Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Slide MHC Hla
Uploaded by
Sandi AuliaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Slide MHC Hla
Uploaded by
Sandi AuliaCopyright:
Available Formats
MHC & HLA
Dr. Tetty Aman Nasution, MMedSc y ,
Departemen Mikrobiologi
FK USU FK USU
Definitions Definitions
Histocompatibility Antigen adalah Histocompatibility Antigen adalah
Antigen yang terdapat pada sel /
j i b d k i jaringan yang berperan pada reaksi
penolakan terhadap organ transplant
Definitions Definitions
Major Histocompatibility Antigen Major Histocompatibility Antigen
adalah Histocompatibility Antigen
b ik i yang memberikan respon imun yang
sangat kuat & berperan penting pada
peristiwa penolakan organ transplant
T cells respond to MHC antigens
G ft j ti i i i di t d b i filt ti T l h t Graft rejection in vivo is mediated by infiltrating T lymphocytes
The in-vitro correlate of graft rejection is the
MIXED LYMPHOCYTE REACTION
T cells do not respond
Responder cells
from an MHC-A mouse
Irradiated stimulator cells
from an MHC-A mouse
T
+
T
Irradiated stimulator cells
from an MHC-B mouse
Responder cells
from an MHC-A mouse
T cells respond
T
+
T
T T
T
T T
T
T
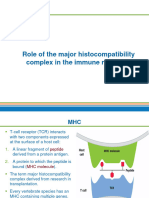
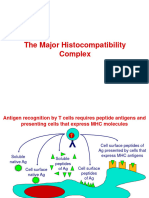
MHC antigens are involved in the activation of T cells
MHC directs the response of T cells to
foreign antigens foreign antigens
MHC antigens PRESENT foreign antigens to T cells
Cells that present antigen areANTIGEN PRESENTING CELLS Cells that present antigen are ANTIGEN PRESENTING CELLS
Y
T Y
T Y
T
Y
T
Y
T
Y
T
Y
T
Y
Y
Ag
Y
Ag
Y
Y
Y
T
Y
Blocking
anti-MHC
antibody antibody
Anti response
No anti response
Antigens must be processed in order
to be recognised by T cells
Y
T
Y
Soluble
Soluble
Cell surface peptides of
Ag presented by cells that
express MHC antigens
Cell surface
peptides
native Ag
Cell surface
nativeAg
Soluble
peptides
of Ag
p p
of Ag
native Ag
T cell
No T cell No T cell No T cell No T cell
ANTIGEN
PROCESSING
T cell
response
No T cell
response
No T cell
response
No T cell
response
No T cell
response
Definitions Definitions
Major Histocompatibility Complex : Major Histocompatibility Complex :
group of genes on a single
h di th MHC chromosome encoding the MHC
antigens
Sekelompok atau kompleks gen
pada satu kromosomyang memberi pada satu kromosom yang memberi
kode pd MHC antigen
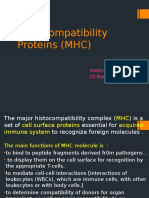
Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC)
Receptors found on all cells except RBCs Receptors found on all cells except RBCs
Also known as human leukocyte antigen
(HLA) (HLA)
Plays a role in recognition of self by the
i t d i j ti f f i immune system and in rejection of foreign
tissue
Genes for MHC are located on
chromosome 6, clustered in a multigene
complex of classes I, II, III
Functions of MHC Functions of MHC
Class I markers that display unique Class I markers that display unique
characteristics of self molecules &
regulation of immune reactions g
Required for T lymphocytes
Class II receptors that recognize & react p g
with foreign antigens. Located primarily on
macrophages & B cells
Involved in presenting antigen to T cells
Class III secreted complement
components, C2 and C4
MHC receptors MHC receptors
Kelompok gen tersebut dikenal sebagai
lokus awal menentukan ekspresi molekul- lokus awal menentukan ekspresi molekul-
molekul permukaan sel tubuh
Sel-sel tubuh yang bernukleus memiliki
epitop permukaan yang ekspresinya epitop permukaan yang ekspresinya
sudah ditentukan secara genetik
Contoh : Sel darah merah yang memiliki
Antigen A B dan Rh (rhesus) Antigen A, B dan Rh (rhesus)
Definitions
Human Leucocyte Antigen = HLA
adalah MHC Antigen pada manusia adalah MHC Antigen pada manusia
Antigen permukaan tersebut pertama
kali digambarkan pada leukosit
Pada penderita yang telah mendapat Pada penderita yang telah mendapat
transfusi darah berulangkali
ditemukan Ab yang dapat ditemukan Ab yang dapat
menggumpalkan lekosit human
l t ti leucocyte antigen
Kompleks HLA
HLA-A
HLA-B HLA B
HLA-C
HLA D(di h j di HLA DR HLA HLA-D (dipecah menjadi HLA-DR, HLA-
DQ, dan terakhir ditemukan HLA-DP)
Setiap lokus polimorf & masih terdiri atas
beberapa haplotype
Setiap haplotype menentukan
pembentukan molekul permukaan sel p p
ciri Ag tersebut
MHC gen pada manusia MHC gen pada manusia
class II class I class II class I
DP DQ DR B C A
B C
A
1
2 2 2 1 1 9 3 1 2 2 1
3
DP DQ DR
Pembagian MHC Pembagian MHC
Molekul MHC kelas I dan kelas II Molekul MHC kelas I dan kelas II
berperan pada pengenalan imun yaitu
d t i f A ti pada presentasi fragmen Antigen
kepada sel T
Berdasarkan rumus bangunnya, MHC
dapat dibagi menjadi 3 golongan dapat dibagi menjadi 3 golongan
T di i d i k l k HLA A HLA B d HLA C
Molekul MHC kelas I Molekul MHC kelas I
Terdiri dari : kompleks HLA-A, HLA-B dan HLA-C
Menetapkan ekspresi atau Ag permukaan kelas I p p g p
beupa protein pada membran permukaan semua sel
tubuh yang memiliki nukleus dan trombosit tubuh yang memiliki nukleus dan trombosit
Mengikat peptida molekul lain yg diproduksi dlmsel
Contoh : protein virus ditranspor ke permukaan
sel bersama MHC kelas I sehingga kompleks MHC sel bersama MHC kelas I sehingga kompleks MHC
kelas I & peptida dikenal oleh sel T CD8
+
(sitotoksik) (sitotoksik)
Molekul MHC kelas II
Terdiri dari : kompleks HLA-D (DR dan
DQ) dan HLA-DP )
Menetapkan ekspresi atau Ag permukaan Menetapkan ekspresi atau Ag permukaan
sel kelas II imuno-kompeten seperti sel B,
monosit makrofag APC (antigen monosit, makrofag, APC (antigen
presenting cells) dan sel T (yg diaktifkan)
Mengikat peptida sesudah diproses sel
APC dibawa ke permukaan sel dikenali
oleh sel CD4+ permulaan respon imun
Molekul MHC kelas III
Sejumlah protein yg ekspresinya ditentukan oleh
MHC kelas III : komponen komplemen (C2,C4),
faktor B properdin, TNF (Tumor Necrosis Factor)
dan Lymphotoxin (LT), bbp jenis enzim, heat y p ( ) p j
shock protein tertentu & molekul pengangkut yg
diperlukan dlm proses antigen p p g
Antigen MHC kelas III tidak mempunyai peranan
pada respon imun yang menentukan p p y g
bertahannya suatu organ transplan
J aringan MHC Kelas I MHC Kelas II
Sel sistem imun
Sel B +++ +++ Sel B
Sel susunan saraf
Perifer +++ - Perifer +++
Sel saluran napas
Trakhea +++ +++ Trakhea +++ +++
Hati
Sel sinusoid +++ +++ Sel sinusoid +++ +++
Endotel
Kapiler(kec otak&
plasenta
+++ +++
MHC locus-allele-haplotype MHC locus-allele-haplotype
Lokus MHC sangat polimorfik
Terdapat banyak alternatif pasangan allele Terdapat banyak alternatif pasangan allele
pada 1 lokus
Lokus berhubungan erat satu dengan yang Lokus berhubungan erat satu dengan yang
lain
P ll l di b t HAPLOTYPE Pasangan allele disebut HAPLOTYPE
Seseorang mendapatkan haplotype
(pasangan allele) dari ibu dan dari ayahnya
Pasangan allele diekspresikan scr codominan g p
Human Leucocyte Antigen Human Leucocyte Antigen
Human MHC/HLA terletak pada
kromosom 6
Nomenklatur : spesifisitas HLA Nomenklatur : spesifisitas HLA
diidentifikasikan dengan Huruf &
(A1 B5 dll) nomor (A1,B5,dll).
Haplotype diidentifikasi dengan p yp g
spesifisitas individu (cth
A1 B7 Cw4 DP5 DQ10 DR8) A1,B7,Cw4,DP5,DQ10,DR8)
Lokus HLA I Lokus HLA II
HLA A HLA B HLA C HLA DP HLA DQ HLA DR HLA-A HLA-B HLA-C HLA-DP HLA-DQ HLA-DR
A1
A2
B7
B8
Cw1
C 2
DPw1
DP 2
DQw5(
w1)
DR1
DR 15 A2
A3
B8
B13
Cw2
Cw3
DPw2
DPw3
w1)
DQw6(
w1)
DRw15
(2)
DR 16
AII
A24(9)
B14
B38(16)
Cw5
Cw6
DPw4
DPw5
w1)
DQw7(
w3)
DRw16
(2)
DRw17
A25(10)
A29
B39(16)
Bw41
Cw7
Cw11
DPw6
DPCp6
w3)
DQw9(
w3)
DRw17
(3)
DRw18
(w19)
Aw68
Bw52
(5)
3
w3)
DRw18
(3)
(28) Bw47
Major Histocompatibility Complex MHC Major Histocompatibility Complex MHC
In mice the MHC is called H 2 In mice the MHC is called H-2
MHC genetics in mice is simplified by inbred strains
The human MHC is the Human Leukocyte Antigen
system HLA
Only monozygous twins are identical at the HLA locus Only monozygous twins are identical at the HLA locus
The human population is extensively outbred
MHC genetics in humans is extremely complex
MHC molecules
Peptide
MHC class I MHC class II
p
Peptide
binding groove binding groove
Cell Membrane Cell Membrane
Differential distribution of MHC molecules
MHC class I MHC class I
Regulation of immune responses to
intracellular parasites such as viruses - all
cells can be infected by viruses, therefore all
cells express MHC class I
MHC class II
Regulation of immune responses to
exogenous pathogens fewcells are exogenous pathogens, few cells are
specialised to take up extracellular antigens,
and so the distribution of MHC class II
expression is restricted
Overall structure of MHC class I molecules
1 2
Anchored to the cell membrane
3
2m
Peptide antigen in a groove formed
from a pair of -helicies on a floor
f ti ll l t d
-chain and 2-microglobulin,
(non covalently bound to -chain)
of anti-parallel strands
( y )
Overall structure of MHC class II molecules Overall structure of MHC class II molecules
1
-chain of 29kDa
-chain of 34kDa
1
2
2
Anchored to the cell membrane
No -2 microglobulin
Antigen in a groove formed from a
pair of -helicies on a floor of anti-
parallel strands
Molecular basis of MHC types and variants
POLYGENISM
Several MHC class I and class II Several MHC class I and class II
genes with a range of peptide-
binding specificities.
POLYMORPHISM
Variation >1% at a single genetic locus
MHC genes are the most polymorphic MHC genes are the most polymorphic
known
MHC molecules do not vary in the lifetime of the individual y
The diversity of MHC molecules exists at the population level
Simplified map of the HLA region
DP
DQ DR
B C A
DP
DQ
DR
1
B C A
Class III
MHC Class II MHC Class I
Polygeny
CLASS I: 3 types HLA-A, HLA-B, HLA-C CLASS I: 3 types HLA A, HLA B, HLA C
CLASS II: 3 types HLA-DP HLA-DQ HLA-DR.
Polymorphism in MHC Class I genes
Variation >1% at a single genetic locus in a population of individuals
Each polymorphic variant is an allele
555 555
o
f
h
i
s
m
s
356
291
N
o
o
p
o
l
y
m
o
r
p
h
106
140
3
20
106
25
56
Class I alleles
A B C
DR DP DQ
Class II alleles
A B1 A1 B1 A1 B1
Data from www.anthonynolan.org.uk/HIG/index.html October 2003
Class I alleles Class II alleles
Stages of antigen processing
UPTAKE
Access of native antigens and pathogens to intracellular pathways Access of native antigens and pathogens to intracellular pathways
of degradation
DEGRADATION DEGRADATION
Limited proteolysis of antigens to peptides
ANTIGEN-MHC COMPLEX FORMATION
Loading of peptides onto MHC molecules
ANTIGEN PRESENTATION
T d i f id MHC l h Transport and expression of peptide-MHC complexes on the
surface of cells for recognition by T cells
Processing of Antigens from Exogenous Pathogens
Endosomes
Cell surface
Endosomes
Uptake
MHC Vesicle
MHC Class II
containing vesicles C
molecules
from the ER
es c e
acidifies
g
fuse with antigen
containing vesicles
Antigens from Endogenous Pathogens
Viruses use the host cell Viruses use the host cell
protein synthesis
machinery to replicate
Y
ENDOGENOUS
PATHOGENS
e.g. Viruses
The mechanism of antigen
processing for these
antigens also uses the
Y
g
cellular machinery used to
destroy host proteins
Peptides from intracellular and extracellular pathogens
load onto MHC class I and II respectively
Y
INTRACELLULAR
PATHOGENS
Peptides loaded onto
EXTRACELLULAR
PATHOGENS
Peptides loaded onto
MHC class I molecules
- the MHC molecules
largely involved with
immunity to
MHC class II molecules
- the MHC molecules
largely involved with
immunity to immunity to
intracellular pathogens
immunity to
extracellular pathogens
Inheritance of MHC alleles Inheritance of MHC alleles Inheritance of MHC alleles Inheritance of MHC alleles
Mother Father
A/B C/D
A/C A/D B/C B/D A/R1 R2/C R2/R1
R1 C D bi ti
Possible children of parents with HLA haplotype A/B and C/D
R1=C-D recombination
R2=A-B recombination
MHC products expressed on cells MHC products expressed on cells
If J k d J ill h f hild B Ki M d L If J ack and J ill have four children; Bo, Kim, Mo and Lee
Theyll all inherit antigens of the parental MHC
Of their haplotypes will be of the father or mother
Unless during meiosis, a crossover should occur
The inheritance of MHC genes The inheritance of MHC genes
J ack J ill Bo
Kim Mo Lee J ill
DP
DQ
1
2
3 4
Bo
1 3 4 1 2 3
4 2
DQ
DR
B
C
A
MHC products expressed on cells MHC products expressed on cells
Crossing over
lt i h l t results in new haplotypes
Fungsi MHC Fungsi MHC
Molekul MHC kelas I meliputi antigen Molekul MHC kelas I meliputi antigen
HLA-A,HLA-B,HLA-C dapat dikenali
l T b d l k sel Tc yang berperan pada penolakan
organ transplant
Molekul MHC kelas I disebut pula
Antigen Transplantasi Antigen Transplantasi
Cytotoxic T cells (Tc)
Menghancurkan sel yang terinfeksi oleh pathogen intraselular g y g g
dan sel kanker
Molekul MHC kelas I (pada sel tubuh bernukleus)
mengekspresikan protein asing mengekspresikan protein asing
Aktivitas diperbesar oleh protein permukaan CD8 yang
dipresentasikan oleh kebanyakan sel T cytotoxic (Tc) mirip
dengan CD4 &MHC kelas II dengan CD4 & MHC kelas II
Sel Tc melepaskan perforin : protein yang membentuk pori2
pada membran sel target sehingga sel menjadi lysis dan
th k t k d A tib di b i k l i pathogen akan terekspos pada Antibodi yg bersirkulasi
Fungsi MHC Fungsi MHC
Peranan fisiologis HLA kelas II untuk Peranan fisiologis HLA kelas II untuk
memberikan sinyal respon imun terhadap
Th yang berinteraksi dengan sel APC y g g
(antigen presenting cell) di satu pihak,
dengan sel B di pihak lain.
Distribusi HLA kelas II bersifat terbatas
supaya aktivasi sel Th juga hanya pada
k d t t t j keadaan tertentu saja
MHC kelas II : mengawasi interaksi antara
l l i k t sel-sel imunokompeten
Helper T lymphocytes (Th)
Berfungsi pada Imunitas Humoral & Imunitas Seluler
Distimulasi oleh antigen presenting cells (APC)
Permukaan T cell (protein CD4) mendorong aktivasi
Cytokines disekresi (stimulasi lymphocyte lainnya): Cytokines disekresi (stimulasi lymphocyte lainnya):
a) interleukin-2 (IL-2): mengaktivasi sel B dan sel T
cytotoxic (Tc)
b) interleukin-1 (IL-1): mengaktivasi sel T helper (Th) T b) interleukin-1 (IL-1): mengaktivasi sel T helper (Th) T
untuk menghasilkan IL-2
Fungsi MHC Fungsi MHC
Oleh karena aktivasi sel Th merupakan Oleh karena aktivasi sel Th merupakan
respon imun, molekul MHC kelas II
disebut pula Antigen Ia (Immune respons disebut pula Antigen Ia (Immune respons
associated)
You might also like
- Antigen Processing and PresentationDocument2 pagesAntigen Processing and PresentationEllya Latifah IlyasNo ratings yet
- Major Histocompatibility ComplexDocument15 pagesMajor Histocompatibility ComplexsanasharNo ratings yet
- MHC (Major Histocompatibility Complex)Document19 pagesMHC (Major Histocompatibility Complex)Kayshu Grover100% (2)
- Cellular and Molecular Mechanisms of Inflammation: Receptors of Inflammatory Cells: Structure—Function RelationshipsFrom EverandCellular and Molecular Mechanisms of Inflammation: Receptors of Inflammatory Cells: Structure—Function RelationshipsCharles G. CochraneNo ratings yet
- Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC) and TCRDocument59 pagesMajor Histocompatibility Complex (MHC) and TCRPuyi Puyenk100% (1)
- Buku Pedoman Nasional Penanggulangan TBCDocument131 pagesBuku Pedoman Nasional Penanggulangan TBCHasrapriliana Hersya100% (1)
- Lecture MHCDocument33 pagesLecture MHCrockyrawat01012003No ratings yet
- HLA system-HLA Typing and Its Role in Tissue TransplantationDocument48 pagesHLA system-HLA Typing and Its Role in Tissue TransplantationAshikNo ratings yet
- Major Histocompatibility Complex Part 1 TranscriptDocument24 pagesMajor Histocompatibility Complex Part 1 Transcriptapi-273068056No ratings yet
- Human Leukocyte Antigens: Dr. B.Vijayasree 1 Year Post-Graduate Department of MicrobiologyDocument30 pagesHuman Leukocyte Antigens: Dr. B.Vijayasree 1 Year Post-Graduate Department of Microbiologyvijayasree bavireddyNo ratings yet
- Major Histocompatibilty Complex (MHC)Document13 pagesMajor Histocompatibilty Complex (MHC)boscomooliNo ratings yet
- His To Comp at AbilityDocument24 pagesHis To Comp at AbilitycyskinkropsNo ratings yet
- Antigen Processing and PresentationDocument23 pagesAntigen Processing and PresentationMin KyuNo ratings yet
- LS3310 Clin Imm WK 1 HLA 2010-2011Document36 pagesLS3310 Clin Imm WK 1 HLA 2010-2011Colbert NcubeNo ratings yet
- In The Name of Allah, Most Gracious, Most MercifulDocument24 pagesIn The Name of Allah, Most Gracious, Most Mercifuljibril channelNo ratings yet
- MHC MoleculeDocument45 pagesMHC MoleculeShah NAWAZNo ratings yet
- 05 - Adaptive Immunity (T Cell Receptors)Document21 pages05 - Adaptive Immunity (T Cell Receptors)star lightNo ratings yet
- Function and Structure of Antibodies and MHC: Dr. Muhammad Zubair FCPS Chemical PathologistDocument60 pagesFunction and Structure of Antibodies and MHC: Dr. Muhammad Zubair FCPS Chemical PathologistZubair YousafNo ratings yet
- Unit - 4 Csir Net: Major Histocompatibility ComplexDocument65 pagesUnit - 4 Csir Net: Major Histocompatibility ComplexGeebee NannyCareNo ratings yet
- Antigen Processing and Presentation PDFDocument36 pagesAntigen Processing and Presentation PDFMarinero CzarNo ratings yet
- MHCDocument22 pagesMHCJanani JayakumarNo ratings yet
- HLA Typing-ImmunologyDocument14 pagesHLA Typing-ImmunologySCREEN SENSE ENTERTAINMENTNo ratings yet
- Immunology MHCDocument7 pagesImmunology MHCAbdullah EssaNo ratings yet
- P Fihir Imun HLADocument32 pagesP Fihir Imun HLAKantorCamat TaliwangNo ratings yet
- HLA and Antigen Presentation: Rania Bakry, MDDocument45 pagesHLA and Antigen Presentation: Rania Bakry, MDRashed LabNo ratings yet
- The Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC) : Human: Human Leukocyte Antigens (HLA)Document21 pagesThe Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC) : Human: Human Leukocyte Antigens (HLA)uniroma2No ratings yet
- MHC (Major Histocompatibility Complex) : StructureDocument5 pagesMHC (Major Histocompatibility Complex) : StructureAhmad Farid OthmanNo ratings yet
- Major Complex: HistocompatabilityDocument42 pagesMajor Complex: HistocompatabilityAshikNo ratings yet
- MHC and Graft RejectionDocument16 pagesMHC and Graft RejectionsharanNo ratings yet
- MHC I, MHC II, ApcDocument33 pagesMHC I, MHC II, ApcFerlinda AgustinaNo ratings yet
- IS3 Antigens and The Major Histocompatibility ComplexDocument28 pagesIS3 Antigens and The Major Histocompatibility ComplexMoy AngNo ratings yet
- Major Histocompatibility Complex: Prepared byDocument16 pagesMajor Histocompatibility Complex: Prepared byمروه عماد عيسىNo ratings yet
- Class 8 MHC - LSDocument32 pagesClass 8 MHC - LSDarwin QuinterosNo ratings yet
- Imma 6Document49 pagesImma 6nokate konkoorNo ratings yet
- MHC Chpt. 7Document21 pagesMHC Chpt. 7Julio MansoNo ratings yet
- Human Leukocyte Antigen (HLA) System: Alkitab University College of Technology Medical Department of Medical AnalysisDocument4 pagesHuman Leukocyte Antigen (HLA) System: Alkitab University College of Technology Medical Department of Medical AnalysisMohammed R.HusseinNo ratings yet
- Sequence Variability Analysis of Human Class I and Class II MHC MoleculesDocument19 pagesSequence Variability Analysis of Human Class I and Class II MHC MoleculesFernando Fernández GarcíaNo ratings yet
- Principles of Transplantation SHDocument93 pagesPrinciples of Transplantation SHqadiraftabNo ratings yet
- Immune SystemDocument32 pagesImmune Systemanupama menonNo ratings yet
- Self - Non Self Limfocite T Si B MHC - Procesare / Prezentare AntigeneDocument52 pagesSelf - Non Self Limfocite T Si B MHC - Procesare / Prezentare AntigeneGigiEnergieNo ratings yet
- 9.MHC in Immune Response-2Document16 pages9.MHC in Immune Response-2alhyarylyn3No ratings yet
- Immunopathology: Normal Immune ResponseDocument13 pagesImmunopathology: Normal Immune ResponseChinedu H. DuruNo ratings yet
- Major Histocompatibility ComplexDocument36 pagesMajor Histocompatibility ComplexSatyanarayana SwamyNo ratings yet
- Antigen Presenting Cells: Parbondeep SaikiaDocument20 pagesAntigen Presenting Cells: Parbondeep SaikiaParbondeep SaikiaNo ratings yet
- Diseases of The Immune SystemDocument115 pagesDiseases of The Immune SystemLucky LuckyNo ratings yet
- MHCDocument25 pagesMHCSAMUELNo ratings yet
- Hla Typing and Transplant Immunology: Moderator: DR Biman SaikiaDocument70 pagesHla Typing and Transplant Immunology: Moderator: DR Biman SaikialbNo ratings yet
- Chap. 6Document46 pagesChap. 6NadineNo ratings yet
- Major Histocompatibility Complex - WikipediaDocument57 pagesMajor Histocompatibility Complex - WikipediaPowell KitagwaNo ratings yet
- 7.MHC and TransplantationDocument34 pages7.MHC and Transplantationعوض الكريمNo ratings yet
- L1b MHCDocument33 pagesL1b MHCashutoshrath209No ratings yet
- Antigen PresentationDocument41 pagesAntigen PresentationDavid lufafaNo ratings yet
- Theoretical Basis For Immunological Specificity and MemoryDocument18 pagesTheoretical Basis For Immunological Specificity and MemoryRakin Bin RaihanNo ratings yet
- Cell-Mediated Immunity (CMI) Lecture 6Document29 pagesCell-Mediated Immunity (CMI) Lecture 6Toga BrandonNo ratings yet
- 4th Week Imunologi Sound ADocument26 pages4th Week Imunologi Sound AWidya NingsiNo ratings yet
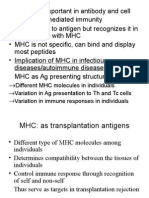
- Different MHC Molecules in Individuals Variation in Ag Presentation To TH and TC Cells Variation in Immune Responses in IndividualsDocument9 pagesDifferent MHC Molecules in Individuals Variation in Ag Presentation To TH and TC Cells Variation in Immune Responses in IndividualskashishNo ratings yet
- Major Histocompatibility ComplexDocument11 pagesMajor Histocompatibility ComplexNurlaily Sofia NazleeNo ratings yet
- Major Histocompatibility ComplexDocument30 pagesMajor Histocompatibility ComplexCherry Reyes-PrincipeNo ratings yet
- Immunologyseminarsreeraj 141113031318 Conversion Gate02Document57 pagesImmunologyseminarsreeraj 141113031318 Conversion Gate02AshikNo ratings yet
- LECTURE 17 Major Histocompatibility MoleculesDocument7 pagesLECTURE 17 Major Histocompatibility MoleculesDomenica Mishel Sandoval SegoviaNo ratings yet
- Minimal Kriteria Diagnostik MDS 2009Document6 pagesMinimal Kriteria Diagnostik MDS 2009Sandi AuliaNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary PhysiologyDocument18 pagesPulmonary PhysiologyAnonymous t5TDwdNo ratings yet
- Anemia WorkupDocument1 pageAnemia WorkupGalyna CyrmachevskaNo ratings yet
- Procalcitonin For Diagnosis of Infection and GuideDocument9 pagesProcalcitonin For Diagnosis of Infection and GuideSandi AuliaNo ratings yet
- Disorders of Hemostasis Associated in Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocument7 pagesDisorders of Hemostasis Associated in Chronic Kidney DiseaseSandi AuliaNo ratings yet
- Inflammatory Biomarkers in Acute Coronary Syndromes: Clinician UpdateDocument9 pagesInflammatory Biomarkers in Acute Coronary Syndromes: Clinician UpdateSandi AuliaNo ratings yet
- KDIGO AKI Guideline DownloadDocument141 pagesKDIGO AKI Guideline DownloadSandi AuliaNo ratings yet
- Practice Essentials: Essential Update: CDC Reports Most Common Sources of Food-Borne IllnessesDocument18 pagesPractice Essentials: Essential Update: CDC Reports Most Common Sources of Food-Borne IllnessesSandi AuliaNo ratings yet
- Professor Birgitta Stegmayr For The Riks-Stroke Steering Committée Medicine, Umeå University Hospital SwedenDocument24 pagesProfessor Birgitta Stegmayr For The Riks-Stroke Steering Committée Medicine, Umeå University Hospital SwedenSandi AuliaNo ratings yet