Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Comparisons For Malaria
Comparisons For Malaria
Uploaded by
Mae Becher0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views2 pagesGives you simple yet comprehensive comparisons between malaria diseases
Original Title
Comparisons for Malaria
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentGives you simple yet comprehensive comparisons between malaria diseases
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views2 pagesComparisons For Malaria
Comparisons For Malaria
Uploaded by
Mae BecherGives you simple yet comprehensive comparisons between malaria diseases
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
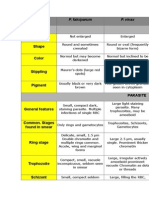
normal;multiple infection of RBC more
common than in other species
delicate cytoplasm;1-2 small chromatin
dots;occasional appliqu (accoll) forms
Ring
Trophozoite
normal;rarely,Maurers clefts
(under certain stainingconditions)
seldomseen in peripheral blood;compact
cytoplasm;dark pigment
Schizont
normal;rarely,Maurers clefts
(under certain stainingconditions)
seldomseen in peripheral blood;mature
=8-24 small merozoites;dark pigment,
clumped in one mass
Gametocyte distorted by parasite
crescent or sausage shape;chromatin in a
single mass (macrogametocyte) or diffuse
(microgametocyte);dark pigment mass
P
.
f
a
l
c
i
p
a
r
u
m
Plasmodium
species
Stages found
in blood
Appearance of Erythrocyte
(RBC)
Appearance of Parasite
normal to 1-1/4 X,round;occasionally fine
Schffners dots;multiple infection of RBC
not uncommon
large cytoplasmwith occasional
pseudopods;large chromatin dot
Ring
Trophozoite
enlarged1-1/22 X;may be distorted;fine
Schffners dots
large ameboid cytoplasm;large chromatin;
fine,yellowish-brown pigment
Schizont
enlarged1-1/22 X;may be distorted;fine
Schffners dots
large,may almost fill RBC;mature =12-24
merozoites;yellowish-brown,coalesced
pigment
Gametocyte
enlarged1-1/22 X;may be distorted;fine
Schffners dots
round to oval;compact;may almost fill
RBC;chromatin compact,eccentric
(macrogametocyte) or diffuse (micro-
gametocyte);scattered brown pigment
P
.
v
i
v
a
x
normal to 1-1/4 X,round to oval;occasionally
Schffners dots;occasionally fimbriated;
multiple infection of RBC not uncommon
sturdy cytoplasm;large chromatin Ring
Trophozoite
normal to 1-1/4 X;round to oval;some
fimbriated;Schffners dots
compact with large chromatin;
dark-brown pigment
Schizont
normal to 1-1/4 X;round to oval;some
fimbriated;Schffners dots
mature =6-14 merozoites with large
nuclei,clustered around mass of
dark-brown pigment
Gametocyte
normal to 1-1/4 X;round to oval;some
fimbriated;Schffners dots
round to oval;compact;may almost fill
RBC;chromatin compact,eccentric
(macrogametocyte) or more diffuse (micro-
gametocyte);scattered brown pigment
P
.
o
v
a
l
e
normal to 3/4 X;rarely,Ziemanns stippling
(under certain stainingconditions)
compact cytoplasm;large chromatin;
occasional band forms;coarse,dark-brown
pigment
Trophozoite
Ring normal to 3/4 X sturdy cytoplasm;large chromatin
Schizont
normal to 3/4 X;rarely,Ziemanns stippling
(under certain stainingconditions)
mature =6-12 merozoites with large
nuclei,clustered around mass of coarse,
dark-brown pigment;occasional rosettes
Gametocyte
normal to 3/4 X;rarely,Ziemanns stippling
(under certain stainingconditions)
round to oval;compact;may almost fill
RBC;chromatin compact,eccentric
(macrogametocyte) or more diffuse (micro-
gametocyte);scattered brown pigment
P
.
m
a
l
a
r
i
a
e
Comparison of the Plasmodium Species
Which Cause Human Malaria
Crescent:PF(gametocytes)
Ameboid:PV
Fimbriation:PO
Elongated:PO
PV,PO <N,N:PM
N:PF
>N:PO
>>N:PV
Keypoints for Plasmodium Species
Which Cause Human Malaria
Size Shape Schffners Dots
Infected RBCs
Rings only
(gametocytes):PF
Numerous:PF
Multiply infected
RBCs:PF
Accessory
chromatin dots:PF
Delicate:PF
Rings
Ameboid:PV
Compact:PO
PM
PF(rarely seen)
Band form:PM
Trophozoites
6-12 nuclei:PM
6-14 nuclei:PO
12-24:PV
8-24:PF(rarely seen)
Rosettes:PM
Schizonts (mature)
PF: P.falciparum
PV: P.vivax
PO: P.ovale
PM: P.malariae
Crescent:PF
Round:PV
PO
PM
Gametocytes
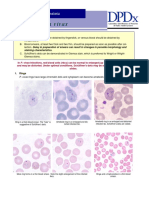
Parasites Found In Circulating Blood
Certain morphologic key characteristics of the infected erythrocytes and parasites
can be used to orient the diagnosis towards one of the four Plasmodiumspecies
that infect humans,as shown above.These characteristics are by no means absolute,
however.The final diagnosis should be based on the combined findings for the various
characteristics:what is the most probable species,based on the available findings.
Legend
You might also like
- RBC InclusionsDocument6 pagesRBC Inclusionsjingx5100% (1)
- Morphological Characteristics of Malaria ParasitesDocument71 pagesMorphological Characteristics of Malaria Parasitesed100% (6)
- SEM2 MALARIA Plasmodium Falciparum 2013Document23 pagesSEM2 MALARIA Plasmodium Falciparum 2013odysseyfairy2739No ratings yet
- Para MidtermsDocument126 pagesPara Midtermshezekiah hezNo ratings yet
- MalariaDocument5 pagesMalariaRina KhazarenNo ratings yet
- MalariaDocument30 pagesMalariaderilNo ratings yet
- Plasmodium Malariae: Laboratory Diagnosis of MalariaDocument4 pagesPlasmodium Malariae: Laboratory Diagnosis of MalariaKals SpartanNo ratings yet
- Malaria TableDocument1 pageMalaria TableJessie PaulNo ratings yet
- Exercise 6: Malarial Parasites: Parasitology LaboratoryDocument2 pagesExercise 6: Malarial Parasites: Parasitology LaboratorySigfred Tarnate AoasNo ratings yet
- Differential Diagnosis of Malaria ParasiteDocument101 pagesDifferential Diagnosis of Malaria ParasiteSohaib Omer Salih100% (1)
- Malaria (Table of Characteristics)Document1 pageMalaria (Table of Characteristics)Noelle Grace Ulep BaromanNo ratings yet
- Sporozoa and CoccidiaDocument155 pagesSporozoa and CoccidiaJosue Luis VillarinNo ratings yet
- HEMOPARASITESDocument80 pagesHEMOPARASITESManasNo ratings yet
- Staining TechniquesDocument62 pagesStaining Techniques1x CzNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 - الملارياDocument5 pagesLecture 6 - الملارياAhmed Qassim MadhloomNo ratings yet
- Praktikum MalariaDocument22 pagesPraktikum MalariaGeniaaldafitriaasgen100% (1)
- Gambar Plasmodium OvaleDocument4 pagesGambar Plasmodium OvaleRonalda BudyantaraNo ratings yet
- MalariaDocument23 pagesMalariafiras frs100% (1)
- Plasmodium Ovale: Laboratory Diagnosis of MalariaDocument4 pagesPlasmodium Ovale: Laboratory Diagnosis of MalariaFitrah QolbinaNo ratings yet
- FalciparumDocument4 pagesFalciparumDandun Dannie-DunNo ratings yet
- Pfalciparum Benchaidv2Document4 pagesPfalciparum Benchaidv2kim hanbinhanbyulNo ratings yet
- Clinical - Parasitology Zero 1Document13 pagesClinical - Parasitology Zero 1Chirag EducationNo ratings yet
- 3rd Handout The Malarial ParasitesDocument4 pages3rd Handout The Malarial ParasitesPatrica Willyn B. DiosoNo ratings yet
- Malaria: EtiologyDocument10 pagesMalaria: EtiologyAlayza Joy GasmenNo ratings yet
- MalariaDocument25 pagesMalariaYelai CarveroNo ratings yet
- By Fawad Khan Marwat Khalid Shakeel BabarDocument26 pagesBy Fawad Khan Marwat Khalid Shakeel BabarksbabarNo ratings yet
- MalariaDocument3 pagesMalariaAnonymous 75TDy2yNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Apicomplexa Malaria-1Document48 pagesUnit 4 Apicomplexa Malaria-1Denise MichelleNo ratings yet
- المحاضرة 11 و 12 مادة الطفيلياتDocument18 pagesالمحاضرة 11 و 12 مادة الطفيلياتdyabw6430No ratings yet
- Malaria: by Kariuki Njaanake, PHDDocument19 pagesMalaria: by Kariuki Njaanake, PHDodhiambo samwelNo ratings yet
- Microbiology - Helminthic InfectionsDocument25 pagesMicrobiology - Helminthic InfectionsvaishnaviNo ratings yet
- Plasmodium ReportDocument43 pagesPlasmodium ReportGenessa Agustin BuenafeNo ratings yet
- 6 Plasmodium SPPDocument1 page6 Plasmodium SPPKaycee Gretz LorescaNo ratings yet
- The Protozoa: Plasmodium Vivax, P. Ovale, P. Malariae, and P. Falciparum. All Are Transmitted by Female Anopheles SPPDocument23 pagesThe Protozoa: Plasmodium Vivax, P. Ovale, P. Malariae, and P. Falciparum. All Are Transmitted by Female Anopheles SPPYusril AhmadNo ratings yet
- ON Plasmodium Vivax (Malarial Parasite)Document10 pagesON Plasmodium Vivax (Malarial Parasite)Raja Marudut SimatupangNo ratings yet
- Parasites PetalsDocument115 pagesParasites PetalsMcarl MatelNo ratings yet
- Atlas MalariaDocument4 pagesAtlas MalariaLaboratorium Pkm ManjaNo ratings yet
- Approach Considerations MALARIADocument3 pagesApproach Considerations MALARIAAnonymous hvOuCjNo ratings yet
- Parasitology PrelimsDocument20 pagesParasitology PrelimsTIffany KimNo ratings yet
- 4 ENG Presentation 4 Malaris Species Identification in Thick and Thin Bloodsmear Oct2019Document41 pages4 ENG Presentation 4 Malaris Species Identification in Thick and Thin Bloodsmear Oct2019Yantek Btklpp ManadoNo ratings yet
- P. VivaxDocument33 pagesP. VivaxAboubakar Moalim Mahad moh'dNo ratings yet
- Plasmodium Vivax: Laboratory Diagnosis of MalariaDocument4 pagesPlasmodium Vivax: Laboratory Diagnosis of MalariaShaiji ShahidNo ratings yet
- Malaria (Autosaved)Document15 pagesMalaria (Autosaved)sajad abasNo ratings yet
- Species Host CELL Size Shape: P. Falciparum P. VivaxDocument2 pagesSpecies Host CELL Size Shape: P. Falciparum P. VivaxFirah RukmanNo ratings yet
- Hemograma Buna 2023 BunaDocument71 pagesHemograma Buna 2023 BunaMirelDabuleanuNo ratings yet
- Merozoites Fills The RBC, 6-16 (Usually 8) : Usually ENLARGED, Often Oval With Fimbrated EdgesDocument1 pageMerozoites Fills The RBC, 6-16 (Usually 8) : Usually ENLARGED, Often Oval With Fimbrated EdgesJqsWattpadNo ratings yet
- Key To Identifying Malaria Parasite Stages in Thin Blood FilmsDocument3 pagesKey To Identifying Malaria Parasite Stages in Thin Blood FilmsRisa RakhaNo ratings yet
- PlasmodiumDocument92 pagesPlasmodiumnitesh rawat100% (1)
- ParasitologyDocument4 pagesParasitologyIan ZyrusNo ratings yet
- Plasmodium SPP.: Parasitology DeptDocument38 pagesPlasmodium SPP.: Parasitology DeptDedy SavradinataNo ratings yet
- Protozoa in Blood and TissuesDocument37 pagesProtozoa in Blood and Tissuesheni arisNo ratings yet
- Plasm Odium SDocument9 pagesPlasm Odium SAnonymous 7zl6IBNo ratings yet
- Ospe - ParasitologyDocument12 pagesOspe - ParasitologyDanial MazukiNo ratings yet
- Malaria ParasiteDocument22 pagesMalaria ParasiteAndy Putra HermawanNo ratings yet
- HaemoparasitesDocument82 pagesHaemoparasitesAshok WiselinNo ratings yet
- PLASMODIUMDocument3 pagesPLASMODIUMsakalam shipper48No ratings yet
- Microbiology NotesDocument16 pagesMicrobiology NotesZeraNo ratings yet
- Plasmodiumspp 230727053539 5ffdb015Document51 pagesPlasmodiumspp 230727053539 5ffdb015راوند اعبيدNo ratings yet