Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Note 1
Uploaded by
HossamJamaykaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Note 1
Uploaded by
HossamJamaykaCopyright:
Available Formats
KFU DAMMAM
COLLEGE OF MEDCINE
207
PHARMACOLOGY SUMMARY & REVIEW
Dr. Abdulaziz Al-Khawaja
Dr. Mohammed Akram
Dr. N. B. Biswas
Done by: Ahmed Ali Al-Ghareeb
P H R M A C O L O G Y - NOTE 1 - Treatment of Asthma
|
2
C
l
i
n
i
c
a
l
f
e
a
t
u
r
e
s
o
f
b
r
o
n
c
h
i
a
l
a
s
t
h
m
a
.
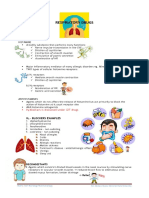
Contraction of airway smooth muscle.
leading to acute dyspnea & airway
obstruction.
Mucus hypersecretion.
leading to mucus pulgging.
Airway inflamation.
leading to bronchodema.
Role of
Leukotrines
in asthma
Broncho-
constriction
Mucosal
inflammation
Mucosal
edema
Mucus
secretion
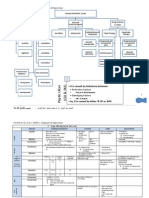
Drugs for Asthma
Bronchodilators
2-adrenergic
agonist
Salbutamole
Terbutaline
Salmaterol
Methylxanthines
Theophylline
Aminophylline
Anti-muscarinic
Ipratropium
Anti-inflammatory
(glucorticosteroids)
Beclomethasone
Hydrocortisone
Prednisolone
Anti-leukotrienes
LT synthesis
inhibitor
Zileuton
LT receptor
antagonist
Montelukast
Mast cell stabilizers
Sodium
Cromoglycate
Uses of bronchodilator
for acute
broncho-
spasm
during acute
phase of
asthma attack
for quick
reduce airway
constriction
P H R M A C O L O G Y - NOTE 1 - Treatment of Asthma
|
3
Bronchodilaters
DRUG PHARMACOKINETIC ACTION USES SIDE EFFECT
2
-
a
d
r
e
n
e
r
g
i
c
a
g
o
n
i
s
t
Salbutamole Fast onest.
Short duration.
Given inhaler or Nebulizer.
Less side effect.
Given orally, S.C, IV or IM.
Large dose.
More side effect.
Bind to -receptor & stimulate
adenylcyclase.
Leading to cAMP.
Bronchodilatation.
Used for acute attack. Tremor.
Vascular headache.
Terbutaline
Salmaterol Slow onest.
Long duration.
Used for long term therapy.
M
e
t
h
y
l
x
a
n
t
h
i
n
e
s
Theophylline
Has narrow theraputic index.
Given orally.
Cause GI irritant.
Inhibit PDEI.
Leading to cAMP.
Ca
++
influx
Bronchodilatation
1) CNS stimulation.
2) Cardiac muscle stimulation.
3) Diuresis.
4) S.M. relaxtion of bronchial & uterus.
5) Periphral & cornory vasodilatation.
6) Cerebral vasoconstriction.
GIT: nausea, vomiting .
CNS: stimulation insomnia,
irritabillity & headach.
CVS: BP, arrhythmia.
Kidney: diuresis.
Aminophylline
Water mixture of Theophylline + Ethylenediamine.
Given orally, rectally (suppositories) or injection.
Anti-
musc
rinic
Ipratropium It is poorly absobed from the GIT.
So,it given by inhalation.
Slower onest & longer duration than salbutamol.
Blocking M receptor in bronchial
smooth muscle.
Bronchodilatation
Dry mouth.
Anti-inflammatory(Glucorticosteroid)
DRUG PHARMACOKINETIC ACTION USES SIDE EFFECT
Beclomethasone Given by inhalation, orally or IV. 1) Reduce mucosal edema.
2) Sensitize 2-agonist.
3) Reduce inflammatory cell activation
If taken by inhalation,
Dysphonia (hoarseness).
Oral candidiasis (fungal
infection).
Hydrocortisone
Prednisolone
Anti-Leukotrienes
DRUG PHARMACOKINETIC ACTION USES SIDE EFFECT
Zileuton 1) Inhibit lipoxygenase enzyme.
2) Reduce conversion of AA to LT.
So, it is
Broncodilater.
Anti-inflammatory.
To prevent asthma caused by
Aspirin.
NASID.
Montelukast 1) Blocking LT receptors.
2) Inhibit bronchoconstriction caused by LT
To prevent asthma caused by
NASID & Exercise.
Mast Cell Stabilizers
DRUG PHARMACOKINETIC ACTION USES SIDE EFFECT
Na Cromoglycate Given by inhalation. Reduce the mediators that release
from mast cell in response to allergen
that cause bronchoconstriction.
Prophylaxis aginst asthma
attack.
Cough.
Wheeze.
Ketotifen Given orally.
You might also like
- Pharmacology Made Insanely Easy PowerPointDocument42 pagesPharmacology Made Insanely Easy PowerPointBetsy Brown Byersmith82% (22)
- Pharmacology of Respiratory SystemDocument67 pagesPharmacology of Respiratory Systemmanish086100% (2)
- ASTHMA TreatmentDocument27 pagesASTHMA TreatmentRho Vince Caño Malagueño0% (1)
- Lecture 14 - Pharmacology of Drugs Used in Bronchial Asthma L0 COPD - EditedDocument42 pagesLecture 14 - Pharmacology of Drugs Used in Bronchial Asthma L0 COPD - EditedAbdallah AlasalNo ratings yet
- Antiasthmatic DrugsDocument36 pagesAntiasthmatic DrugsJannah ZahraaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Tract PharmacologyDocument68 pagesRespiratory Tract PharmacologyRohaan SharmaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory EmergenciesDocument34 pagesRespiratory EmergenciesRoshana MallawaarachchiNo ratings yet
- 2&3-Pharmacology of Drugs Used in Bronchial Asthma & COPDDocument58 pages2&3-Pharmacology of Drugs Used in Bronchial Asthma & COPDKishan SethNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology of drugs for bronchial asthma and COPDDocument71 pagesPharmacology of drugs for bronchial asthma and COPDBriana NdayisabaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory PharmacologyDocument89 pagesRespiratory PharmacologyEka PuspitasariNo ratings yet
- Antiasthma and Cough MedicineDocument47 pagesAntiasthma and Cough MedicineYordanos EshetuNo ratings yet
- Drugs Effecting Respiratory System (MSCN)Document63 pagesDrugs Effecting Respiratory System (MSCN)Irshad SahilNo ratings yet
- CH-V Cough, ASthmaDocument40 pagesCH-V Cough, ASthmaC velmuruganNo ratings yet
- Anti Asthmatic DrugsDocument8 pagesAnti Asthmatic DrugsNavjot BrarNo ratings yet
- Module 3.2 - Respiratory DrugsDocument3 pagesModule 3.2 - Respiratory DrugsCatherine Sinen ObinqueNo ratings yet
- Cology 3 Unit 1Document28 pagesCology 3 Unit 1imrujlaskar111No ratings yet
- Drugs Used in Bronchial Asthma & COPDDocument71 pagesDrugs Used in Bronchial Asthma & COPDShabnam Binte AlamNo ratings yet
- Drugs Acting On Respiratory System of AnimalsDocument8 pagesDrugs Acting On Respiratory System of AnimalsSunil100% (4)
- Respiratory DrugsDocument20 pagesRespiratory DrugsMelanesiaNo ratings yet
- At Least 5 Days of Fever PLUS 4 or 5Document11 pagesAt Least 5 Days of Fever PLUS 4 or 5Atiqah ShahNo ratings yet
- Sas1 ClinpharDocument7 pagesSas1 ClinpharAlyssa Marie Petonio BialaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Pharmacolo... Asthma1Document55 pagesRespiratory Pharmacolo... Asthma1ahmed mahamedNo ratings yet
- Autacoids, Respiratory Diseases Drug Treatment 2023Document38 pagesAutacoids, Respiratory Diseases Drug Treatment 2023adetola adetayoNo ratings yet
- Dr. Rishi Pal: Asstt. ProfessorDocument40 pagesDr. Rishi Pal: Asstt. ProfessortamaNo ratings yet
- Bronchial Asthma 2.0Document15 pagesBronchial Asthma 2.0Bisweswar OjhaNo ratings yet
- Asthma MedicationDocument6 pagesAsthma Medicationmomina arshidNo ratings yet
- All DrugsDocument482 pagesAll DrugsJessica IbañezNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Stimulant and Nesal DecongestantDocument22 pagesRespiratory Stimulant and Nesal DecongestantAyesha AlamNo ratings yet
- antitussivesDocument5 pagesantitussivesAditya PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology of Drugs Used in Bronchial Asthma & COPDDocument84 pagesPharmacology of Drugs Used in Bronchial Asthma & COPDdfngjlnNo ratings yet
- Saba Hanif Presentation...Document19 pagesSaba Hanif Presentation...Saba KhanNo ratings yet
- Unit-Seven (Vii) : Drugs Affecting The Respiratory SystemDocument55 pagesUnit-Seven (Vii) : Drugs Affecting The Respiratory Systemdinberu tadesseNo ratings yet
- Respiratory DrugsDocument6 pagesRespiratory DrugsCurtney PedriaNo ratings yet
- 6 Asthma and Copd HandoutDocument10 pages6 Asthma and Copd HandoutMd Sakil AminNo ratings yet
- Drugs For Treatment of Bronchial Asthma: DR Sanjay Junior Resident Department of Pharmacology Ims-BhuDocument19 pagesDrugs For Treatment of Bronchial Asthma: DR Sanjay Junior Resident Department of Pharmacology Ims-BhuBisweswar OjhaNo ratings yet
- Common Pediatric Emergencies - A2Document46 pagesCommon Pediatric Emergencies - A2Ahmad JustNo ratings yet
- DRUG INDUCED PULMONARY DISEASESDocument30 pagesDRUG INDUCED PULMONARY DISEASESShanthi Jaggala Shanthi YadavNo ratings yet
- Status Asthmaticus DR Divya JainDocument45 pagesStatus Asthmaticus DR Divya JainParvathy R NairNo ratings yet
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary DiseaseDocument33 pagesChronic Obstructive Pulmonary DiseasealexpharmNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4, 5 - Drugs Used in Bronchial Asthma & COPDDocument57 pagesLecture 4, 5 - Drugs Used in Bronchial Asthma & COPDBalakrishnan Thangaraj100% (1)
- Drugs in Treatment of Bronchial AsthmaDocument46 pagesDrugs in Treatment of Bronchial AsthmaNikita JangraNo ratings yet
- 5 - Drugs For AsthmaDocument75 pages5 - Drugs For Asthmanica velano100% (1)
- Pharmacotherapy of Bronchial AsthmaDocument7 pagesPharmacotherapy of Bronchial AsthmaAhmedshaker21100% (2)
- Respiratory SystemDocument27 pagesRespiratory SystemSowndariyaNo ratings yet
- Asthma + COPDDocument60 pagesAsthma + COPDNur HasanahNo ratings yet
- Current Management of Asthma 2Document43 pagesCurrent Management of Asthma 2dan ekelemeNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology RCR1 RespiratoryDocument10 pagesPharmacology RCR1 RespiratoryeamcrawleyNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Diseases: Medically Compromised PatientDocument50 pagesPulmonary Diseases: Medically Compromised Patientمحمد عبدالهادي إسماعيلNo ratings yet
- Anti-Asthmatics: Dr. Sadia Shahid PGT-Pharmacology IimcDocument30 pagesAnti-Asthmatics: Dr. Sadia Shahid PGT-Pharmacology IimcWafaa AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Sialogogues & Anti SailogoguesDocument43 pagesSialogogues & Anti SailogoguesTavleen KaurNo ratings yet
- BP602T Unit 1-3Document207 pagesBP602T Unit 1-3Gyampoh SolomonNo ratings yet
- Drugs for Cough, Bronchial Asthma and InflammationDocument47 pagesDrugs for Cough, Bronchial Asthma and InflammationNavlika DuttaNo ratings yet
- Asthma Harrisons ClubDocument84 pagesAsthma Harrisons ClubLady AngodNo ratings yet
- Antiasthamatic DrugsDocument72 pagesAntiasthamatic DrugsDeepak kumarNo ratings yet
- Hyperaldosteronism Is Treated With: Adverse ReactionsDocument7 pagesHyperaldosteronism Is Treated With: Adverse ReactionsGizelle CorpuzNo ratings yet
- Relieve Angina & Congestive Heart FailureDocument6 pagesRelieve Angina & Congestive Heart FailureBij Hilario100% (1)
- Acute Asthma Exacerbations: Treatment GuideDocument36 pagesAcute Asthma Exacerbations: Treatment GuideYousef Al-AmeenNo ratings yet
- Fast Facts: Asthma: Improve patient self-management and drug use, achieve asthma controlFrom EverandFast Facts: Asthma: Improve patient self-management and drug use, achieve asthma controlNo ratings yet
- Note 4 & 5Document7 pagesNote 4 & 5HossamJamaykaNo ratings yet
- Treatment of Peptic Ulcer & Eradication of H. PyloriDocument3 pagesTreatment of Peptic Ulcer & Eradication of H. PyloriHossamJamaykaNo ratings yet
- Cough DrugsDocument4 pagesCough DrugsAhmed SobhNo ratings yet