Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 1: Transportation: Generate Electrical Impulse
Chapter 1: Transportation: Generate Electrical Impulse
Uploaded by
rihanni0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views6 pagesSPM Biology
Original Title
01 Transportation
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentSPM Biology
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views6 pagesChapter 1: Transportation: Generate Electrical Impulse
Chapter 1: Transportation: Generate Electrical Impulse
Uploaded by
rihanniSPM Biology
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 6
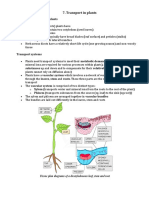
CHAPTER 1: TRANSPORTATION
- initiated and coordinated by pacemaker Sinoatrial nodes (SA Nodes)
Atria Atrial wall blood pumped
Wall contract into ventricles
SA nodes
AV Ventricles Venrical Blood pump out of
Wall Contract ventricles to lungs
and body
- controlled by:
i. parasympathetic nerve slow down the pacemaker
ii. sympathetic nerve
iii. hormone e.g: adrenaline
Diagram: The pumping of the Heart
Generate electrical
impulse
Bundle branches
Bundle of His fibres
Purkinje fibres
P1
P2
P3
P4 P5
P6
P7
P8 P9 P10
speed up the pacemaker
}
D1
Spread
Cause
Effect
Impulse
reach
Spread
impulse
Throughout Cause Effect
Change of BP Baroreceptor } location: arch of aorta and carotid arteries
BP increases
Baroreceptor
BP decreases
Cardiovascular centre
Weaker cardiac muscles contraction
Heart Stronger cardiac muscles contraction
Relax and widening (vasodilation)
To lower the resistance of blood flow
Smooth muscles of the arteries Contract and narrowing (vasoconstriction)
To higher the resistance of blood flow
Normal BP
Diagram: How blood pressure is regulated
D2
Clumped platelets
Damage cells
Clotting factors in vit K & Ca
+
the plasma (soluble protein)
(inactive plasma (active plasma
protein) proptein)
(insoluble protein)
(trapping RBC)
Diagram: Mechanisme of Blood Clotting
Form activator:
Thromboplastin
Prothrombin Thrombin
Fibrinogen
Fibrin
Mesh
Scab
D3
Interstitial fluid
diffuses
transported
1. blood that enter the arterial end of a capillary is under high hydrostatic pressure
2. cause some of plasma diffuse blood capillaries to space between cells.
3. form
4. Content: all blood components except RBC, plasma protein, albumin, globulin,
fibrinogen, platelets
5. Function: exchange materials between blood capillaries and cells occurs
6. 85% of the interstitial fluid re-enter blood circulation at the end of the venule
7. 15% diffused into lymphatic vessels 10.
fatty acids
8. to form lymph ileum lacteal
9. 11. glyserol
lymphatic system
subclavian vein
12. blood circulatory system
Diagram: Formation of Lymphatic system
D4
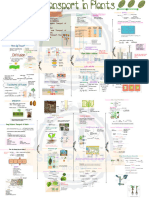
1. Surface of mesophyll covered with a thin layer of water
2. heat from the sun cause water on the external surface evaporate
4. concentration water vapour compare in surrounding
3. saturating the air spaces
5. water vapour evaporate and diffuse out through
stomata
6. movement of air carry away water vapour
Root pressure
8. Create a pushing force that result the inflow of water into the xylem root pressure
Capillary action
9. Cohesive force between water molecules draw up water in the xylem vessels
10. Adhesive force between water molecule and wall of xylem vessel
Transpiration pull
11. water evaporates from the surface of the mesophyll cells into air spaces
12. the water evaporates into surrounding through stomata
13. the water is lost from mesophyll cell is replaced by water in the xylem
Diagram: Transportation of water from soil to leaves
Root hair
1. surrounding soil
is hypotonic
2. water
osmosis
Cortex
3. hypotonic
5. moves inward
through:
i. cytoplasm
ii. vacuole
iii. cell walls
7. moves inward
through:
i. cytoplasm
ii. vacuole
Endodermis
6. has Cosparian strip
block the water
through cell wall
Xylem
vessel
4. diffuse
Adjacent cell
D6
You might also like
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (843)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5810)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1092)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (346)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- 7.transport in Plants NotesDocument18 pages7.transport in Plants NotesAhmed Noor100% (1)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- Bio Factsheet: TranspirationDocument4 pagesBio Factsheet: Transpirationlastjoe71100% (1)
- Transport of Water in PlantsDocument27 pagesTransport of Water in PlantssaketgolyanNo ratings yet
- Agriculture Imp MCQDocument200 pagesAgriculture Imp MCQsac100% (1)
- Formula Matematik Dan Nota RingkasDocument9 pagesFormula Matematik Dan Nota RingkasPurawin Subramaniam100% (11)
- Pceia - Bi Full NotesDocument407 pagesPceia - Bi Full Notesmohdhafizmdali100% (3)
- Spiking Into Aqueous Samples: Standard Guide ForDocument6 pagesSpiking Into Aqueous Samples: Standard Guide Formohdhafizmdali100% (1)
- PCE Study Guide (ENG)Document36 pagesPCE Study Guide (ENG)mohdhafizmdali0% (2)
- Synergistic Effects of Bimetallic PtPd-TiO2 Nanocatalysts in Oxidation ofDocument54 pagesSynergistic Effects of Bimetallic PtPd-TiO2 Nanocatalysts in Oxidation ofmohdhafizmdaliNo ratings yet
- Strengthening Conceptual Connections in Introductory ChemistryDocument9 pagesStrengthening Conceptual Connections in Introductory ChemistrymohdhafizmdaliNo ratings yet
- Establishing An Organic Chemistry Intuition For ElectrochemistryDocument11 pagesEstablishing An Organic Chemistry Intuition For ElectrochemistrymohdhafizmdaliNo ratings yet
- Standard Practice Sampling ASTM D 5451-93Document2 pagesStandard Practice Sampling ASTM D 5451-93mohdhafizmdaliNo ratings yet
- SainsDocument32 pagesSainsmohdhafizmdaliNo ratings yet
- Latihan Lines and AngelsDocument2 pagesLatihan Lines and AngelsAlnalyn A JamilNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Foam Polystyrene Granules On Cement Composite PropertiesDocument7 pagesThe Effect of Foam Polystyrene Granules On Cement Composite Propertiesmohdhafizmdali100% (1)
- Microsoft Word - Trial STPM Kedah Bio (Answer)Document14 pagesMicrosoft Word - Trial STPM Kedah Bio (Answer)Rozaini OthmanNo ratings yet
- Transport of Materials in Flowering Plants + Trans LocationDocument71 pagesTransport of Materials in Flowering Plants + Trans LocationCarolyn KhooNo ratings yet
- Transport in Plants - Micronotes by Seep PahujaDocument2 pagesTransport in Plants - Micronotes by Seep PahujamanojchodharyhathrasNo ratings yet
- Biology Questions and Answers Form 2Document41 pagesBiology Questions and Answers Form 2Zubin Jammaa FulaniNo ratings yet
- CAPE Biology Syllabus With Specimen Papers - Split - 2Document5 pagesCAPE Biology Syllabus With Specimen Papers - Split - 2Enz JosephNo ratings yet
- Resource Acquisition & Transport in Vascular Plants: Campbell and ReeceDocument94 pagesResource Acquisition & Transport in Vascular Plants: Campbell and ReeceJezterE.BalladosItsujiNo ratings yet
- TOEFL Reading Practice 3-12Document10 pagesTOEFL Reading Practice 3-12OpacarophileNo ratings yet
- Biology (Chapter 1 - Life Processes Notes)Document18 pagesBiology (Chapter 1 - Life Processes Notes)Manisha Tripathi Xth A 23No ratings yet
- KSSM Form 5 Biology Textbook-84-105Document22 pagesKSSM Form 5 Biology Textbook-84-105Fatin Liyana AhmadNo ratings yet
- Bot 421Document24 pagesBot 421Gary BhullarNo ratings yet
- Class 11 Neet Transport in PlantsDocument14 pagesClass 11 Neet Transport in PlantsViswaNo ratings yet
- Second Lecture Exam ReviewerDocument7 pagesSecond Lecture Exam ReviewerKen RubioNo ratings yet
- Transport in PlantsDocument5 pagesTransport in PlantsAlex LochaiNo ratings yet
- NEET UG Biology Transport in PlantsDocument17 pagesNEET UG Biology Transport in PlantsEr Purushottam PalNo ratings yet
- MODULE 2 Part 2A Organisation of Living Things - Nutrient and Gas RequirementsDocument94 pagesMODULE 2 Part 2A Organisation of Living Things - Nutrient and Gas RequirementsZenaNo ratings yet
- Botany Outline Characteristics of Living Things and Manifestations of LifeDocument33 pagesBotany Outline Characteristics of Living Things and Manifestations of LifeElma GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Cabbage Water Movement ExperimentDocument16 pagesCabbage Water Movement ExperimentvnnrbkahNo ratings yet
- A Blog Class 9 First Bell Biology Chapter 3 Science Diary Class 20 em 1Document3 pagesA Blog Class 9 First Bell Biology Chapter 3 Science Diary Class 20 em 1Anaina AnnaNo ratings yet
- Water Transport in PlantsDocument10 pagesWater Transport in PlantsRizal Restu FaldNo ratings yet
- Plant Physiology: Chapter - 1: Absorption by RootsDocument17 pagesPlant Physiology: Chapter - 1: Absorption by RootsSaad ZulfiqarNo ratings yet
- Gujcet Sample Paper For Biology - EnglishDocument171 pagesGujcet Sample Paper For Biology - EnglishDharav Solanki100% (3)
- Biology Paper 2Document14 pagesBiology Paper 2Adam K C TiongNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Long Distance Transport in T - 2012 - Marschner S Mineral NutritionDocument22 pagesChapter 3 - Long Distance Transport in T - 2012 - Marschner S Mineral NutritionFederico GarciaNo ratings yet
- Transport in Plants PDFDocument26 pagesTransport in Plants PDFMasOom Si ChuRail100% (2)
- Ncert Page Wise Q Transport in PlantsDocument21 pagesNcert Page Wise Q Transport in PlantsSagarNo ratings yet
- Biology Paper I - Botany Plant Water RelationsDocument4 pagesBiology Paper I - Botany Plant Water RelationsAnonymous X4QS89Um8wNo ratings yet