Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Shapes Formula Rectangle:: Sponsored Links
Uploaded by
abidhira39Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Shapes Formula Rectangle:: Sponsored Links
Uploaded by
abidhira39Copyright:
Available Formats
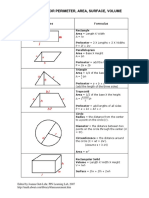
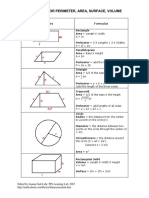
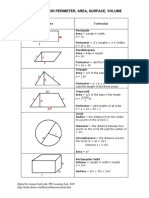
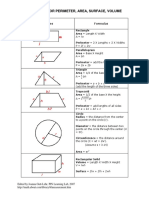
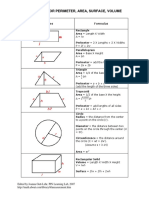
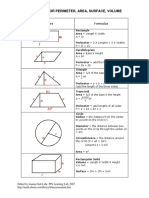
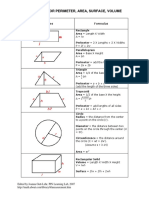
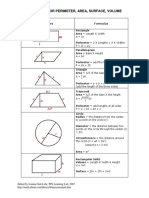
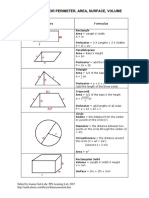
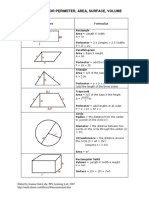
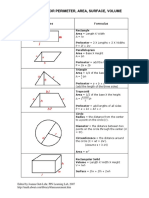
Shapes Formula
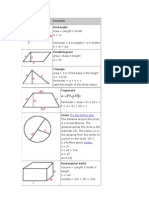
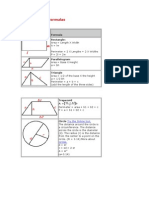
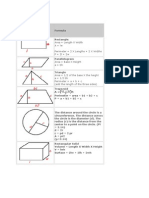
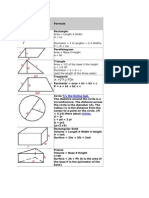
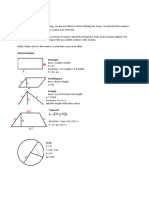
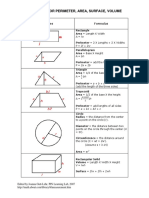
Rectangle:
Area = Length X Width
A = lw
Perimeter = 2 X Lengths + 2 X Widths
P = 2l + 2w
Parallelogram
Area = Base X Height
a = bh
Triangle
Area = 1/2 of the base X the height
a = 1/2 bh
Perimeter = a + b + c
(add the length of the three sides)
Sponsored Links
CBSE Subjects: VI to XIIStudy CBSE Maths/Science VI to XII from Home . Register
freewww.LearnNext.com
Dynamic Vapor SorptionLeaders in sorption analyzers and gravimetric moisture
measurements.www.thesorptionsolution.com
3D Non-contact ProfilerHigh value, hi-res optical surface metrology, easy to use
ZeScopewww.zemetrics.com/optical-profiler
Trapezoid
Perimeter = area + b1 + b2 + c
P = a + b1 + b2 + c
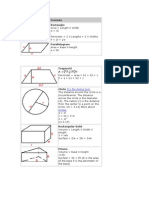
Circle Try the Online tool.
The distance around the circle is a
circumference. The distance
across the circle is the diameter
(d). The radius (r) is the distance
from the center to a point on the
circle. (Pi = 3.14) More about
circles.
d = 2r
c=π d=2π r
A = π r2
( π =3.14)
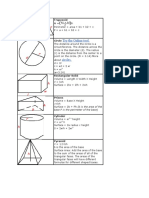
Rectangular Solid
Volume = Length X Width X
Height
V = lwh
Surface = 2lw + 2lh + 2wh
Prisms
Volume = Base X Height
v=bh
Surface = 2b + Ph (b is the area
of the base P is the perimeter of
the base)
Cylinder
Volume = π r2 x height
V = π r2 h
Surface = 2π radius x height
S = 2π rh + 2π r2
Pyramid
V = 1/3 bh
b is the area of the base
Surface Area: Add the area of the
base to the sum of the areas of all
of the triangular faces. The areas
of the triangular faces will have
different formulas for different
shaped bases.
Cones
Volume = 1/3 π r2 x height
V= 1/3 π r2h
Surface = π r2 + π rs
S = π r2 + π rs
=π r2 + π r
Sphere
Volume = 4/3 π r3
V = 4/3 π r3
Surface = 4π r2
S = 4π r2
You might also like
- Nonlinear Functional Analysis and Applications: Proceedings of an Advanced Seminar Conducted by the Mathematics Research Center, the University of Wisconsin, Madison, October 12-14, 1970From EverandNonlinear Functional Analysis and Applications: Proceedings of an Advanced Seminar Conducted by the Mathematics Research Center, the University of Wisconsin, Madison, October 12-14, 1970Louis B. RallNo ratings yet
- Area and VolumesDocument2 pagesArea and VolumesSwapnil RathodNo ratings yet
- TrapezoidDocument2 pagesTrapezoidAchillies ReyesNo ratings yet
- Area and Perimeter FormulaDocument2 pagesArea and Perimeter FormulaAllison Nadine MarchandNo ratings yet
- Compound Interest: Sphere, Solid Cylinder, Hollow Cylinder, Cone PyramidDocument9 pagesCompound Interest: Sphere, Solid Cylinder, Hollow Cylinder, Cone PyramidMuhammad Faheem KhanNo ratings yet
- Apes Formula Rectangle:: Try The Online ToolDocument2 pagesApes Formula Rectangle:: Try The Online TooltharazainNo ratings yet
- Formula For Areas, Volume, Surface AreaDocument2 pagesFormula For Areas, Volume, Surface AreaJojo YongNo ratings yet
- Measurement Formulas: Shapes Formula RectangleDocument2 pagesMeasurement Formulas: Shapes Formula RectangleSuganya SelvarajNo ratings yet
- ShapesDocument2 pagesShapesDitdit Raditya AditNo ratings yet
- Area and PerimetreDocument2 pagesArea and PerimetreSaro Fernando-Koppe100% (1)
- ShapesDocument2 pagesShapesMaricar Acosta-PetillaNo ratings yet
- Geometry FormulasDocument2 pagesGeometry FormulasKingpinNo ratings yet
- TrapezoidDocument2 pagesTrapezoidChester Allan Miguel-Eduria100% (1)
- English FormulaesDocument3 pagesEnglish FormulaesDanuar Trianur RohmanNo ratings yet
- Parallelogram BH: (Heron's Formula)Document3 pagesParallelogram BH: (Heron's Formula)நளின் கான்No ratings yet
- Geometry Formulae 2D-3D Shapes - Perimeter, Area, VolumeDocument2 pagesGeometry Formulae 2D-3D Shapes - Perimeter, Area, VolumeNazmul Hassan BatchuNo ratings yet
- Measurement Formulas GuideDocument3 pagesMeasurement Formulas GuideHarsha RajaiNo ratings yet
- Geometry Formulas Perimeter Area VolumeDocument3 pagesGeometry Formulas Perimeter Area Volumeconnie villasNo ratings yet
- Math Formula Cheat SheetsDocument11 pagesMath Formula Cheat SheetsbrunerteachNo ratings yet
- Volume FormulasDocument3 pagesVolume FormulasSanket SatpathyNo ratings yet
- Common Equations For AreaDocument4 pagesCommon Equations For AreaATHULNo ratings yet
- Math definitions, formulas, and theorems explainedDocument3 pagesMath definitions, formulas, and theorems explainedKevin GazaliNo ratings yet
- Formulas for Calculating Shapes' Areas, Volumes and SurfacesDocument6 pagesFormulas for Calculating Shapes' Areas, Volumes and SurfacesRazali ZainalNo ratings yet
- Geometry Formulas 2D 3D Perimeter Area VolumeDocument2 pagesGeometry Formulas 2D 3D Perimeter Area VolumePalma, Arrabela M.No ratings yet
- Formulas Geometry Shapes Perimeter Area Surface VolumeDocument2 pagesFormulas Geometry Shapes Perimeter Area Surface VolumeKalyan KumarNo ratings yet
- Geometry Formulas 2D 3D Perimeter Area Volume PDFDocument2 pagesGeometry Formulas 2D 3D Perimeter Area Volume PDFArajit SarkarNo ratings yet
- Geometry Formulas 2D 3D Perimeter Area Volume PDFDocument2 pagesGeometry Formulas 2D 3D Perimeter Area Volume PDFRUSHIKESHNo ratings yet
- Geometry Formulas 2D 3D Perimeter Area VolumeDocument2 pagesGeometry Formulas 2D 3D Perimeter Area VolumeMahmudul BappiNo ratings yet
- Geometry Formulas 2D 3D Perimeter Area Volume PDFDocument2 pagesGeometry Formulas 2D 3D Perimeter Area Volume PDFManoj kittyNo ratings yet
- Geometry Formulas 2D 3D Perimeter Area Volume PDFDocument2 pagesGeometry Formulas 2D 3D Perimeter Area Volume PDFsagar sagarNo ratings yet
- Geometry Formulas 2D 3D Perimeter Area Volume PDFDocument2 pagesGeometry Formulas 2D 3D Perimeter Area Volume PDFJulian AshbourneNo ratings yet
- Geometry Formulas 2D 3D Perimeter Area Volume PDFDocument2 pagesGeometry Formulas 2D 3D Perimeter Area Volume PDFAnondo SarbabidyaNo ratings yet
- Geometry Formulas 2D 3D Perimeter Area VolumeDocument2 pagesGeometry Formulas 2D 3D Perimeter Area VolumeHeet RamiNo ratings yet
- Geometry Formulas 2D 3D Perimeter Area Volume PDFDocument2 pagesGeometry Formulas 2D 3D Perimeter Area Volume PDFBenson AnselmoNo ratings yet
- Geometry Formulas 2D 3D Perimeter Area Volume PDFDocument2 pagesGeometry Formulas 2D 3D Perimeter Area Volume PDFLucky MalhotraNo ratings yet
- Geometry Formulas 2D 3D Perimeter Area Volume PDFDocument2 pagesGeometry Formulas 2D 3D Perimeter Area Volume PDFvishuNo ratings yet
- Formulas Geometry Shapes Perimeter Area Surface VolumeDocument2 pagesFormulas Geometry Shapes Perimeter Area Surface VolumeSwen Digdigan-EgeNo ratings yet
- Formulas Geometry Shapes Perimeter Area Surface VolumeDocument2 pagesFormulas Geometry Shapes Perimeter Area Surface VolumeLaithZNo ratings yet
- Geometry Formulas 2D 3D Perimeter Area Volume PDFDocument2 pagesGeometry Formulas 2D 3D Perimeter Area Volume PDFTANMAY DALVINo ratings yet
- Geometry Formulas Perimeter Area Volume PDFDocument2 pagesGeometry Formulas Perimeter Area Volume PDFFawad MalikNo ratings yet
- Geometry Formulas 2D 3D Perimeter Area Volume PDFDocument2 pagesGeometry Formulas 2D 3D Perimeter Area Volume PDFJQNo ratings yet
- Geometry Formulas 2D 3D Perimeter Area VolumeDocument2 pagesGeometry Formulas 2D 3D Perimeter Area VolumesaidurgaNo ratings yet
- Geometry Formulas 2D 3D Perimeter Area Volume PDFDocument2 pagesGeometry Formulas 2D 3D Perimeter Area Volume PDFAlonzo Luis PamintuanNo ratings yet
- Geometry Formulas 2D 3D Perimeter Area VolumeDocument2 pagesGeometry Formulas 2D 3D Perimeter Area VolumeDan DiaconescuNo ratings yet
- Geometry Formulas 2D 3D Perimeter Area Volume PDFDocument2 pagesGeometry Formulas 2D 3D Perimeter Area Volume PDFMoni JanaNo ratings yet
- Geometry Formulas 2D 3D Perimeter Area VolumeDocument2 pagesGeometry Formulas 2D 3D Perimeter Area VolumeJason RomanNo ratings yet
- Geometry Formulas 2D 3D Perimeter Area Volume PDFDocument2 pagesGeometry Formulas 2D 3D Perimeter Area Volume PDFprateek SinghNo ratings yet
- Geometry Formulas 2D 3D Perimeter Area Volume PDFDocument2 pagesGeometry Formulas 2D 3D Perimeter Area Volume PDFEver Luv EsquillaNo ratings yet
- Formulas Geometry Shapes Perimeter Area Surface VolumeDocument2 pagesFormulas Geometry Shapes Perimeter Area Surface VolumeMademoiselle ArrenNo ratings yet
- Formulas Geometry Shapes Perimeter Area Surface VolumeDocument2 pagesFormulas Geometry Shapes Perimeter Area Surface VolumeJames JamesNo ratings yet
- Geometry Formulas 2D 3D Perimeter Area Volume PDFDocument2 pagesGeometry Formulas 2D 3D Perimeter Area Volume PDFTrisha DasNo ratings yet
- Formulas Geometry Shapes Perimeter Area Surface VolumeDocument2 pagesFormulas Geometry Shapes Perimeter Area Surface VolumeAbdul Rafey NawazNo ratings yet
- Formulas Geometry Shapes Perimeter Area Surface VolumeDocument2 pagesFormulas Geometry Shapes Perimeter Area Surface Volumebabu1438No ratings yet
- Geometry Formulas 2D 3D Perimeter Area Volume PDFDocument2 pagesGeometry Formulas 2D 3D Perimeter Area Volume PDFErwin Mars UyNo ratings yet
- Geometry Formulas 2D 3D Perimeter Area Volume PDFDocument2 pagesGeometry Formulas 2D 3D Perimeter Area Volume PDFDream CakeNo ratings yet
- Geometry Formulas 2D 3D Perimeter Area VolumeDocument2 pagesGeometry Formulas 2D 3D Perimeter Area Volumepiyush100% (1)
- Formulas Geometry Shapes Perimeter Area Surface VolumeDocument2 pagesFormulas Geometry Shapes Perimeter Area Surface VolumedonNo ratings yet
- Geometry Formulas 2D 3D Perimeter Area Volume PDFDocument2 pagesGeometry Formulas 2D 3D Perimeter Area Volume PDFRawat HeeraNo ratings yet
- Geometry Formulas 2D 3D Perimeter Area Volume PDFDocument2 pagesGeometry Formulas 2D 3D Perimeter Area Volume PDFMuhamed NajeebNo ratings yet
- 311 54 - OSS - 1 Set A MathematicsDocument11 pages311 54 - OSS - 1 Set A MathematicsManaswini ReddyNo ratings yet
- Integral Calculus SyllabusDocument3 pagesIntegral Calculus SyllabusSpica Dim100% (5)
- Building Java Programs: Inheritance and InterfacesDocument90 pagesBuilding Java Programs: Inheritance and InterfacesMuhamad IhsanNo ratings yet
- Maths Class X Sample Paper Test 05 For Board Exam 2024Document6 pagesMaths Class X Sample Paper Test 05 For Board Exam 2024suiiironaldo255No ratings yet
- Geometry ProblemsDocument10 pagesGeometry ProblemsAphrocamsieNo ratings yet
- AP1 Student WorkbookDocument358 pagesAP1 Student WorkbookThe vegetal saiyanNo ratings yet
- Singapore Math Secondary Two Math Tutor 2BDocument472 pagesSingapore Math Secondary Two Math Tutor 2BMarie-Emmanuelle LamelotNo ratings yet
- Refreshers Math T2Document4 pagesRefreshers Math T2ShafirNo ratings yet
- Syllabus - FIT303 v11 FINALDocument9 pagesSyllabus - FIT303 v11 FINALRavishangerNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 10 Maths Sample Paper Solution Set 3Document16 pagesCBSE Class 10 Maths Sample Paper Solution Set 3Krish GajeraNo ratings yet
- N5 Mathematics All 2017Document36 pagesN5 Mathematics All 2017doaaNo ratings yet
- Frustum of a Pyramid ProblemsDocument7 pagesFrustum of a Pyramid ProblemsStevenzel Eala EstellaNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Syllabus D. 2 - NodrmDocument460 pagesMathematics Syllabus D. 2 - NodrmAmmad Rehman/ IT/ KK ZAR100% (1)
- Mensuration Level Up Mains CaseletsDocument14 pagesMensuration Level Up Mains CaseletssailuteluguNo ratings yet
- Mathematics n2 August Question Paper 2021Document9 pagesMathematics n2 August Question Paper 2021Dennis Mbegabolawe100% (1)
- Upcat 2015 - Simulated Exam - Set A - Section 3 - Mathematics Proficiency v.4.16.2015Document8 pagesUpcat 2015 - Simulated Exam - Set A - Section 3 - Mathematics Proficiency v.4.16.2015Kenneth DuroNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plans To Be Submitted VUDocument19 pagesLesson Plans To Be Submitted VUSakina ImranNo ratings yet
- Math 09 2012 13 Value Based QuestionsDocument46 pagesMath 09 2012 13 Value Based QuestionsUditSharma0% (1)
- Test Paper:7 Paper Type: Whole Testpaper Test Date: 19 January 2010 Posted By: Admin Written TestDocument19 pagesTest Paper:7 Paper Type: Whole Testpaper Test Date: 19 January 2010 Posted By: Admin Written TestJoydeep MazumderNo ratings yet
- GCSEKS3 AreaCircumferenceOfCirclesDocument5 pagesGCSEKS3 AreaCircumferenceOfCircles4jgp7nyscfNo ratings yet
- GM Q1 W1.SLK4Document6 pagesGM Q1 W1.SLK4Pantz Revibes PastorNo ratings yet
- Geometry Questions For CAT ExamDocument41 pagesGeometry Questions For CAT ExamGuilherme Dos Santos MoreiraNo ratings yet
- A1 C2 L8 Solution Key Worked OutDocument27 pagesA1 C2 L8 Solution Key Worked OutVhenSerdanNo ratings yet
- Pre-Board General Education-Math and Social StudiesDocument20 pagesPre-Board General Education-Math and Social StudiesJohn Paul PendonNo ratings yet
- Areas and centroids table shapesDocument1 pageAreas and centroids table shapesMpumeleloNo ratings yet
- Logic Excercise 1Document3 pagesLogic Excercise 1alanokeNo ratings yet
- Iemh 1 AnDocument27 pagesIemh 1 AnBishal Kumar GiriNo ratings yet
- Gujarat PDFDocument20 pagesGujarat PDFjatin sanehiNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Paper 2 Trigonomery and Graphs of FunctionsDocument42 pagesMathematics Paper 2 Trigonomery and Graphs of FunctionsLweendo Wiz MunyangaNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 10 Math Paper 2019 SolutionsDocument68 pagesCBSE Class 10 Math Paper 2019 SolutionsDanishNo ratings yet