcid Ba See QuilosmanaydınNo ratings yet
- 5.lipd Metabolism and Diseases - Part 1 - GVDocument33 pages5.lipd Metabolism and Diseases - Part 1 - GVNOMKHULEKO ALICENo ratings yet
- Carboxylic Acid 2Document20 pagesCarboxylic Acid 2brettNo ratings yet
- Carboxylic Acids and Esters and Amines New Edition Chm096Document26 pagesCarboxylic Acids and Esters and Amines New Edition Chm096Irsyad KamilNo ratings yet
- The Acid Dissociation ConstantDocument21 pagesThe Acid Dissociation ConstantLarry Villones Jr.100% (1)
- Selecting Buffer PH in Reversed-Phase HPLCDocument1 pageSelecting Buffer PH in Reversed-Phase HPLCCristian MeneguzziNo ratings yet
- Non Polar-Hydrophobic-Buried in Protein Core-AliphaticDocument4 pagesNon Polar-Hydrophobic-Buried in Protein Core-AliphaticRob FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Promod Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesPromod Cheat SheetAsad YaminNo ratings yet
- Ap Lab Manual 21 - Determination of Ka of Weak AcidsDocument4 pagesAp Lab Manual 21 - Determination of Ka of Weak AcidsSerena RoyNo ratings yet
- Systematic Nomenclature of Organic Compounds - Part 1: Rahmana Emran KartasasmitaDocument429 pagesSystematic Nomenclature of Organic Compounds - Part 1: Rahmana Emran KartasasmitaAbdullah FayzanNo ratings yet
- 5-Acids and BasesDocument57 pages5-Acids and BasessofeeNo ratings yet
- AlcaradiDocument1 pageAlcaradiJUANKARLOS70No ratings yet
- Understanding The Acid/Base Chemistry of Functional Groups in Organic MoleculesDocument43 pagesUnderstanding The Acid/Base Chemistry of Functional Groups in Organic MoleculeschnhnmNo ratings yet
- Anthranilic Acid Chemical PropertiesDocument3 pagesAnthranilic Acid Chemical PropertiesDanNo ratings yet
- PH P Log PH P When (HA) (A), or HA Is Half-IonizedDocument1 pagePH P Log PH P When (HA) (A), or HA Is Half-IonizedCharlie MakNo ratings yet
- AlcaradiDocument2 pagesAlcaradipeter_br3adNo ratings yet
- Lecture 9 - The Amino Acids II - Acid-Base CharacteristicsDocument33 pagesLecture 9 - The Amino Acids II - Acid-Base CharacteristicsThomas JonesNo ratings yet
- Buffers - Principles and PracticeDocument15 pagesBuffers - Principles and PracticeLaura NogueraNo ratings yet
- Metabolic Breakdown of Individual Amino Acids: To Citric Acid Cycle Intermediates or Their PrecursorsDocument36 pagesMetabolic Breakdown of Individual Amino Acids: To Citric Acid Cycle Intermediates or Their PrecursorsakmalsatibiNo ratings yet
- Buffer 0Document27 pagesBuffer 0Adinda Nur AdilaNo ratings yet
- Stereochemistry - Classification - Properties: Reactions: ¡Biologically Different! ¡Biologically Different!Document8 pagesStereochemistry - Classification - Properties: Reactions: ¡Biologically Different! ¡Biologically Different!Alberto CancelaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4: The Acid-Base ReactionDocument33 pagesChapter 4: The Acid-Base ReactionLaura BeltranNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 2 Quarter 4 - Week 4 Module 4: PH of Buffer SolutionsDocument12 pagesGeneral Chemistry 2 Quarter 4 - Week 4 Module 4: PH of Buffer SolutionsHazel EncarnacionNo ratings yet
- Protecting Groups - Tactical ConsiderationsDocument40 pagesProtecting Groups - Tactical ConsiderationsGuery SaenzNo ratings yet
- Mareial Complementar Unidade 4 Quimica Organica Gupos FuncionaisDocument10 pagesMareial Complementar Unidade 4 Quimica Organica Gupos FuncionaisepambarbaNo ratings yet
- WINSEM2022-23 BBIT206P LO VL2022230503900 Reference Material I 16-12-2022 Experiment 1 Buffer Stock Preparation FADocument4 pagesWINSEM2022-23 BBIT206P LO VL2022230503900 Reference Material I 16-12-2022 Experiment 1 Buffer Stock Preparation FAGravity JaiNo ratings yet
- PBOOKDocument151 pagesPBOOKPax TonNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan Dec 30, 2023Document7 pagesAdobe Scan Dec 30, 2023singh.freefiregamer2009No ratings yet
- Lecture 4 - Alkanes and Cycloalkanes Smart BoardDocument59 pagesLecture 4 - Alkanes and Cycloalkanes Smart Boardapi-19824406No ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Chemical Properties of WaterDocument28 pagesChapter 2: Chemical Properties of WaterKyle Broflovski100% (1)
- Alkanes: Contain Single Bonds CH - CH - CH - CH Saturated Hydrocarbon Substitution ReactionDocument28 pagesAlkanes: Contain Single Bonds CH - CH - CH - CH Saturated Hydrocarbon Substitution ReactionHesham El-RoussassiNo ratings yet
- 有机化学英文命名Document113 pages有机化学英文命名HAIRIN LeeNo ratings yet
- HYDROCARBONSDocument45 pagesHYDROCARBONSTherese Eva Marie DequitoNo ratings yet
- Assembly Instructions for Polypeptide Models: Academic Press/Molecular Design Inc. Precision Molecular ModelsFrom EverandAssembly Instructions for Polypeptide Models: Academic Press/Molecular Design Inc. Precision Molecular ModelsNo ratings yet
- Halogenated Benzenes, Toluenes and Phenols with Water: Solubility Data SeriesFrom EverandHalogenated Benzenes, Toluenes and Phenols with Water: Solubility Data SeriesAri L. HorvathRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Handbook of Reagents for Organic Synthesis: Reagents for OrganocatalysisFrom EverandHandbook of Reagents for Organic Synthesis: Reagents for OrganocatalysisNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Exam 1 Study GuideDocument5 pagesChemistry Exam 1 Study GuideTeddy LarkinNo ratings yet
- Final Paper - SchuylerDocument5 pagesFinal Paper - SchuylerTeddy LarkinNo ratings yet
- King Letter From Birmingham JailDocument3 pagesKing Letter From Birmingham JailTeddy LarkinNo ratings yet
- Summary and Analysis of Lincoln's "Gettysburg Address"Document2 pagesSummary and Analysis of Lincoln's "Gettysburg Address"Teddy Larkin100% (1)
- The Effects of Electronic Light On Sleep: Teddy Larkin Freshman Biology MajorDocument7 pagesThe Effects of Electronic Light On Sleep: Teddy Larkin Freshman Biology MajorTeddy LarkinNo ratings yet
- The Colonizer and The Colonized According To Frantz FanonDocument8 pagesThe Colonizer and The Colonized According To Frantz FanonTeddy LarkinNo ratings yet
- Black Skin White Masks Chapter 5 SummaryDocument1 pageBlack Skin White Masks Chapter 5 SummaryTeddy Larkin50% (2)
- Understanding Extra CreditDocument1 pageUnderstanding Extra CreditTeddy LarkinNo ratings yet
- Bio Lab Midterm StudyDocument3 pagesBio Lab Midterm StudyTeddy LarkinNo ratings yet
- Teddy Larkin Yeast Sunscreen LabDocument12 pagesTeddy Larkin Yeast Sunscreen LabTeddy LarkinNo ratings yet
- The Ethics of Ambiguity 35-50Document1 pageThe Ethics of Ambiguity 35-50Teddy LarkinNo ratings yet
- Beau Travail (Claire Denis, France, 1999)Document1 pageBeau Travail (Claire Denis, France, 1999)Teddy LarkinNo ratings yet
- Odysseus Analysis FINALDocument7 pagesOdysseus Analysis FINALTeddy LarkinNo ratings yet
- Masterseal 588: Description Packaging and ColorsDocument2 pagesMasterseal 588: Description Packaging and ColorsmariaNo ratings yet
- Formative Assessment (Module 6)Document2 pagesFormative Assessment (Module 6)Keisha Gabrielle RabanoNo ratings yet
- Chemistry P22 F - M 2024Document16 pagesChemistry P22 F - M 2024mharis0903No ratings yet
- Titration of Total Base Number TBN DIN ISO 3771 ASTM 2896Document10 pagesTitration of Total Base Number TBN DIN ISO 3771 ASTM 2896vektron6No ratings yet
- CP10 Onshore Painting Coating SpecificationDocument37 pagesCP10 Onshore Painting Coating SpecificationherdiansyahNo ratings yet
- CopperDocument24 pagesCopperUmesh DuwalNo ratings yet
- Patrick B. Smith and Richard A. Gross Eds. Biobased Monomers, Polymers, and MaterialsDocument358 pagesPatrick B. Smith and Richard A. Gross Eds. Biobased Monomers, Polymers, and MaterialsAmbadas GarjeNo ratings yet
- Boron DopingDocument23 pagesBoron Dopingdbinod281No ratings yet
- JEE 12 - Test 1 - Paper 1 - Main PatternDocument42 pagesJEE 12 - Test 1 - Paper 1 - Main PatternMohammed YusufNo ratings yet
- Admixtures in Concrete - NotesDocument55 pagesAdmixtures in Concrete - Notesnital poteNo ratings yet
- Solvent Extraction NoteeDocument13 pagesSolvent Extraction NoteeGandiyaNo ratings yet
- BiosurfactatsDocument6 pagesBiosurfactatsNoor Ul NaeemNo ratings yet
- Jee Advanced Principles of Qualitative Analysis Revision NotesDocument12 pagesJee Advanced Principles of Qualitative Analysis Revision Noteslakshyajeetbhati05No ratings yet
- Formula and Mass MCQDocument19 pagesFormula and Mass MCQDefaults rulezNo ratings yet
- Name: Vine Ortega Bsmls - 1Document4 pagesName: Vine Ortega Bsmls - 1Vine OrtegaNo ratings yet
- 4 The Control and Destruction of MicroorganismsDocument4 pages4 The Control and Destruction of MicroorganismsJernyNo ratings yet
- Divosan Forte VT6 PISDocument2 pagesDivosan Forte VT6 PISSubhra AddisNo ratings yet
- Astm 2913 MercaptanoDocument4 pagesAstm 2913 MercaptanoRaymi MorenoNo ratings yet
- Books Doubtnut Question BankDocument280 pagesBooks Doubtnut Question BankLakshya ChandakNo ratings yet
- The Production of Furfural Directly From Hemicellulose in Lignocellulosic Biomass& A ReviewDocument11 pagesThe Production of Furfural Directly From Hemicellulose in Lignocellulosic Biomass& A ReviewArif HidayatNo ratings yet
- Campion College 6B Chemistry ' LaboratoryDocument3 pagesCampion College 6B Chemistry ' LaboratoryNickolai AntoineNo ratings yet
- Gelatinized Sweet Potato Starches Obtained at Different Preheating Temperatures in A Spray DryerDocument8 pagesGelatinized Sweet Potato Starches Obtained at Different Preheating Temperatures in A Spray DryerThaís PaesNo ratings yet
- Target: LipidsDocument12 pagesTarget: LipidsFeaid Aina OrnedoNo ratings yet
- Isomerism 3Document25 pagesIsomerism 3Sudipto OraonNo ratings yet
- Rice Husk AshDocument7 pagesRice Husk Ashian yuhuNo ratings yet
- NEET Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry Important QuestionsDocument27 pagesNEET Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry Important QuestionsJiya KhanNo ratings yet
- PRICAT99xx Products - Tech Seminar - Updated 2016 SWDocument56 pagesPRICAT99xx Products - Tech Seminar - Updated 2016 SWKathe Molina CarvajalNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 4CH1 1CRDocument6 pagesChemistry 4CH1 1CRLoki .7thNo ratings yet
- Handbook Exercises: A. 1.1582 G/CCDocument2 pagesHandbook Exercises: A. 1.1582 G/CCPaul Philip LabitoriaNo ratings yet